Are you feeling the pressure of rising injection molding costs? Let’s unravel this puzzle together!
To reduce injection mold costs, focus on optimizing part designs to minimize complexity, select appropriate materials to balance quality and cost, and increase production volumes where feasible. Additionally, collaborating with experienced suppliers can lead to better cost efficiencies.
But reducing costs doesn’t mean compromising on quality. This blog dives deeper into practical strategies that help balance cost with quality in injection molding, offering insights you won’t want to miss.
Design optimization reduces injection mold costs.True
Simplifying part geometry and precision requirements lowers manufacturing expenses.
What Are the Key Factors Influencing Injection Mold Costs?
Discover the critical elements that drive the cost of injection molds, from design intricacies to material choices and beyond.
Injection mold costs are influenced by mold design complexity, material selection, manufacturing processes, mold size, production batch size, and supplier selection. Simplifying designs, choosing cost-effective materials, and optimizing production volumes can effectively manage these costs.

Mold Design and Complexity
The design and complexity of the mold significantly affect its cost. Parts with intricate geometries, such as complex curves or deep cavities, necessitate sophisticated mold designs incorporating features like sliders and core pulls. This complexity can lead to increased manufacturing costs due to the need for precise machining and additional components.
Conversely, simpler part designs result in less expensive molds due to reduced manufacturing complexity. This highlights the importance of thoughtful design planning1 to minimize unnecessary intricacies without sacrificing functionality.
Material Selection
The choice of mold material plays a crucial role in determining cost. High-quality steel offers excellent wear resistance and longevity but comes at a higher price. For applications requiring durability, investing in superior materials like H13 tool steel can enhance mold lifespan, justifying the initial cost outlay.
Special material requirements, such as corrosion resistance for specific applications, further drive up costs. Balancing material quality with budget constraints is essential for cost-effective production2.
Manufacturing Process
Advanced manufacturing processes like CNC machining and EDM ensure precision but incur higher costs. These methods are essential for achieving tight tolerances and complex shapes. On the other hand, traditional machining methods may reduce expenses but might not meet precision requirements for all parts.
Surface treatments such as nitriding or chrome plating add to the cost but improve mold performance by enhancing wear resistance and ease of demolding. These treatments can ultimately reduce long-term maintenance costs and extend the mold’s operational life.
Mold Size and Production Batch
Larger molds require more materials and longer processing times, increasing overall costs. However, these costs can be offset by economies of scale in high-volume production. A large production batch allows the fixed mold cost to be distributed across a greater number of units, lowering the cost per part.
For smaller batches, consider simpler molds or alternative manufacturing methods to keep costs in check without compromising quality. Strategic production planning3 is vital for optimizing cost-effectiveness.
Supplier Selection and Design Changes
Choosing a reputable mold supplier ensures quality but might come with a higher price tag. Experienced suppliers can provide valuable insights and after-sales support that contribute to long-term savings.
Furthermore, design changes during manufacturing can significantly increase costs. It’s crucial to finalize designs before production begins to avoid unnecessary rework and expenditure. Effective communication with suppliers during the design phase can prevent costly adjustments later on.
Complex mold designs increase manufacturing costs.True
Intricate geometries require precise machining and additional components.
Choosing high-quality steel always reduces mold costs.False
High-quality steel increases initial costs but enhances mold lifespan.
How Can Design Optimization Help in Reducing Mold Costs?
Unlock the potential of design optimization to cut costs in injection molding without sacrificing quality.
Design optimization reduces mold costs by simplifying part geometry, lowering precision requirements, and choosing cost-effective manufacturing processes. By focusing on these areas, manufacturers can significantly lower expenses while maintaining functionality and aesthetics.
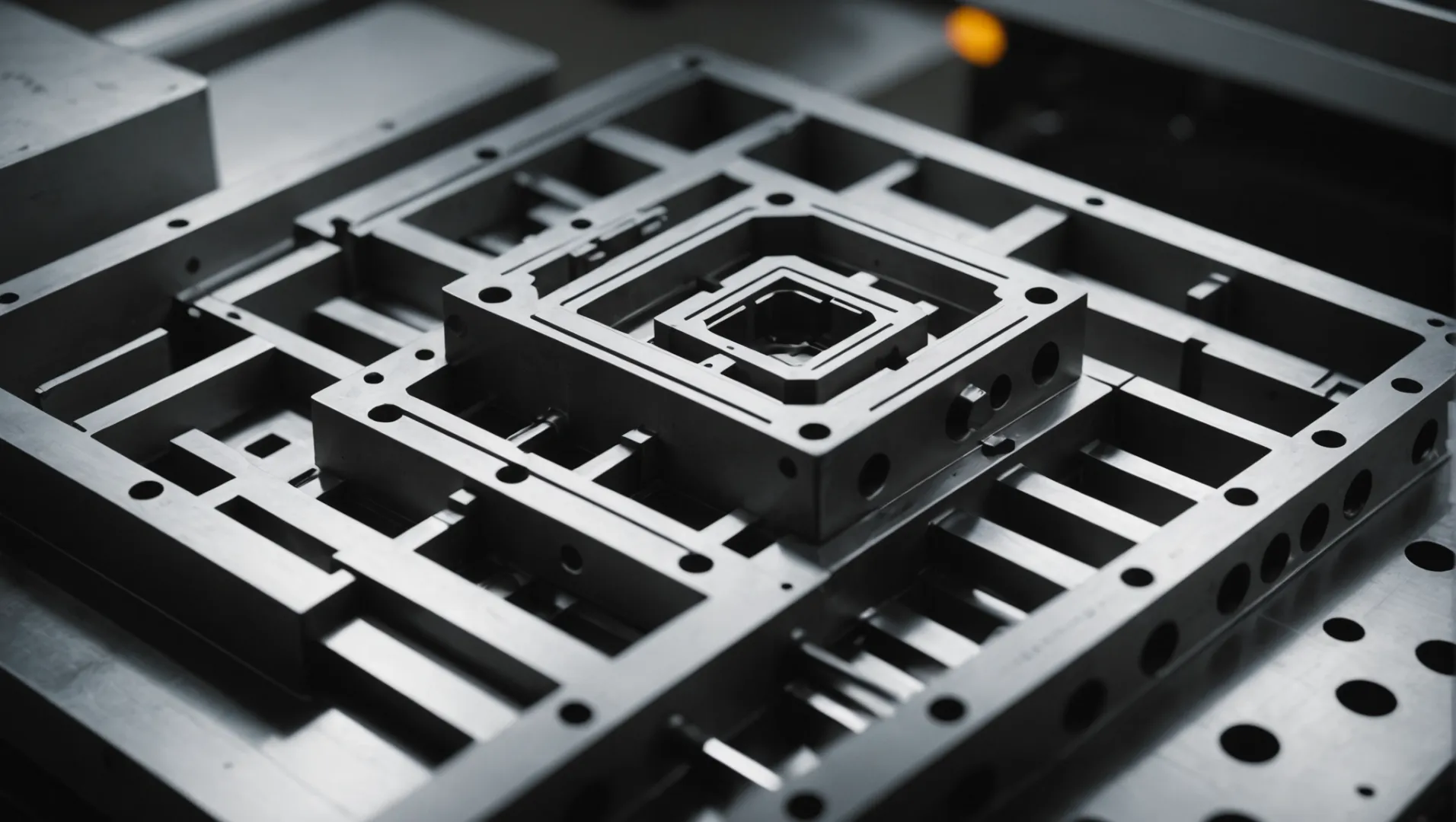
Simplifying Part Geometry
One of the primary ways design optimization can cut costs is through simplifying the geometry of the part being molded. Complex designs often require intricate molds, which increase not only the initial manufacturing cost but also the complexity of maintenance and repairs. By opting for simpler geometric shapes, such as flat surfaces or basic curves, you can reduce the need for advanced mold features like multiple sliders or core pulling mechanisms.
For instance, converting a part with deep cavities into a more straightforward shape can eliminate the necessity for complex mold components. This change alone can result in substantial savings.
Precision Requirements
Another significant factor is precision. The tighter the dimensional tolerances, the more expensive the mold due to the need for high-precision machining and quality materials. By reevaluating the precision requirements, manufacturers can opt for standard tolerances where applicable without affecting the product’s performance.
For example, consider a scenario where a non-critical part was initially designed with a 0.01mm tolerance. By relaxing this to 0.1mm, the use of more affordable mold processing techniques becomes viable.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing Processes
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing process is crucial. While high-precision methods like CNC machining are often necessary, they are also costly. Where possible, substituting these with traditional methods like milling or turning can slash costs significantly.
Table: Comparison of Manufacturing Methods
| Method | Accuracy | Cost | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High | High | Complex shapes |
| Milling | Medium | Medium | Simple to medium complexity |
| Turning | Low | Low | Cylindrical parts |
Collaborative Supplier Engagement
Working closely with experienced mold suppliers can also yield cost benefits. Suppliers often have insights into cost-saving opportunities that might not be apparent during the initial design phase. Engaging them early in the design process can lead to suggestions that reduce costs without compromising quality.
To explore more about how suppliers can impact cost, check out supplier engagement strategies4. This resource provides insights into maximizing supplier relationships for better pricing and service.
By focusing on these elements, manufacturers can achieve a balance between quality and cost-efficiency, paving the way for more sustainable production practices.
Simplifying part geometry reduces mold costs.True
Simpler shapes reduce complexity, cutting costs in mold manufacturing.
High precision always increases mold costs.True
Tighter tolerances require costly high-precision machining.
Why Is Material Selection Crucial for Cost-Effective Molding?
Choosing the right material is key to achieving cost-effective molding without compromising quality.
Material selection influences mold longevity, precision, and cost efficiency. High-quality materials may incur higher initial costs but reduce long-term expenses through durability and performance.

The Role of Steel Quality in Mold Cost-Effectiveness
When considering steel quality5, it’s crucial to balance the upfront costs with the benefits it provides. High-grade steel like H13 offers superior wear resistance and can withstand higher injection pressures, ultimately extending mold life. Although more expensive initially, it reduces the need for frequent replacements or repairs, saving costs in the long run.
For example, molds made from lower-grade steel might face wear and deformation more quickly, leading to increased downtime and maintenance costs.
Special Material Requirements and Their Impact
In certain applications, molds require specific materials due to environmental or operational demands. For instance, molds used in corrosive environments benefit from corrosion-resistant stainless steel, despite the higher cost. This not only ensures the mold’s longevity but also maintains the quality of the molded parts.
When high temperature or hardness is required, specialized alloys can significantly improve performance but at a price. Evaluating these needs carefully can prevent unnecessary expenditures while ensuring that the mold performs efficiently.
Weighing Cost Against Precision and Performance
Choosing materials based on dimensional accuracy requirements6 is another critical factor. High-precision requirements necessitate materials that can handle advanced processing techniques, such as EDM or CNC machining. While these might increase costs, they ensure the production of high-quality parts with minimal defects, reducing waste and rework.
In summary, material selection is not just about the initial cost but about evaluating long-term performance and maintenance. Understanding these aspects can lead to significant savings over the mold’s lifecycle.
High-grade steel reduces mold replacement costs.True
High-grade steel like H13 extends mold life, saving on replacements.
Low-quality materials enhance mold precision.False
Low-quality materials lead to wear, reducing mold precision.
How Do Production Volume and Supplier Choice Impact Mold Pricing?
Production volume and supplier choice can significantly influence mold pricing in the injection molding process, affecting both initial and long-term costs.
Higher production volumes can lower per-unit mold costs by spreading the initial investment across more products, while experienced suppliers may offer better quality at a premium price.

The Role of Production Volume in Mold Pricing
Production volume is a critical factor in determining the cost efficiency of injection molds. For high-volume production runs, molds need to withstand more cycles, which necessitates using durable materials and complex designs, thereby increasing the initial investment. However, this investment can be amortized over a larger number of units, effectively reducing the cost per unit.
For instance, if a mold costs $50,000 and produces 100,000 parts, the cost per unit is $0.50. Conversely, if the same mold is used for only 10,000 parts, the cost per unit jumps to $5.00. Therefore, optimizing production volume is a key strategy for reducing mold costs per part.
Supplier Choice: Price vs. Quality Trade-off
Choosing the right supplier is another crucial decision that impacts mold pricing. Reputable suppliers often charge more due to their expertise and quality assurances, which can save costs in the long run through enhanced mold longevity and reduced defect rates.
| Supplier Type | Initial Cost | Quality Assurance | Long-term Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-end | High | Excellent | Significant |
| Mid-range | Moderate | Good | Moderate |
| Low-cost | Low | Variable | Minimal |
An experienced supplier might also offer valuable insights into optimizing mold design7 and material selection, further reducing costs. It’s vital to balance the initial cost with potential savings from fewer defects and longer mold life.
Balancing Production Volume and Supplier Choice
When considering production volume and supplier choice together, businesses must evaluate their specific needs. For example, if high precision and durability are required due to large production runs, investing in a high-end supplier might be justified. In contrast, for short runs or prototype development, a mid-range supplier might suffice.
Understanding these dynamics helps in negotiating terms with suppliers to find an optimal balance between cost and quality. It’s also beneficial to explore case studies8 of similar companies to understand how they have optimized their mold costs through strategic supplier selection and volume management.
Higher production volume reduces unit mold costs.True
Spreading initial investment over more units lowers cost per unit.
Low-cost suppliers offer the best long-term savings.False
Low-cost suppliers often lead to higher defect rates and less durability.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors influencing injection mold costs empowers informed decision-making. Optimize designs, select suitable materials, and choose the right suppliers to achieve cost efficiency without sacrificing quality.
-
Understand how thoughtful design planning reduces mold complexity and costs.: Understanding your goals and what your part does is important. Your molder should want to know what the part does, where it goes, how it works, … ↩
-
Learn how selecting appropriate materials balances quality and cost.: If it needs to be cheap and rigidity and cosmetics aren’t really important, try polypropylene (PP). Our design cube is made of PP. If you need something a … ↩
-
Explore strategies for optimizing production to reduce mold costs.: Establish strategic partnerships to leverage economies of scale, negotiate favorable terms, and gain access to new markets. ↩
-
Discover how effective supplier collaboration can enhance cost efficiency.: Establish strategic partnerships to leverage economies of scale, negotiate favorable terms, and gain access to new markets. ↩
-
Discover how high-quality steel can enhance mold durability.: Stability during heat treating, and resistance to softening at high temperatures · Excellent wear properties, which are especially important when preventing … ↩
-
Learn why precision is crucial in material selection.: The shrinkage rate of molding raw materials has a great impact on the dimensional accuracy of plastic parts. If the precision of molding … ↩
-
Learn how design optimization can significantly reduce mold costs.: Learn how to optimize mold design for efficient injection molding and improve product quality while reducing costs. ↩
-
Explore real-world examples of cost optimization strategies.: Using side-action cores and other in-mould mechanisms can bump up tooling costs by 15% to 30%. This means you might face an extra tooling … ↩






