Have you ever wondered how those intricate plastic parts are made? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of plastic injection molding!
Plastic injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts. The process includes heating plastic, injecting it into a mold, cooling it to solidify, and then ejecting the finished product. This method is known for its efficiency and precision.
While this summary provides a basic understanding, the intricacies of plastic injection molding are vast and fascinating. From raw material preparation to the nuances of mold design, each step is crucial. Let’s delve deeper into the process to uncover its complexities and practical applications.
Injection molding creates parts by injecting plastic into molds.True
Molten plastic is injected into a mold, cooled, and ejected as a part.
What Are the Key Steps in Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a systematic process transforming raw plastic into intricate components. What are its critical stages?
The key steps in plastic injection molding include raw material preparation, injection molding, cooling, and demolding. Each step is vital for ensuring the final product’s quality and consistency.
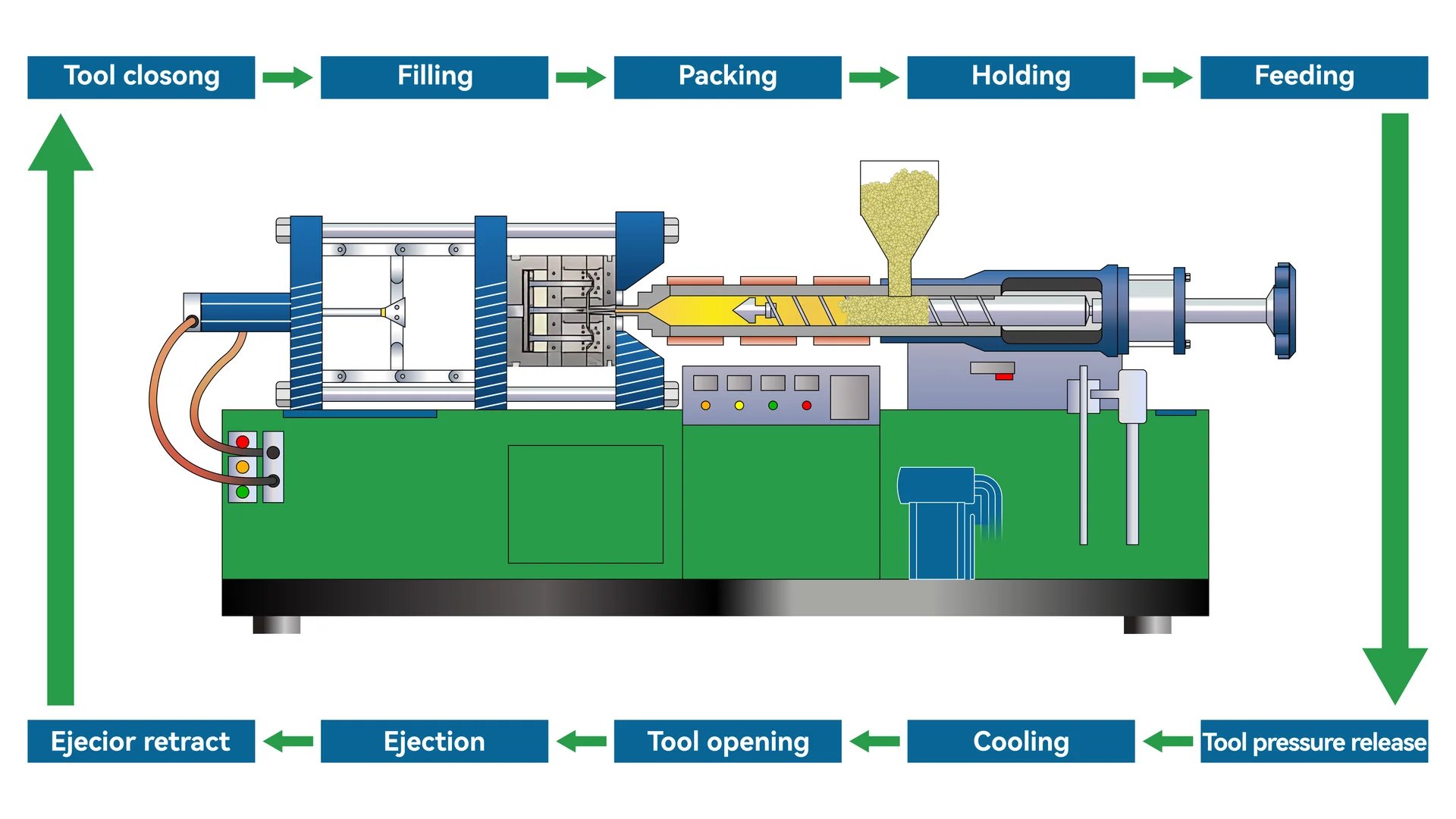
Raw Material Preparation
The journey begins with selecting the appropriate plastic material. Common choices include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene. It’s crucial to dry these materials to eliminate moisture, which could lead to defects such as bubbles during molding.
| Raw Material | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Flexible, durable |
| Polypropylene | Chemical resistance, stiffness |
| Polystyrene | Clarity, rigidity |
Injection Molding
In this phase, dried plastic granules are fed into the injection molding machine’s hopper. The machine heats the granules to a molten state before injecting them into a closed mold cavity. This is where precision is paramount; parameters like injection pressure, speed, and time must be meticulously controlled to achieve high-quality results. The role of the screw is pivotal here, as it facilitates the rotation and advancement needed for injection.
Cooling
Once inside the mold, the molten plastic cools and solidifies. Cooling time varies based on factors like the product’s thickness and the material’s thermal properties. An efficient cooling system is vital for maintaining production speed without compromising quality.
Demolding
The final step involves opening the mold to eject the finished product. Care is needed to avoid damaging the freshly molded item during ejection. This stage is where automation can significantly enhance efficiency, especially in high-volume production.
Features and Applications
- High Production Efficiency: The process allows for rapid production cycles, often lasting only seconds.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Precision in mold design ensures consistent quality.
- Complex Shapes: Capable of producing detailed and intricate parts.
- Material Versatility: Works with a wide range of thermoplastics.
Applications span from automotive components1 to medical devices2, showcasing the method’s versatility.
Polyethylene is used for its flexibility.True
Polyethylene is chosen for its flexibility and durability in molding.
Cooling time depends solely on product thickness.False
Cooling time depends on both product thickness and material's thermal properties.
How Does Mold Design Affect the Quality of Plastic Products?
The intricacies of mold design significantly impact the quality, performance, and consistency of plastic products. Let’s explore how this critical component shapes the final outcome.
Mold design affects plastic product quality through precision, cooling efficiency, and material flow. Proper design ensures dimensional accuracy and minimizes defects.
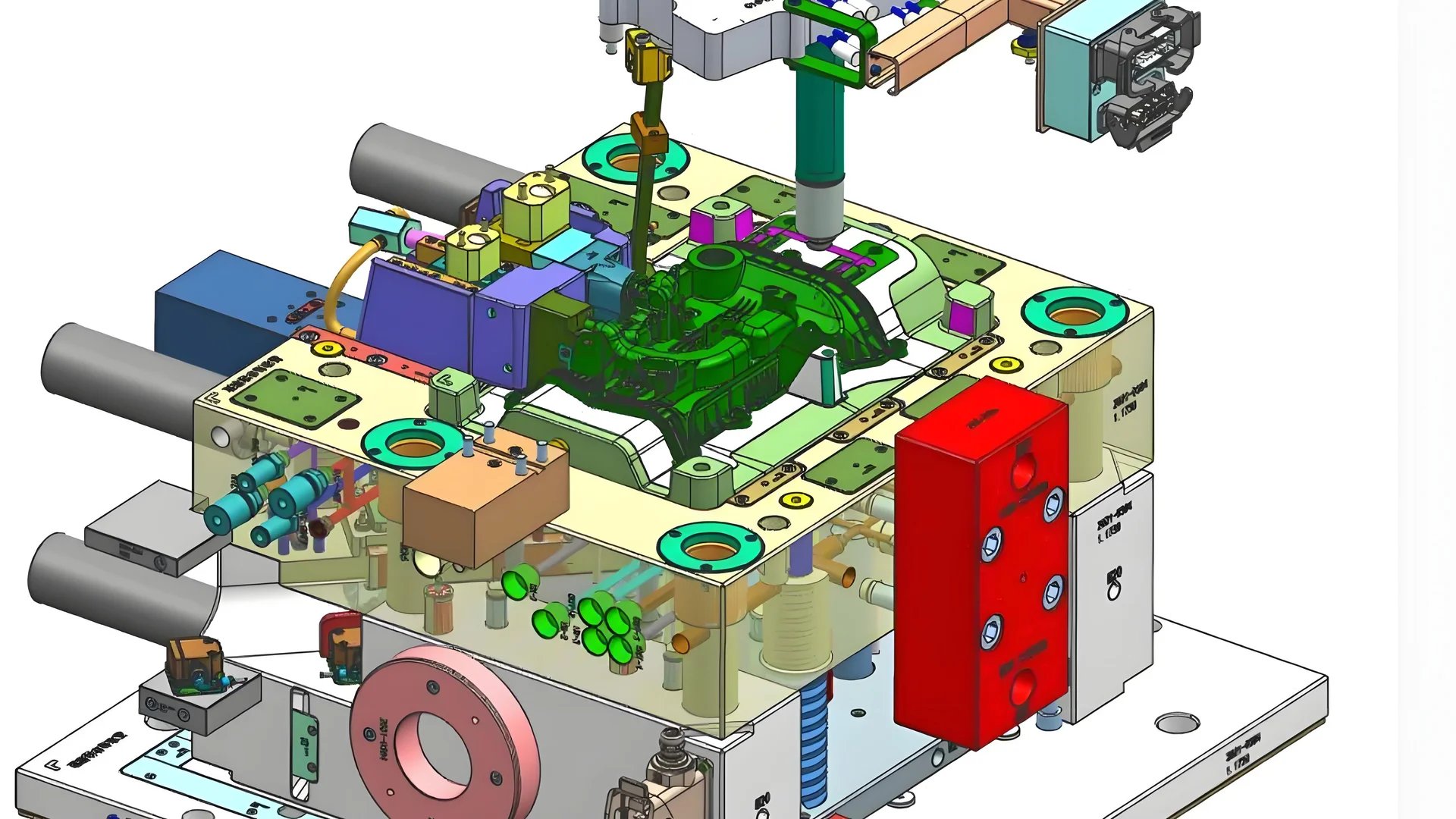
The Role of Precision in Mold Design
Precision in mold design is fundamental to producing high-quality plastic products. A well-designed mold can control the dimensions and intricacies of the product, ensuring that each item meets exact specifications. This precision is crucial for applications in industries like automotive and electronics, where even minor deviations can lead to malfunctions or failures. Factors such as cavity size, shape, and tolerance levels must be meticulously planned and executed.
Cooling Systems and Their Impact
An efficient cooling system within the mold is essential for maintaining product quality. Rapid and uniform cooling helps prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage, which can compromise the integrity of the product. Cooling channels must be strategically placed to ensure even temperature distribution throughout the mold. The choice of cooling system can also influence production speed and energy consumption, making it a vital consideration in mold design.
Material Flow and Gate Design
The design of the gates — the entry points for molten plastic into the mold — significantly affects material flow and ultimately the quality of the finished product. Poor gate design can lead to issues such as incomplete filling, air traps, or weld lines. To optimize flow, factors like gate size, shape, and placement must be carefully considered. Analyzing flow simulations3 can help identify potential issues before manufacturing begins.
Surface Finish and Texturing
The surface finish of a mold directly impacts the aesthetic and functional aspects of a plastic product. For instance, a smooth surface may be required for products needing high gloss finishes, while textured surfaces might be essential for grip or appearance in consumer goods. Techniques such as polishing or texturing need to be applied according to the intended use of the final product. Understanding how different finishes affect end-use applications is crucial for designers and engineers.
By considering these factors — precision, cooling, material flow, and surface finish — manufacturers can enhance product quality and meet industry standards effectively. Evaluating these components during the design phase reduces production errors and improves overall efficiency.
Precision in mold design ensures dimensional accuracy.True
Precision controls dimensions, crucial for quality in industries like automotive.
Cooling efficiency does not affect product quality.False
Efficient cooling prevents defects like warping, crucial for product integrity.
What Challenges Are Common in Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a complex process with unique challenges that can impact product quality and efficiency.
Common challenges in plastic injection molding include material selection, mold design, process control, and quality assurance. Proper management of these factors is crucial to minimize defects and ensure high-quality production.
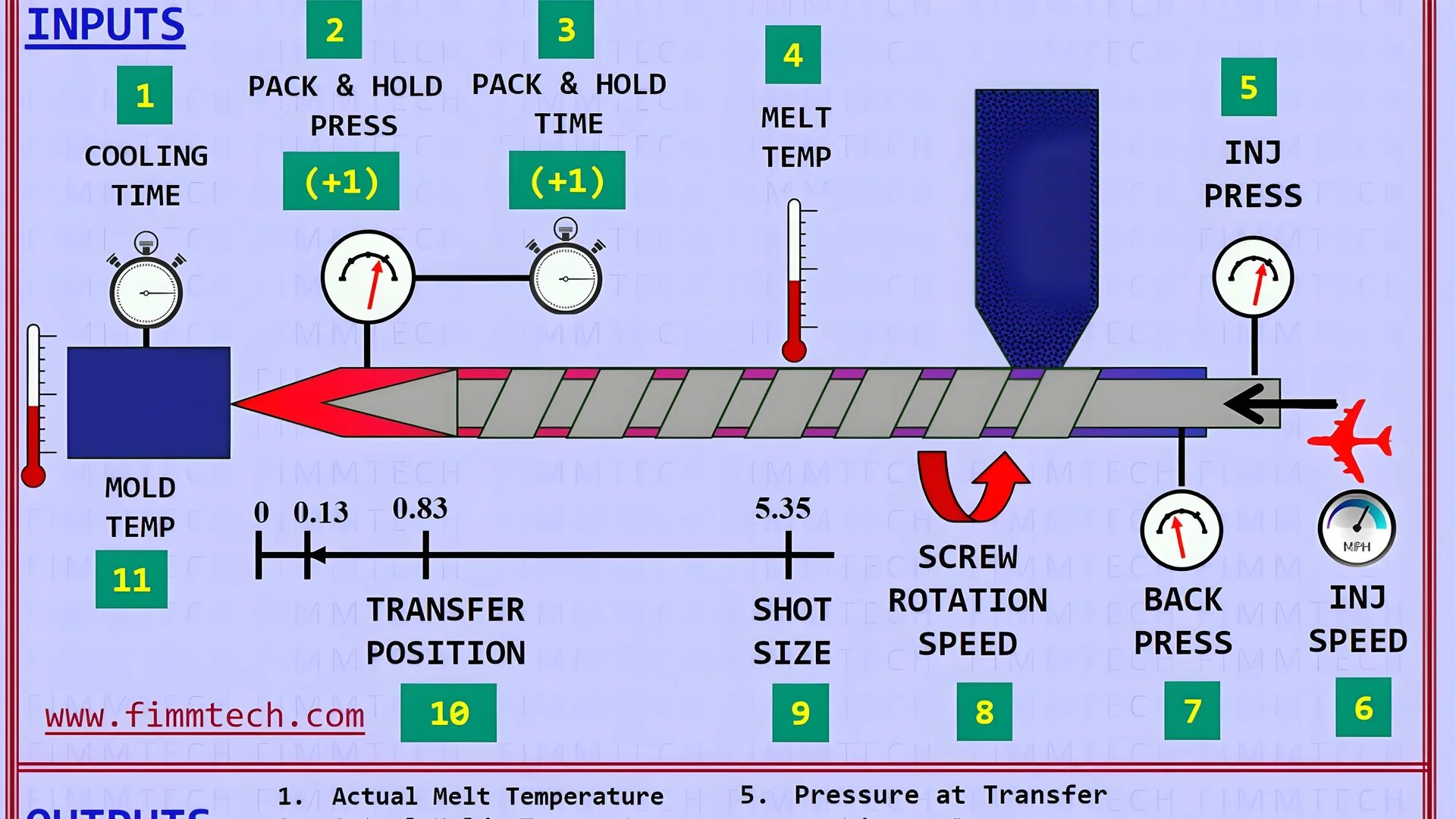
Material Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right material is essential in plastic injection molding4. Different materials exhibit distinct properties, such as melting temperature, viscosity, and shrinkage rates, all of which can affect the final product. For instance, using a material with poor heat resistance can lead to warping or deformation under high temperatures.
Proper preparation is also vital. Plastic materials must be adequately dried to remove moisture. Failure to do so can result in defects such as bubbles or inconsistent density within the final product.
Mold Design Complexities
The design of the mold significantly influences the quality and precision of the molded product. A poorly designed mold can lead to issues such as flash, sink marks, or short shots.
Moreover, molds must accommodate the cooling and solidification process. Uneven cooling can cause warping or residual stresses in the product. Therefore, incorporating efficient cooling channels is imperative for consistent quality.
Process Control and Optimization
Effective process control is crucial to mitigate common challenges in injection molding5. This includes monitoring injection pressure, speed, and temperature throughout the cycle. Deviations can result in defects like burn marks or weld lines.
Utilizing advanced software for simulation and process optimization helps predict potential issues and adjust parameters accordingly. This proactive approach reduces trial-and-error phases and minimizes material wastage.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Implementing stringent quality assurance measures is necessary to ensure that each product meets predefined standards. Techniques such as automated visual inspection, dimensional checks, and material testing are used to identify defects early in the production process.
Regular maintenance of the machinery and molds is equally important to prevent unexpected downtime or defects caused by wear and tear.
Understanding these challenges in detail allows manufacturers to take preemptive actions, ensuring efficient production cycles and high-quality output.
Material selection impacts product quality in molding.True
Choosing the right material affects properties like shrinkage and heat resistance.
Uneven mold cooling causes no defects in products.False
Uneven cooling leads to warping or residual stresses, affecting quality.
Why Choose Plastic Injection Molding Over Other Methods?
Choosing the right manufacturing method can make or break a product’s success. So, why do many industries opt for plastic injection molding over other techniques?
Plastic injection molding is favored for its high production efficiency, ability to produce complex shapes, and precision. It excels in creating intricate designs quickly and cost-effectively, making it the go-to choice for industries like automotive and electronics.

High Production Efficiency
Plastic injection molding stands out for its rapid production cycles. Unlike other methods, this process can churn out thousands of identical parts in a matter of hours. High production efficiency6 not only reduces costs but also shortens time-to-market, which is crucial in fast-paced industries like consumer electronics.
Superior Precision and Consistency
The precision of plastic injection molding is unmatched. Thanks to advanced mold design and process controls, manufacturers can produce parts with exacting dimensions and tight tolerances. This level of dimensional accuracy7 ensures uniformity across batches, which is critical for applications in the medical field, where even a minor defect could have serious implications.
Versatility in Material Usage
Plastic injection molding supports a wide array of materials, from common thermoplastics like polyethylene to more specialized thermosetting plastics. This versatility allows designers to select materials that best meet the performance requirements of their products. For example, in the automotive industry, choosing the right plastic can improve durability while reducing vehicle weight.
Ability to Produce Complex Shapes
One of the most significant advantages of plastic injection molding is its ability to create complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible with other methods. This capability is essential for producing detailed parts such as intricate electronic housings or ergonomic handles for consumer goods.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Long Runs
While the initial investment in molds can be high, the cost per part decreases significantly over large production runs. This economy of scale makes plastic injection molding an attractive option for high-volume manufacturing. For instance, producing millions of plastic containers or bottles becomes financially viable when each unit’s cost is minimized.
Broad Application Range
From automotive interiors to everyday household items, plastic injection molding finds its application across a diverse range of industries. Its adaptability and efficiency make it a preferred choice for mass production, particularly when quality and consistency are paramount.
Plastic injection molding allows for rapid production cycles.True
It can produce thousands of parts in hours, reducing costs and time.
Plastic injection molding is unsuitable for complex geometries.False
It excels at creating complex shapes that other methods struggle with.
Conclusion
Understanding plastic injection molding equips you with essential insights into manufacturing efficiencies and capabilities. Reflect on how this process can innovate your projects or industry applications.
-
Explore how plastic injection molding shapes automotive components efficiently.: Automotive injection molding is a manufacturing process that uses a high-pressure plastic injection to form a variety of automotive parts. ↩
-
Learn about the critical role of injection molding in creating medical tools.: Injection molding involves melting and injecting plastic into a mold, cooling it, and ejecting the finished product. Injection molding is … ↩
-
Discover how flow simulations prevent defects in injection molding.: What are the benefits of mold flow analysis? · Optimize the runner system · Predict the pattern of the fill · Determine shrinkage rate · Reduce lead times. ↩
-
Discover factors affecting material choice for optimal product performance.: Learn how to select the right material for your injection molding design with this technical overview of thermoplastic resins. ↩
-
Learn about effective strategies for monitoring injection molding processes.: Understanding Injection Molding Process Control · Injection pressure · Melt temperature · Mold temperature · Air temperature · Screw position · Filling time · Packing/ … ↩
-
Discover how rapid cycles boost efficiency and reduce costs.: What are the advantages of injection molding? · 1. Efficient high production · 2. Low cost per part · 3. Repeatability · 4. Large material choice · 5 … ↩
-
Learn about the precision that ensures uniformity in products.: Although 3D printed products have lower accuracy, typically within +/- 0.1-0.2 mm, they are cost-effective and have short production cycles, making them … ↩






