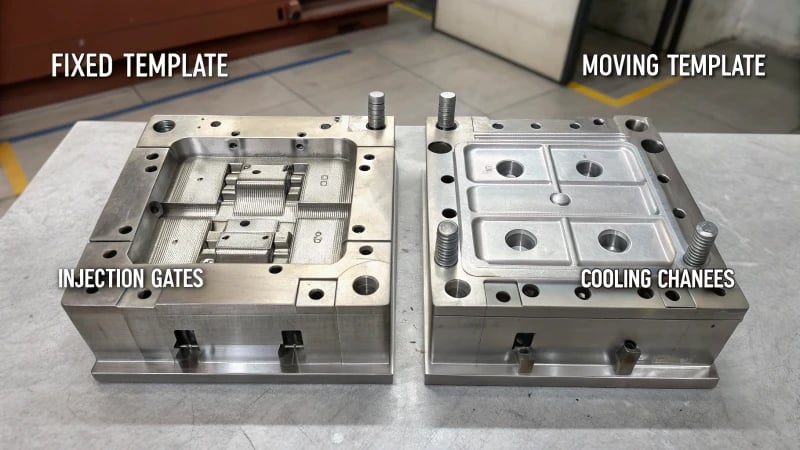
Peeling back the layers of a two-plate mold is like uncovering the secrets of a magic trick in injection molding.
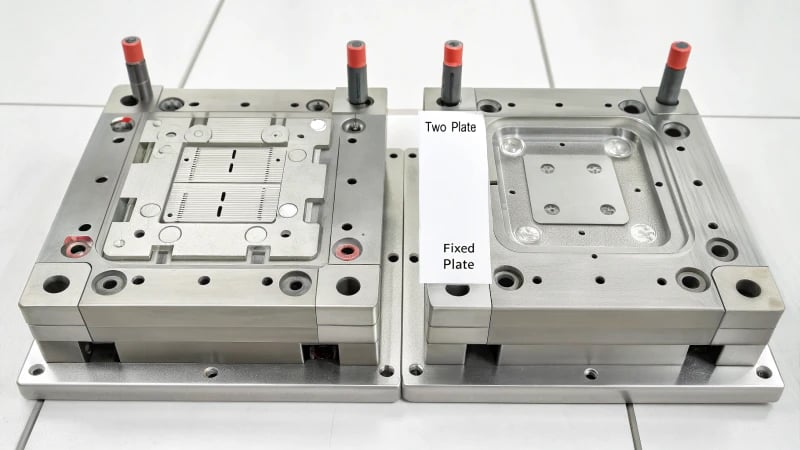
A two-plate mold functions in injection molding by using a fixed and a moving template to form a cavity. Molten plastic is injected, cooled, and the moving template separates to release the finished product.
I remember the first time I watched a two-plate mold in action. It was mesmerizing to see how seamlessly the molten plastic flowed into the mold, like watching an artist paint a masterpiece. These molds are a staple in injection molding, with their straightforward design making them a favorite for many.
Understanding their structure is like knowing the blueprint of a well-oiled machine. The fixed template is your anchor, while the moving template dances back and forth, orchestrating the perfect mold every time. It’s fascinating how each part plays its role, ensuring that the plastic product emerges flawless from its cocoon.
Whether it’s crafting sleek phone cases or vibrant toys, the versatility of two-plate molds never ceases to amaze me. Their simplicity not only cuts down costs but also speeds up production, making them indispensable in any manufacturing toolkit. As I delve deeper into the world of injection molding, I find these molds to be like old friends—reliable and efficient.
Two-plate molds have both moving and fixed templates.True
A two-plate mold consists of a moving and a fixed template.
Molten plastic is injected through gates in two-plate molds.True
In two-plate molds, molten plastic enters the cavity via gates.
- 1. What is the Basic Structure of a Two-Plate Mold?
- 2. How Does the Injection Molding Process Work with Two-Plate Molds?
- 3. What are the Different Types of Gating Systems Used?
- 4. Where Are Two-Plate Molds Typically Applied?
- 5. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Two-Plate Molds?
- 6. Conclusion
What is the Basic Structure of a Two-Plate Mold?
Have you ever wondered how everyday plastic items are brought to life? The secret often lies in the humble yet ingenious two-plate mold.
A two-plate mold consists of a moving plate for mold operation and a fixed plate, forming the cavity where plastic shapes.
Key Components of a Two-Plate Mold
Let me take you on a little journey through my workshop, where the two-plate mold plays a starring role in my daily grind. It all starts with two main components: the moving plate and the fixed plate. Each has its own story and purpose.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Moving Plate | Facilitates the opening and closing of the mold during the injection process. |
| Fixed Plate | Remains stationary, providing a stable base for the mold cavity. |
The Moving Plate
Imagine the moving plate as the dance partner of the fixed plate. In my early days, I remember being fascinated by how it moves with precision during the molding process. It’s like watching a perfectly synchronized dance as it closes in to form a snug cavity, then glides back to release a newly minted product.
The mold opening mechanism1 ensures this dance is seamless, allowing for smooth product ejection and easy maintenance.
The Fixed Plate
The fixed plate is like the steadfast friend who always has your back, providing stability in the chaotic world of injection molding. I’ve often relied on its support for aligning everything just right, using guide pins to ensure perfect harmony between plates.
- Guide Pins: Keep everything aligned like a maestro leading an orchestra.
- Sprue Bush: Guides molten plastic into its destiny within the mold.
The construction2 of this plate is crucial for achieving precision and efficiency, a detail I’ve learned never to overlook.
Gating Systems in Two-Plate Molds
Now, when it comes to gating systems, it’s like choosing the best route to reach your destination. Two-plate molds offer several options:
- Direct Gate: Quick and efficient but sometimes leaves a mark—much like taking a shortcut.
- Side Gate: Great for complex shapes, allowing better control over how things flow.
- Point Gate: A hidden gem that minimizes marks but requires intricate mold design3.
Each choice impacts aesthetics and functionality, much like deciding which brushstroke to use on a painting.
Applications of Two-Plate Molds
In my experience, these molds are versatile workhorses ideal for producing items like:
- Plastic shells for electronics—think of your phone case or remote control cover.
- Toys that bring joy to children.
- Everyday containers that keep our lives organized.
Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them favorites in many manufacturing sectors. If you’re curious about how these molds impact various industries, explore related industries4.
The moving plate remains stationary during molding.False
The moving plate moves to form a closed cavity and retracts to release the product.
Two-plate molds use direct, side, or point gates.True
These gating systems control how molten plastic enters the mold cavity.
How Does the Injection Molding Process Work with Two-Plate Molds?
Ever wondered how those everyday plastic items come to life? Let me take you behind the scenes of the fascinating world of injection molding with two-plate molds.
The two-plate mold process in injection molding uses a fixed and a moving template to form cavities, efficiently producing various plastic components with minimal waste.

Understanding the Basic Structure
I remember the first time I laid eyes on a two-plate mold during my early days in the factory. Its simplicity amazed me. Essentially, it consists of two main parts: the moving template5 and the fixed template6. These templates dance together to create a mold cavity where plastic takes shape. The fixed template is like an anchor on the injection machine’s fixed side, while the moving template joins the party on the movable side.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Moving Template | Mounted on the machine’s movable plate |
| Fixed Template | Mounted on the machine’s stationary plate |
Operational Principle
When I first learned about this, I was fascinated by how the process begins. Imagine heating plastic raw materials until they’re like hot syrup, ready to pour. This molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity at high pressure. As the moving template nudges closer to the fixed template, they form a sealed space—a perfect mold cavity. Once it cools down, the mold opens up like a treasure chest, and an ejector system releases the final product.
Gating System Characteristics
The choice of gates in two-plate molds is like picking the right tool for a job. Whether it’s direct gates, side gates, or point gates:
- Direct Gates: They reduce pressure loss but might leave marks—perfect for when aesthetics aren’t top priority.
- Side Gates: These offer greater control over fill speed and direction, ideal for diverse shapes.
- Point Gates: They’re all about minimal gate marks but require a more complex mold structure.
Applications of Two-Plate Molds
Thinking back to when I first started working with these molds, their versatility was a game-changer. They’re perfect for producing everything from plastic shells7 like cellphone cases to toys and containers. The beauty lies in their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them a favorite in injection molding.
With their efficiency and adaptability, two-plate molds are essential tools in manufacturing. Choosing the right gating system can significantly impact product quality and appearance—it’s a decision that weighs heavily in design processes8.
Two-plate molds have three main components.False
Two-plate molds consist of two main components: the moving and fixed templates.
Direct gates in two-plate molds reduce pressure loss.True
Direct gates are ideal for reducing pressure loss but may affect appearance.
What are the Different Types of Gating Systems Used?
Ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in casting and molding processes?
Gating systems in manufacturing include pressurized and unpressurized systems with types like top, bottom, side, and direct gating, each offering unique applications and advantages.

Pressurized vs. Unpressurized Gating Systems
In the world of casting, I’ve always been fascinated by how gating systems are categorized into pressurized and unpressurized types. Pressurized systems maintain back pressure to control metal flow speed, which is crucial for reducing turbulence—something I learned the hard way after a batch didn’t quite meet my expectations. On the other hand, unpressurized systems allow the metal to flow freely, reducing backpressure but can sometimes feel like giving up control. Each system has its unique advantages based on specific application needs9.
Types of Gating Systems
Top Gating
Top gating is like letting gravity do the heavy lifting. When I first encountered it, I was amazed at how introducing molten metal from the top of the mold could benefit tall castings. However, as with anything that seems too good to be true, it may lead to defects like inclusions if not designed properly.
Bottom Gating
I remember my first project that required bottom gating. It was a delicate casting that needed a smooth surface finish, and bottom gating was perfect because it introduced metal from the bottom, reducing splash and turbulence. Watching the mold fill gradually was like seeing a masterpiece come to life, minimizing oxidation in the process.
Side Gating
Side gating is my go-to for versatility. It’s common in both casting and injection molding, and I appreciate how it allows better control over the filling speed and direction10 of molten material. It’s like having an artist’s precision brush for various shapes.
| Gate Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Top Gating | Uses gravity | Potential defects |
| Bottom Gating | Smooth finish | Complex design |
| Side Gating | Versatile | Gate marks |
Choosing the Right Gating System
Choosing the right gating system feels like matchmaking for molds. The decision depends heavily on product requirements and material characteristics. Factors like desired surface finish, production speed, and material type11 are crucial in determining which system will be most effective. Over the years, I’ve learned that understanding these parameters is key to designing efficient molds that enhance product quality. It’s an art as much as it is a science.
Pressurized gating reduces metal flow turbulence.True
Pressurized systems maintain back pressure, controlling flow speed.
Side gating is not used in injection molding.False
Side gating is common in both casting and injection molding.
Where Are Two-Plate Molds Typically Applied?
Have you ever wondered where two-plate molds make their mark in the world of plastic manufacturing? Let’s dive into their everyday applications.
Two-plate molds are ideal for producing small to medium plastic parts like electronics cases, toys, and containers, due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness in high-volume production.

Applications in Consumer Electronics
When I first started exploring the world of injection molding, I was amazed at how often two-plate molds popped up in consumer electronics. Picture your everyday mobile phone cases or the shell of a remote control—these are often crafted using these molds. Their simple design12 allows for rapid production cycles, which is crucial when dealing with high-demand items.
| Product Type | Example | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Cases | Mobile phone shells | High precision, low cost |
| Remote Controls | TV remote casings | Fast cycle time, durability |
Use in Toy Manufacturing
I remember walking down the aisles of a toy store, marveling at the intricate details on plastic toys. Little did I know then that many of these toys, from toy cars to action figures, are produced using two-plate mold designs13. These molds are a favorite because they can handle detailed designs while keeping efficiency in check.
Application in Packaging
Ever wondered how those perfectly uniform plastic containers and bottle caps are made? The packaging industry leans heavily on two-plate molds for just that reason. Their straightforward design means fewer production errors and consistent quality, ensuring every cap and container meets the necessary standards.
Example Table: Packaging Applications
| Application | Common Products | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Food Containers | Snack boxes | Lightweight, stackable |
| Bottle Caps | Soft drink caps | Precision, efficiency |
Advantages Over Other Mold Types
Compared to other mold types, like three-plate or hot-runner molds, I’ve found that two-plate molds are more cost-effective14 and simpler to maintain. This simplicity reduces potential technical hiccups during production—a big win for anyone looking to keep operations smooth and costs low.
Conclusion
In understanding where two-plate molds are typically applied, we gain valuable insights into their indispensable role in manufacturing. Thanks to their versatility and cost-effectiveness, these molds remain a staple across multiple industries.
Two-plate molds are used for mobile phone cases.True
They provide high precision and low cost, ideal for electronics.
Toy manufacturers avoid using two-plate molds.False
They are favored for their efficiency in creating detailed designs.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Two-Plate Molds?
When I first stumbled into the world of injection molding, two-plate molds quickly became a fascinating cornerstone. They’re simple, versatile, and a bit like an old reliable friend in the manufacturing world.
Two-plate molds are cost-effective and versatile for small to medium-sized products but lack precision compared to multi-plate molds and may leave visible gating marks.
Understanding the Basics of Two-Plate Molds
When I first started exploring the nuances of injection molding, two-plate molds caught my attention because of their simplicity. Imagine them as two puzzle pieces coming together to create something wonderful. These molds comprise two main parts: a moving template and a fixed template. During the molding process, these plates embrace each other tightly, forming a cavity where melted plastic is injected to craft the product.
Advantages of Two-Plate Molds
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplicity | Easier to design and manufacture, making them cost-effective. |
| Versatility | Suitable for various products, such as plastic shells and toys. |
| Quick Cycle Time | Simple design leads to faster molding cycles. |
I’ve often found that these molds are the go-to for products that don’t require overly complex mold structures. Their straightforward design makes them a popular choice among smaller manufacturing setups, which brings back memories of working in nimble teams where speed was key.
Disadvantages of Two-Plate Molds
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Limited Precision | Not ideal for intricate designs, where multi-plate molds excel. |
| Gating Marks | Visible marks can affect the aesthetic of the product. |
| Less Flexibility | Not suitable for large, complex products. |
Although I appreciate the efficiency these molds provide, I’ve encountered scenarios where their straightforward nature was a limitation. For instance, when dealing with high-end or highly detailed products, the precision just wasn’t there, reminding me of times when I had to seek more complex solutions for demanding projects.
Application Scenarios
In my experience, two-plate molds thrive in production environments15 where cost and speed are prioritized over precision. They’re excellent for churning out components where those pesky visual blemishes from gating aren’t a deal-breaker.
Whenever I’m weighing different molding options for a project, I make sure to consider multi-plate systems16 as well—they often present better solutions for complex needs without sacrificing quality.
Reflecting on your project’s specific requirements can help determine if two-plate molds align with your manufacturing goals. It’s all about balancing simplicity against precision to make the best choice for your unique situation.
Two-plate molds are cost-effective for simple designs.True
Their straightforward design makes them cheaper to produce.
Two-plate molds are ideal for intricate designs.False
They lack the precision needed for complex mold structures.
Conclusion
A two-plate mold in injection molding consists of a moving and fixed template, efficiently creating plastic products through a simple design that enhances production speed and cost-effectiveness.
-
Learn about the systems that enable smooth operation of moving plates in molds. ↩
-
Discover how fixed plates contribute to mold stability and function. ↩
-
Understand the complexities involved in designing molds with point gates. ↩
-
Explore various industries that benefit from using two-plate molds. ↩
-
Learn how the moving template contributes to forming and releasing products efficiently. ↩
-
Understand how the fixed template stabilizes and supports the molding process. ↩
-
Discover various products that benefit from using two-plate molds. ↩
-
Find out how different gating systems affect product design and functionality. ↩
-
Explore how each system impacts casting quality and their specific industrial applications. ↩
-
Discover why side gating is a popular choice for complex shapes and its benefits in controlling fill direction. ↩
-
Learn about material properties that dictate the best gating system to use for optimal results. ↩
-
Explore how the simplicity of two-plate molds benefits manufacturing processes with reduced complexity and increased efficiency. ↩
-
Learn about the design flexibility of two-plate molds and how they enable detailed and complex toy designs. ↩
-
Discover why two-plate molds are considered cost-effective compared to other mold types in manufacturing. ↩
-
Learn about scenarios where two-plate molds excel, offering cost-effective and efficient solutions. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of using multi-plate systems for complex product designs. ↩