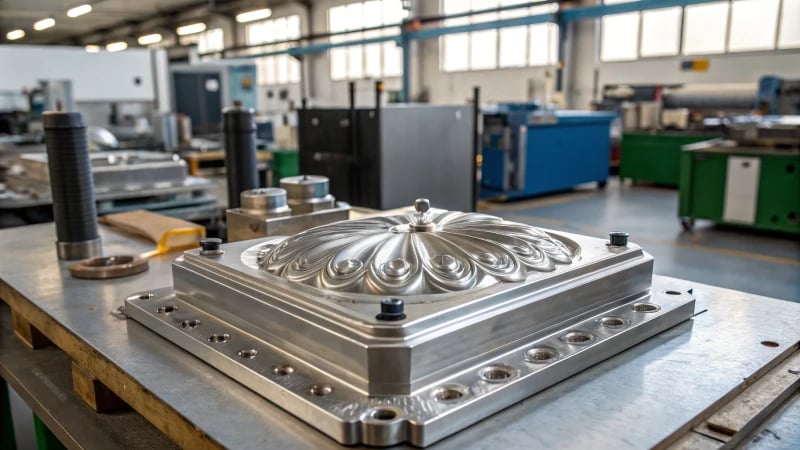
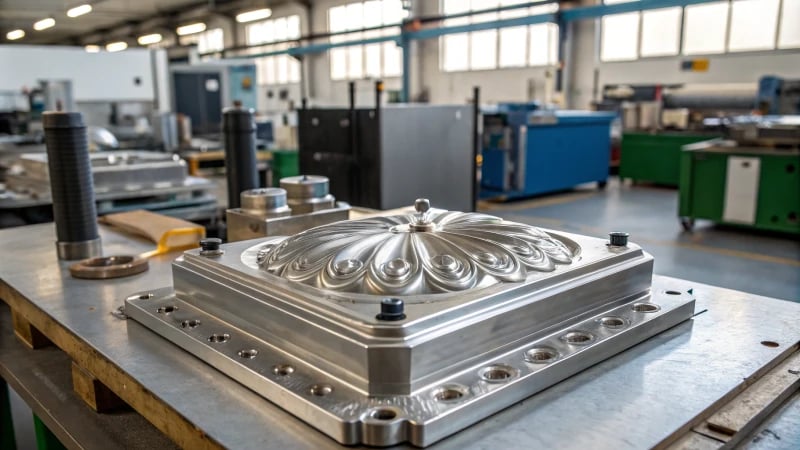
Did you ever think about how those perfect plastic bottles, seen everywhere, get created? Let’s go on a journey into the really interesting world of preform molds!
A preform mold creates PET bottle preforms by injecting molten plastic into a mold. These preforms, with finished necks, are later reheated and blow-molded into final shapes, ensuring precision and efficiency.
A preform mold is more than just a tool. It is the heartbeat of the plastic manufacturing process. I remember learning about them for the first time. It was like finding a hidden magic trick. These specialized molds shape raw materials into exact designs. They are crucial for industries like packaging. Bottles and containers are produced in an efficient and accurate way.
This article explores what preform molds are. It covers their structure and material types. It also discusses where they fit in the industry. Understanding these concepts is very important. It really could transform your own work and projects.
Preform molds are used exclusively for metal components.False
This claim is false as preform molds are primarily used for plastic components, not metal.
Preform molds play a crucial role in manufacturing plastic bottles.True
This claim is true because preform molds are essential for shaping plastic into bottle forms efficiently.
- 1. What Are the Key Components of a Preform Mold?
- 2. How Do Material Choices Affect Preform Mold Performance?
- 3. What Is the Manufacturing Process Involved with Preform Molds?
- 4. Which Industries Benefit the Most from Preform Molds?
- 5. What Innovations Are Shaping the Future of Preform Molding Technology?
- 6. Conclusion
What Are the Key Components of a Preform Mold?
Have you ever thought about creating the perfect preform mold? Someone with experience in the detailed world of manufacturing knows that understanding these parts is key to success. Recognizing the importance of these components really helps in making great designs.
The main parts of a preform mold include the core and cavity, cooling channels, ejector systems, guide pins, bushings and ventilation systems. These components are crucial. They determine the quality of the final product. They also affect the manufacturing process’s efficiency. Knowing these parts can really improve your designs and production results.
Understanding Preform Molds
Preform molds are truly important in creating prefabricated pieces, especially plastic items like PET bottles. Their design and structure have a big impact on the manufacturing process’s quality and efficiency.
Key Components of a Preform Mold
-
Core and Cavity
Core and cavity act as the brain of every preform mold. The core creates the inner space. The cavity shapes the outer form. Both must really align perfectly to keep measurements accurate and the product strong.- Material Choices: The materials you choose affect durability and cost. Some common materials include:
-
Cooling Channels
Cooling channels are where things get very fascinating. Effective cooling controls cycle times and keeps product quality uniform. These channels dissipate heat well during molding, which is vital for fast timelines.- Design Considerations: The layout changes based on:
- The part’s complexity
- The material used
- The necessary cooling time
- Explore advanced cooling techniques for better molding.
-
Ejector System
Picture this: the product cools and hardens perfectly. Now, how to remove it from the mold? Ejector pins or plates handle this part without harming the preform.- Ejector Pin Design: Smart design ensures:
- Pins are placed to reduce marks on the part
- Ejection happens smoothly with no stress
-
Guide Pins and Bushings
Guide pins and bushings are vital. They align the core and cavity correctly during molding. Misalignment can cause flaws. Precision matters.- Importance of Precision: Precision affects:
- Mold performance
- Product quality
- Learn more about maintaining alignment.
-
Ventilation Systems
Finally, the ventilation systems. Proper ventilation stops air from trapping in molds. Air pockets result in incomplete filling or surface flaws. Venting systems release air during injection. Quality control needs this.- Types of Vents:
- Slot Vents: Quickly let air escape in larger molds.
- Pin Vents: Smaller, used in detailed designs.
- Discover effective venting solutions .
Conclusion
Knowing these key components has really helped in designing better projects. It allows for both efficient and quality outputs. Precision in mold design and correct material use can really elevate the manufacturing process. It’s a journey of learning that keeps me inspired.
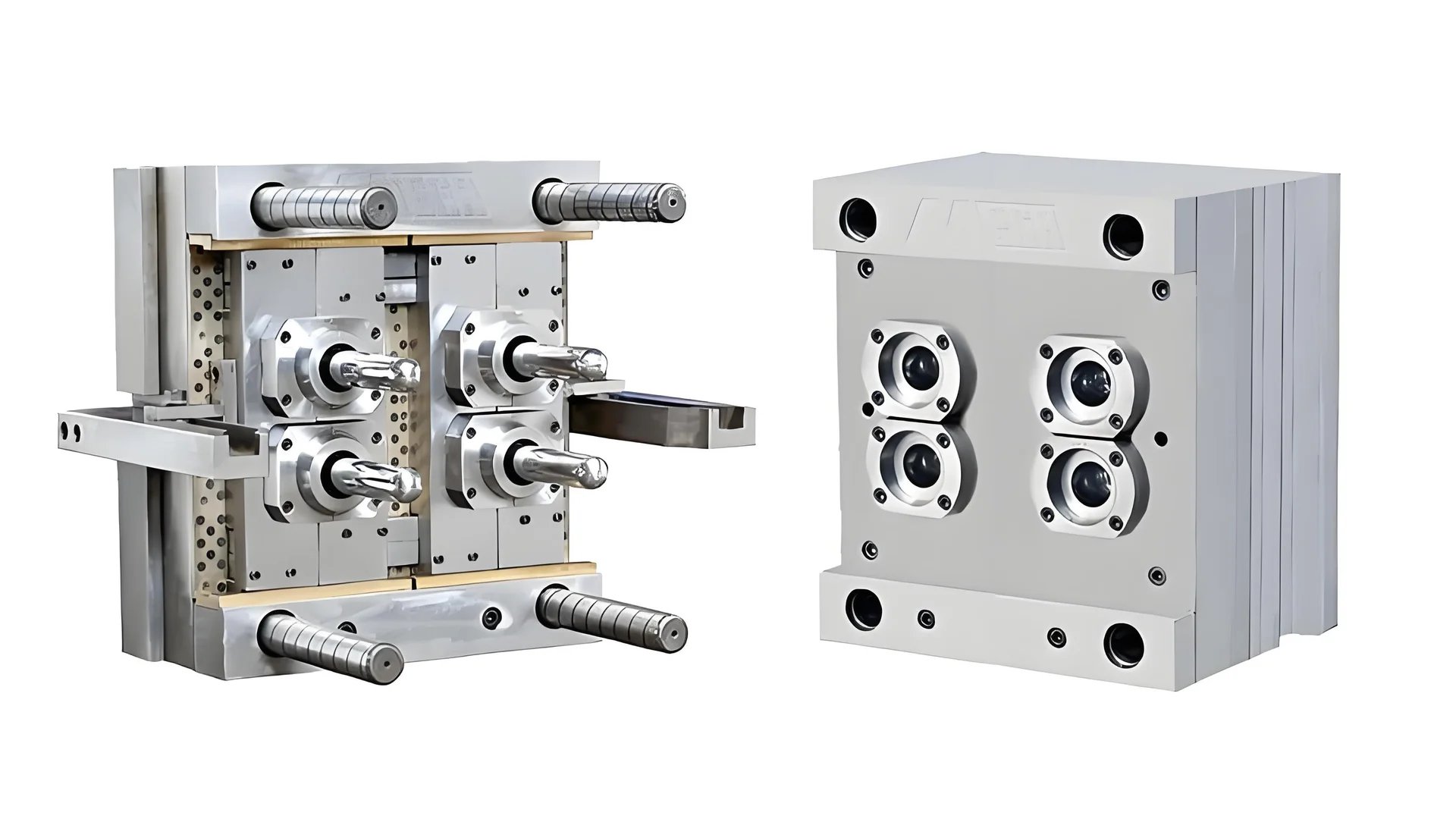
Understanding Preform Molds
In my journey as a designer, I have grown to value the art and science of preform molds. When I entered this field, I felt amazed by molds. Molds may seem simple. However, they decide the quality of the final product. It’s much like a sculptor. Each part plays a vital role in shaping the end result. Let’s explore these components together, okay?
Key Components of a Preform Mold
- Core and Cavity
The core and cavity are the heart of any preform mold. They define the shape and internal structure of the final product. The core is the inner part that creates the hollow space, while the cavity forms the outer shape. Together, they must align perfectly to ensure dimensional accuracy and product integrity.- Material Choices: The choice of materials for these components can impact durability and cost. Common materials include:
| Material Type | Characteristics | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High strength, good wear resistance | Large production runs |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, cost-effective | Low-volume production |
-
Cooling Channels
Effective cooling is crucial to maintaining cycle times and ensuring uniform product quality. Cooling channels are strategically placed within the mold to dissipate heat efficiently during the molding process.- Design Considerations: The layout of cooling channels can vary based on:
- The complexity of the part being produced
- The material used
- The required cooling time
- Explore advanced cooling techniques1 to optimize your molding process.
- Design Considerations: The layout of cooling channels can vary based on:
-
Ejector System
Once the product has cooled and solidified, it needs to be ejected from the mold. An ejector system, which may include ejector pins or plates, facilitates this process without damaging the newly formed preform.- Ejector Pin Design: Proper design ensures that:
- Pins are positioned to minimize marking on the part
- Ejection occurs smoothly without stress on the mold
- Ejector Pin Design: Proper design ensures that:
-
Guide Pins and Bushings
Guide pins and bushings are essential for ensuring that the core and cavity align correctly during the molding process. Misalignment can lead to defects in the finished product.- Importance of Precision: The precision in these components affects:
- Overall mold performance
- Product quality
- Learn more about maintaining alignment2.
- Importance of Precision: The precision in these components affects:
-
Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation is necessary to avoid trapping air in the mold, which can cause defects such as incomplete filling or surface blemishes. Venting systems help release air during injection.- Types of Vents:
- Slot Vents: Used for larger molds where air needs to escape quickly.
- Pin Vents: Smaller and often used in intricate designs.
- Discover effective venting solutions3.
- Types of Vents:
Conclusion
Understanding these key components of a preform mold helps designers like Jacky optimize their designs for efficiency and product quality. By focusing on precision in mold design and utilizing appropriate materials, manufacturers can significantly improve their production processes.
Cooling channels are essential for uniform product quality.True
Cooling channels dissipate heat during molding, ensuring consistent temperatures and preventing defects, which is vital for high-quality plastic products.
Ejector systems are unnecessary in preform molds.False
Ejector systems are crucial for safely removing finished products from molds without damage, making them a necessary component in preform mold design.
How Do Material Choices Affect Preform Mold Performance?
Have you ever thought about how the materials we pick improve or ruin the performance of preform molds? I have for sure! Knowing these material choices changes not just how efficiently we manufacture but also the overall quality of the products we produce.
Material choices greatly impact preform mold performance due to their influence on durability, precision and cost. Metal molds offer strength and long life. Plastic molds provide flexibility and lower costs. These impacts extend from production speed to product quality. Let’s explore this important topic further!
Importance of Material Selection in Mold Performance
Material choice is crucial for preform mold performance. Each material has unique properties. These properties affect mold efficiency and the quality of produced components.
For example, molds made of steel deliver strength and resist wear. I recall a project needing intricate components with high pressure. Steel molds worked perfectly, maintaining precision throughout. However, plastic molds, being lightweight and budget-friendly, appeal to simpler designs. Yet, they struggle under high-stress conditions.
Knowing these characteristics enables informed choices. My colleague Jacky wisely chooses the material based on each component’s needs.
Structural Features Influenced by Material
Mold structure design is also vital for performance. Here are key aspects affected by material:
Shape and Dimensional Accuracy: The right material must withstand stress for products to meet strict size requirements. I once faced a project where a steel mold’s accuracy under heat saved us costly errors.
Components: Molds have many parts like templates and frames. Material choice for templates affects surface finish, impacting look and function. I vividly remember swapping plastic for steel templates, which improved product quality greatly.
Material Types and Their Impact
-
Metal Materials
Metal molds are robust. Steel grades like NAK80 and S136 provide:
High Wear Resistance: They endure repeated cycles with little wear – great for high-volume production.
Temperature Tolerance: They stay stable when heated, ensuring consistency. -
Plastic Materials
Plastic molds suit smaller or simple parts due to lower costs. However:
Limited Durability: They might not handle high stress well.
Lower Precision: They aren’t suitable for tight tolerance applications. -
Composite Materials
Composite molds mix materials to harness strengths. For example:
Fiber-Reinforced Composites: These offer great surface quality while being lightweight – ideal for reducing production burden.
Balanced Performance: They optimize cost and longevity across various uses.
Application Fields Influencing Material Choice
Specific industry needs often dictate mold performance material choices:
Construction Industry: Needs strong molds for large, precise components. Metal molds are favored.
Municipal Engineering: Requires durable molds for constant infrastructure element production.
Gardening and Landscape Design: Uses plastic molds for intricate, quick designs without needing high durability.
Understanding these applications guided my past project decisions. I always aim to choose wisely based on expected performance.
In conclusion, choosing the right material is personal. It affects quality and efficiency in our work. Each project reminds me of the importance of these choices. They shape the final product and fulfill our craft satisfaction.
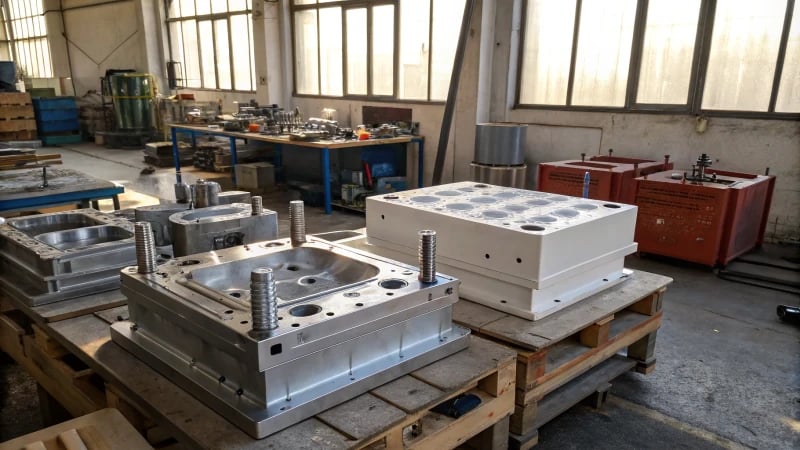

Importance of Material Selection in Mold Performance
When I began my journey in mold design, I was surprised by how greatly material choice affects mold performance. It involves more than picking something strong. It requires finding a perfect mix of durability, precision and cost. This understanding came during a tough project. I realized how critical it is to select the right material for each application. I really learned this the difficult way.
Structural Features Influenced by Material
The structural design of a mold also plays a critical role in its performance. Key aspects influenced by material choices include:
- Shape and Dimensional Accuracy:The chosen material must maintain its form under operational stresses to ensure that the final products meet strict dimensional tolerances.
- Components: Molds consist of various parts such as templates and frames. The material used for templates directly impacts the surface finish of the molded parts, affecting aesthetics and functionality.
| Component | Material Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Template | Steel | High strength, excellent surface finish |
| Frame | Composite | Lightweight, strong support |
| Connectors | Metal | Durable, secure connections |
| Demoulding Device | Plastic | Cost-effective, easy to handle |
Material Types and Their Impact
1. Metal Materials
Metal molds are commonly utilized due to their robust nature. Steel, particularly grades like NAK80 and S136, offers:
- High Wear Resistance: Ensures molds can endure repetitive cycles without significant wear.
- Temperature Tolerance: Maintains stability and performance during heating processes.
For more on the properties of different types of steel, check out this material selection guide4.
2. Plastic Materials
Plastic molds are preferred for smaller components or less complex shapes due to their lower costs. However:
- Limited Durability: They may not withstand the same stresses as metal molds.
- Lower Precision: Not ideal for high-precision applications where tight tolerances are crucial.
You can explore more about advantages and disadvantages of plastic molds5.
3. Composite Materials
Composite molds combine multiple materials to leverage their strengths. For example:
- Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Offer excellent surface quality and reduced weight while providing adequate support through metal reinforcements.
- Enhanced Performance: These molds can deliver higher performance in diverse applications, balancing cost and longevity effectively.
To learn more about composite materials in mold design, see this composite material overview6.
Application Fields Influencing Material Choice
Different industries dictate specific requirements for mold performance, influencing material selection:
- Construction Industry: Requires molds that can produce large prefabricated components with precise dimensions; thus, metal molds are often favored for their strength.
- Municipal Engineering: Molds need to be durable enough to produce various infrastructure elements consistently and efficiently.
- Gardening and Landscape Design: Here, plastic molds may be used to create intricate designs quickly without the need for extensive durability.
Understanding these applications can help in making informed decisions about material choices based on performance expectations. For additional insights into application-specific requirements, refer to this industry analysis7.
Metal molds provide better dimensional accuracy than plastic molds.True
Metal molds, especially steel, maintain form under stress, ensuring precise dimensions compared to plastic molds which may deform easily.
Plastic molds are always more cost-effective than metal molds.False
While plastic molds are generally cheaper, their lower durability and precision can lead to higher costs in high-volume applications.
What Is the Manufacturing Process Involved with Preform Molds?
Do you ever think about how those perfectly shaped plastic parts, like the bottles we use every day, are created? Let’s explore the amazing world of preform molds and how they are made!
The manufacturing process of preform molds involves several steps. First, designers work on the design. Next, experts select materials. Then, machining takes place. Testing follows machining. Finally, producers create preforms using injection molding. Each step is very important. Every step ensures precision and quality in creating reliable plastic parts.
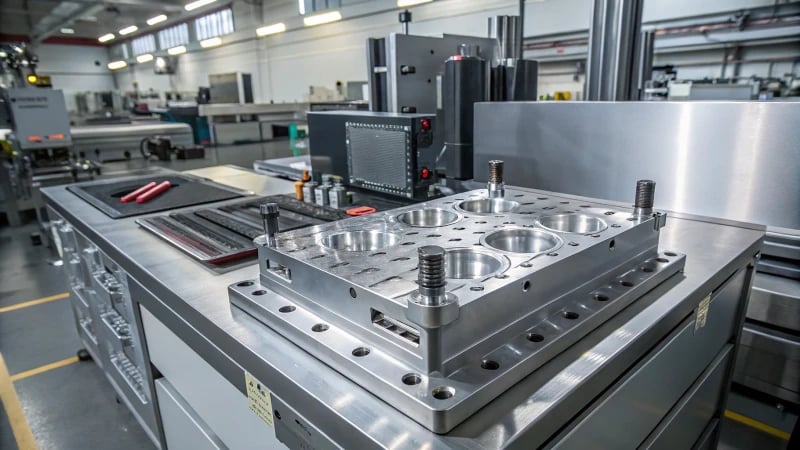

Understanding Preform Molds in Manufacturing
The manufacturing process of preform molds is crucial for producing plastic components, particularly in the production of PET bottles. This process involves several key stages, each essential to ensuring high-quality outputs.
1. Designing the Mold
The first step in creating a preform mold is the design phase. Designers utilize CAD software to create precise 3D models of the molds, taking into account the dimensions and features required for the preforms. The mold design must ensure:
- Shape accuracy: The final product’s shape is determined by the mold design.
- Dimensional precision: High precision is necessary to ensure proper fitting during assembly.
This stage often involves collaboration between product designers and engineers to finalize the mold specifications. For more on design processes, check out this detailed guide8.
2. Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for preform molds is vital. Typically, molds are made from:
| Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Metal | High strength and durability | More expensive; heavier |
| Plastic | Lightweight; low cost | Less durable; shorter lifespan |
| Composite | Combines strengths of metal and plastic | Can be complex to manufacture |
Metal molds are favored for their strength, while plastic molds may be used for less demanding applications. The choice depends on production volume and the complexity of the preforms required. To learn more about materials, explore this insightful article9.
3. Manufacturing the Mold
Once the design and materials are finalized, the manufacturing process begins:
- CNC Machining: This is commonly used for metal molds, where CNC machines carve out the mold from solid blocks of material with high precision.
- Injection Molding: For plastic molds, injection molding techniques may be employed to create complex shapes efficiently.
The manufacturing stage is pivotal in ensuring that all specifications are met to avoid issues during production. For further understanding of CNC processes, visit this informative resource10.
4. Testing and Quality Control
After manufacturing, each mold undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets the required standards. This includes:
- Dimensional checks: Verifying that all measurements align with design specifications.
- Performance testing: Assessing how the mold performs under real production conditions.
Quality control ensures that only molds that meet all criteria are used in production, minimizing defects in preforms. For tips on quality assurance practices, refer to this quality control handbook11.
5. Production of Preforms
With tested molds in place, the actual production of preforms can commence. The process typically involves:
- Injection Molding: Heated plastic (like PET) is injected into the mold under high pressure.
- Cooling: The material cools and solidifies into the shape of the preform before being ejected from the mold.
This entire cycle can be repeated multiple times, allowing for efficient mass production of high-quality preforms ready for blow molding into bottles. To get a deeper understanding of injection molding techniques, check this detailed overview12.
Preform molds are primarily used for producing PET bottles.True
Preform molds are essential in manufacturing preforms, which are the initial shapes used to create PET bottles through blow molding.
CNC machining is not used for metal mold manufacturing.False
CNC machining is a common technique for creating precise metal molds in the preform manufacturing process.
Which Industries Benefit the Most from Preform Molds?
Take a moment to discover the interesting world of preform molds. Many industries use these molds to create exact, high-quality parts. You will probably be amazed by their broad influence!
Preform molds are vital to industries like construction, municipal engineering, landscaping, packaging and car manufacturing. They produce prefabricated parts with high accuracy. These molds increase both efficiency and quality in many applications.
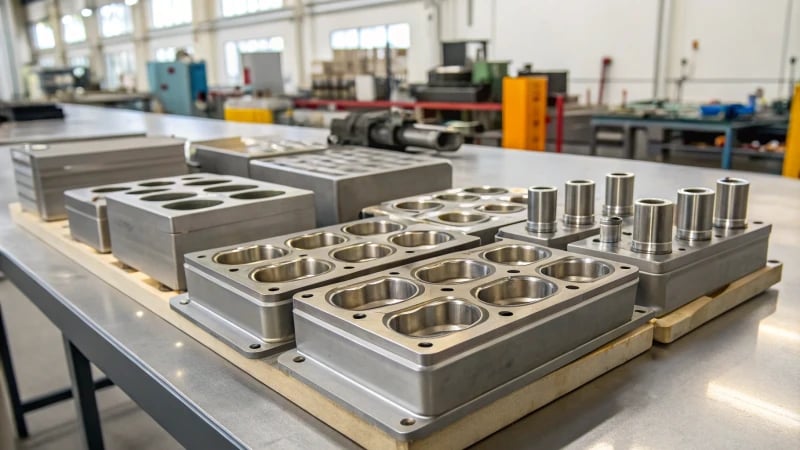

Understanding Preform Molds
Preform molds play a quiet, essential role in manufacturing. They help everything fit together correctly. My first experience with these molds was fascinating because of their precision. These molds create items with great accuracy. Their strong design ensures products are reliable and efficient.
In construction, prefabricated wall panels13 and curbstones are produced using these molds, showcasing their versatility. Additionally, these molds enable rapid assembly at construction sites, enhancing productivity.
Key Industries Utilizing Preform Molds
Preform molds find applications across multiple industries:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Construction | Prefabricated wall panels, floor slabs, stairs |
| Municipal Engineering | Curbstones, drainage pipes |
| Landscaping & Gardening | Flower pots, decorative elements |
| Packaging | Bottles, containers for food and beverages |
| Automotive | Components for vehicle assembly |
Construction Industry
In the construction sector, preform molds are crucial for producing components that are essential for modern building practices. They allow for the quick fabrication of items like:
- Prefabricated wall panels: Reducing on-site labor and material waste.
- Prefabricated beams and columns: Enhancing structural integrity and speed of assembly.
These advancements not only save time but also improve project quality. Learn more about construction technologies . It’s really fascinating!
Municipal Engineering
In municipal engineering, preform molds shape daily infrastructure. I often admire:
- Curbstones: Ensuring uniformity in cities.
- Manhole covers: Essential for public safety.
Prefabricated parts help cities keep high construction standards while quickly completing projects. Discover more about municipal engineering. There’s a lot to explore!
Landscaping & Gardening
In landscaping, designers love preform molds. I enjoy seeing:
- Prefabricated flower beds: They ease garden installation.
- Decorative rockery stones: They add charm to outdoor spaces.
These molds invite creativity in design, offering options for any style. Check out landscape design trends . There are many expert resources available!
Packaging Industry
In packaging, preform molds are very important. They help create:
- Plastic bottles: Necessary for drinks like water and juice.
- Containers: For various consumer products.
These molds enable high production rates while ensuring quality. Discover packaging innovations. It’s a whole new world!
Automotive Sector
in the automotive industry, preform molds are crucial for car parts. It fascinates me how they help make:
- Dashboards and interior trims: Enhancing looks and usefulness.
- Underbody components: Vital for safety and stability.
the use of preform molds in automotive production shows their importance in car design. Keep up with automotive manufacturing. It’s worth it!
Preform molds are essential in the construction industry.True
These molds are crucial for producing prefabricated components like wall panels and beams, optimizing construction processes.
Preform molds are not used in the packaging industry.False
This claim is false; preform molds are vital for manufacturing containers and bottles in packaging.
What Innovations Are Shaping the Future of Preform Molding Technology?
Have you ever thought about how new ideas in preform molding technology are changing the way we produce things? Exciting progress is happening. It not only improves how fast we work but also helps our industry become more environmentally friendly.
Advancements in materials, structural designs and applications are shaping the future of preform molding technology. Various industries are experiencing greater efficiency and sustainability. This evolution shows a move towards more innovative and green practices. These practices resonate with both manufacturers and consumers. It really does.
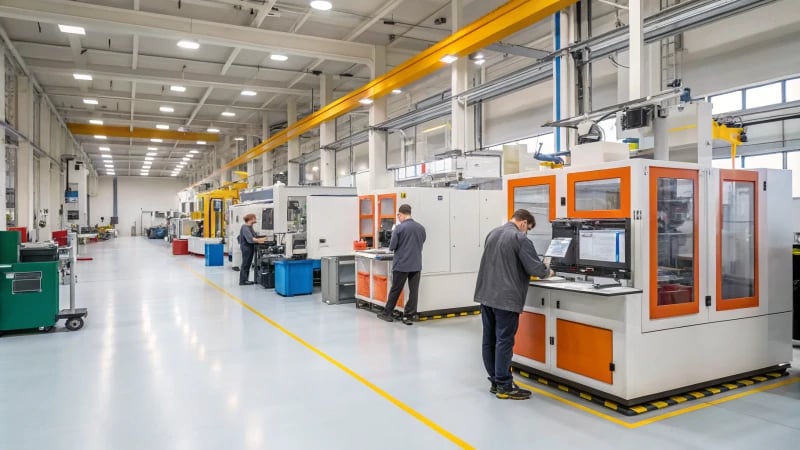

Definition of Preform Molding Technology
Preform molding technology involves special molds that turn raw materials, like concrete or plastics, into perfect shapes. Imagine a magic trick, but it happens in real life! In construction, these molds shape wall panels and floor slabs that can be assembled on-site, thus streamlining the building process. This process makes building faster and more efficient. Knowing this basic idea helps us understand the innovations that come next.
Innovations in Material Types
Advancements in materials have really changed the production of prefabricated components. Once, I worked on a project needing perfect mold materials for a new product. Some materials have become very important lately:
| Material Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Metal Materials | Steel molds are predominant due to their high strength and durability. For example, NAK80 and S136 steel are commonly used for their wear resistance. |
| Plastic Materials | Lightweight and cost-effective, but typically used for smaller parts where precision isn’t critical. Commonly used plastics include polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). |
| Composite Materials | These combine the strengths of metals and plastics, utilizing fiber-reinforced composites for templates with metal skeletons for structural support. |
The ongoing research into composite materials is particularly noteworthy as they promise better mold performance while lowering production costs. Explore composite innovations14.
Structural Features Enhancements
Structural innovations greatly impact mold efficiency. Precision engineering now lets us achieve amazing shape and size accuracy which is very important as it means that components fit perfectly during assembly. Some key features include:
- High Dimensional Accuracy: New manufacturing methods allow tighter control in mold design.
- Advanced Components: Modern molds often have complex demolding devices and connectors that make production smoother.
These enhancements can significantly cut waste and reduce repairs while aligning well with sustainable manufacturing practices. Learn more about structural enhancements15.
Application Fields Expansion
Another exciting thing is the new uses for molds outside traditional construction. In a past project, we used them in municipal engineering; it was amazing to see their flexibility! Molds are now important in many industries:
- Municipal Engineering: Molds help create uniform components like curbstones and drainage pipes which speed up construction while guaranteeing uniformity.
- Landscape Design: Innovative molds are making items like flower pots and intricate rockery stones that add beauty to outdoor spaces.
This broad use shows the flexibility of molding technology while highlighting its growing role in sustainability across various fields. Discover application innovations16.
Composite materials enhance mold performance and reduce costs.True
Innovations in composite materials improve the efficiency of preform molding technology while lowering production expenses, making them a key focus in the industry.
Preform molds are only used in construction applications.False
Prefabricated molds are utilized in various fields, including municipal engineering and landscape design, showcasing their versatility beyond just construction.
Conclusion
Preform molds shape raw materials into precise forms, crucial for industries like construction and packaging, enhancing efficiency and product quality.
-
Clicking this link will provide you with advanced techniques that can greatly enhance your cooling system design in molds. ↩
-
This resource is ideal for understanding how to maintain alignment in mold components, critical for high-quality production. ↩
-
This link offers insights into effective venting solutions that can improve your molding process by minimizing defects. ↩
-
Clicking this link will provide you with comprehensive information on material properties essential for mold design decisions. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the pros and cons of using plastic versus metal molds in manufacturing. ↩
-
This link offers valuable insights into composite materials used in molds, enhancing your understanding of advanced mold design techniques. ↩
-
This link will guide you through industry-specific requirements for mold materials, helping you make informed choices based on your application. ↩
-
This link offers valuable insights into the intricate details of preform mold manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Learn about CNC machining and its role in creating precise molds for enhanced quality and efficiency. ↩
-
Get insights on different materials used in preform molds and their advantages for various applications. ↩
-
Understand how quality control practices are integrated into the mold manufacturing process for superior results. ↩
-
Explore injection molding techniques and their significance in mass production of plastic components. ↩
-
Explore this link to gain insights into how preform molds contribute to the manufacturing process across different industries. ↩
-
Clicking this link will provide you with detailed insights into the latest trends and technologies in preform molding, ensuring you stay ahead in your field. ↩
-
This link will lead you to comprehensive information about structural advancements in preform molds, enhancing your understanding of current innovations. ↩
-
By exploring this link, you will gain insights into how prefabricated molds are applied across different industries, broadening your knowledge base. ↩






