Ever wondered how those sleek plastic products are made? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of injection moulding!
The best materials for injection moulding include thermoplastics like polyethylene, polypropylene, and ABS, as well as thermosetting plastics such as phenolic and epoxy resins. Each offers unique properties suited to different applications, enhancing performance and cost-effectiveness.
While this overview provides a snapshot of top materials used in injection moulding, understanding the nuances of each material’s properties and applications can be pivotal in making informed decisions. Let’s explore further!
Polyethylene is a thermosetting plastic used in injection moulding.False
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic, not a thermosetting plastic.
- 1. How Do Thermoplastics Compare to Thermosetting Plastics in Injection Moulding?
- 2. What Are the Advantages of Using Polyethylene in Injection Moulding?
- 3. How Does Material Choice Affect Product Longevity and Performance?
- 4. What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting Materials for Injection Moulding?
- 5. Conclusion
How Do Thermoplastics Compare to Thermosetting Plastics in Injection Moulding?
Navigating the complexities of injection moulding requires understanding the differences between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Each offers distinct advantages that can significantly impact production outcomes.
Thermoplastics, like polyethylene and ABS, offer flexibility and reusability, while thermosetting plastics, such as phenolic resins, provide superior heat resistance and structural integrity. The choice between them depends on application needs and processing conditions.

Understanding Thermoplastics in Injection Moulding
Thermoplastics are characterized by their ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing any significant chemical change. This property makes them highly versatile and cost-effective for many applications.
Key Advantages of Thermoplastics:
-
Flexibility and Reusability: Thermoplastics like polyethylene (PE) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) can be reheated and remoulded, allowing for easy recycling and waste reduction.
-
Wide Range of Applications: With options like polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), these materials are used in everything from automotive parts to household items.
-
Varied Mechanical Properties: Each type of thermoplastic offers unique properties such as low density in PP or high transparency in polycarbonate (PC), catering to specific industrial needs.
| Thermoplastic Type | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PE | Chemical stability, electrical insulation | Plastic films, containers |
| PP | Heat resistance, stiffness | Automotive interiors, appliances |
| PVC | Flame retardancy, mechanical strength | Pipes, wire insulation |
Exploring Thermosetting Plastics in Injection Moulding
Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics undergo an irreversible chemical reaction during curing, which enhances their heat resistance and structural integrity.
Key Advantages of Thermosetting Plastics:
-
Superior Heat Resistance: Thermosets like phenolic plastics maintain their form and performance even at high temperatures, making them ideal for electrical insulation applications.
-
Durability: Once set, these materials do not melt. This quality makes them suitable for products that require long-term structural stability.
-
Excellent Bonding Properties: Epoxy resins provide strong adhesive properties, which are crucial in coatings and electronic packaging.
| Thermosetting Plastic Type | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Phenolic | High mechanical strength | Electrical parts |
| Epoxy Resin | Excellent bonding properties | Coatings, adhesives |
Choosing the Right Material for Injection Moulding
The decision between thermoplastics1 and thermosetting plastics2 hinges on several factors:
-
End-use Environment: Consider the operating temperatures and conditions the final product will face.
-
Mechanical Requirements: Evaluate the need for flexibility versus rigidity in the product design.
-
Cost Implications: Factor in material cost, potential recycling benefits, and overall production efficiency.
Understanding these materials’ properties enables manufacturers to optimize performance and ensure product longevity across various industries.
Thermoplastics can be reshaped multiple times.True
Thermoplastics can be melted and remoulded without chemical change.
Thermosetting plastics are easily recyclable.False
Once set, thermosetting plastics cannot be remelted or reshaped.
What Are the Advantages of Using Polyethylene in Injection Moulding?
Polyethylene stands out in the injection moulding world due to its unique properties and versatile applications. But what exactly makes it advantageous for manufacturers?
Polyethylene offers excellent low temperature resistance, chemical stability, and electrical insulation, making it ideal for diverse injection moulding applications such as films, containers, and pipes.
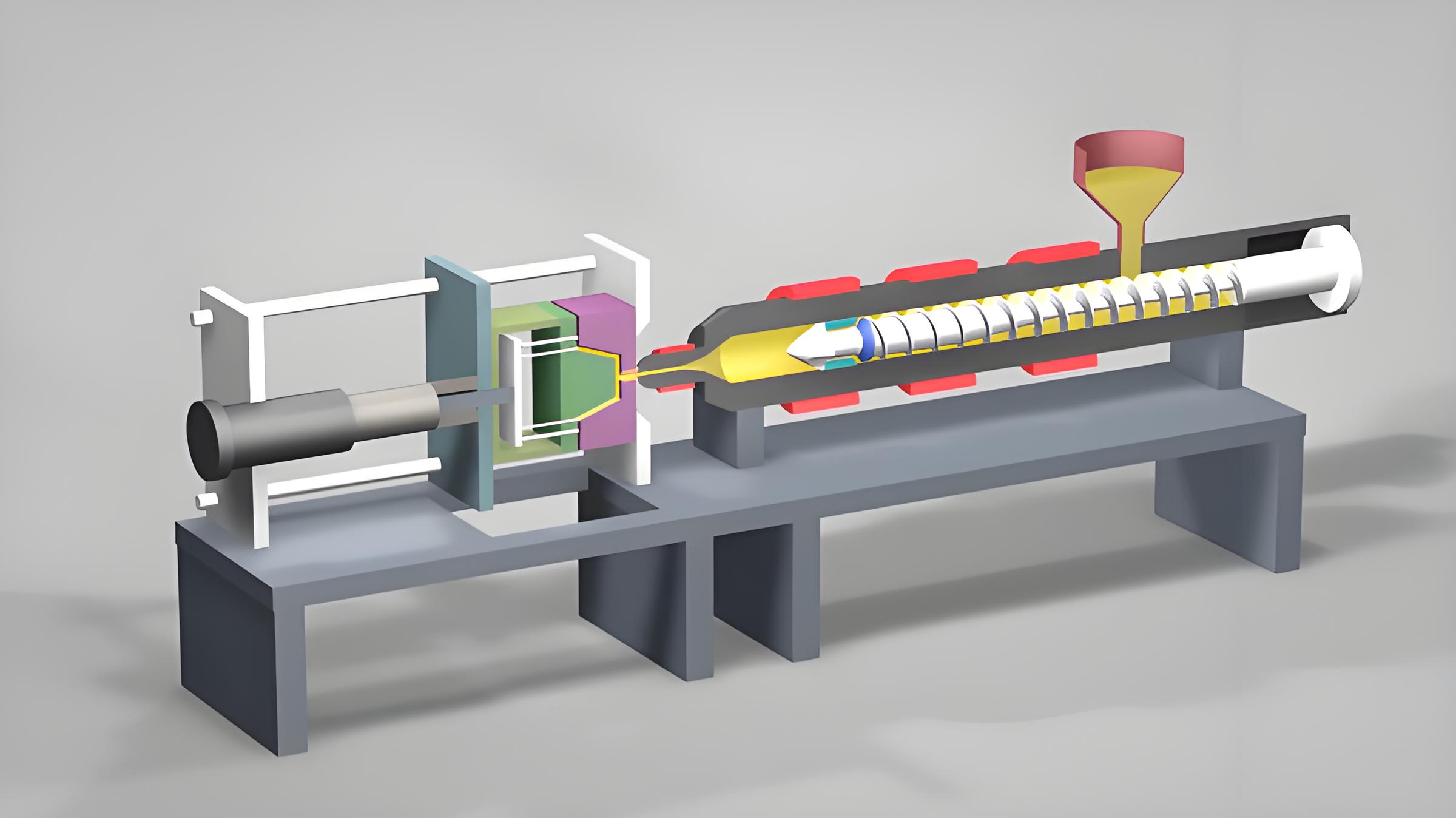
Key Properties of Polyethylene
Polyethylene (PE) is a standout choice in injection moulding3 due to its remarkable attributes. It boasts good low temperature resistance, ensuring durability even in colder environments. Its chemical stability allows it to resist most acids and alkalis, making it highly corrosion-resistant. Additionally, PE‘s excellent electrical insulation properties make it ideal for applications where electrical safety is paramount.
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low Temperature Resistance | Durability in cold environments |
| Chemical Stability | Resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Electrical Insulation | Safety in electrical applications |
Practical Applications of Polyethylene
Given these properties, polyethylene is extensively used across various industries. For instance, it is commonly employed to manufacture plastic films, which are used in everything from packaging to agriculture. Its use in containers and pipes showcases its versatility, as these products benefit significantly from PE‘s robustness and resistance to chemicals.
- Plastic Films: Often found in packaging, agricultural covers, and more.
- Containers: Utilized for food storage, chemical transportation, etc.
- Pipes: Integral in plumbing and irrigation systems.
Comparing Polyethylene with Other Thermoplastics
While other thermoplastics like polypropylene and polyvinyl chloride also offer distinct advantages, polyethylene’s combination of flexibility, resistance to environmental stressors, and ease of processing often gives it an edge. Compared to polypropylene, PE may lack high heat resistance but excels in flexibility and impact resistance.
For example, while polypropylene is favored for automotive parts due to its rigidity and heat resistance, polyethylene is preferred for applications requiring flexibility and chemical resistance.
Understanding these nuances can guide manufacturers in selecting the appropriate material based on specific application requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
In terms of sustainability, polyethylene is recyclable, although recycling rates vary based on local facilities. Its long life cycle in durable goods reduces the need for frequent replacements, contributing to resource conservation.
Exploring the advantages of polyethylene recycling4 can offer insights into its role in sustainable manufacturing practices.
Polyethylene has excellent low temperature resistance.True
Polyethylene remains durable even in colder environments due to its properties.
Polyethylene is not suitable for electrical applications.False
PE provides excellent electrical insulation, ideal for electrical safety.
How Does Material Choice Affect Product Longevity and Performance?
Material selection is a critical factor influencing the durability and efficiency of products created through injection molding.
Material choice directly impacts product longevity and performance by determining properties such as strength, resistance to environmental factors, and maintenance requirements. Selecting the appropriate material ensures optimal functionality and lifespan for the intended application.

Understanding Material Properties
The intrinsic properties of materials determine how a product will perform over its lifetime. For instance, polyethylene5 offers excellent chemical stability and electrical insulation, making it ideal for items like electrical cables and piping systems that require durability under diverse conditions.
On the other hand, polypropylene6 is favored for its balance of strength and heat resistance, which suits it for automotive components and home appliances that endure temperature fluctuations.
Resistance to Environmental Stressors
Each material’s reaction to environmental factors significantly affects product longevity. For example, PVC7 provides high chemical resistance and flame retardancy, crucial for construction applications where exposure to harsh substances is common. However, its poor thermal stability requires careful consideration during long-term heating scenarios.
Impact on Maintenance Requirements
Materials also dictate the level of maintenance required to ensure optimal performance. ABS8 is notable for its high toughness and chemical corrosion resistance, which reduces maintenance needs in electronic and automotive applications.
In contrast, products made from phenolic plastics9 might require more frequent inspections due to their brittleness, despite their excellent mechanical strength and heat resistance.
| Material | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Good chemical stability, electrical insulation | Electrical cables, piping systems |
| Polypropylene | Heat resistance, low density | Automotive components, home appliances |
| PVC | Chemical resistance, flame retardancy | Construction applications |
| ABS | High toughness, corrosion resistance | Electronics, automotive parts |
| Phenolic | Mechanical strength, heat resistance | Electrical insulation parts |
Balancing Cost and Performance
Ultimately, the choice of material involves balancing initial costs with long-term performance benefits. Opting for high-quality materials can lead to longer-lasting products that require fewer repairs or replacements over time, thereby offering better value.
Understanding the specific demands of the application will guide the selection process, ensuring that the chosen material enhances both the product’s longevity and performance.
Polyethylene is ideal for electrical cables.True
Polyethylene offers excellent chemical stability and electrical insulation.
ABS requires frequent maintenance in automotive applications.False
ABS's high toughness and corrosion resistance reduce maintenance needs.
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting Materials for Injection Moulding?
Choosing the right material for injection moulding requires considering several factors that impact both functionality and production.
Key factors in selecting materials for injection moulding include material properties, application requirements, cost, and environmental impact. Evaluating these aspects ensures optimal performance and sustainability.

Material Properties
Understanding the intrinsic properties of materials is essential. Factors such as tensile strength, thermal resistance, and chemical stability can significantly influence the final product’s performance.
- Tensile Strength: Materials like polycarbonate10 (PC) offer high strength and durability, making them ideal for load-bearing applications.
- Thermal Resistance: Thermoplastics like polypropylene can withstand higher temperatures, whereas thermosetting plastics like epoxy resin provide exceptional heat stability.
Application Requirements
The intended use of the product dictates material choice. For instance, electrical insulation components often use phenolic plastics due to their high resistance to electrical currents.
- Electrical Applications: Consider using materials with excellent insulating properties, such as amino plastics.
- Structural Applications: Use high-strength materials like ABS for automotive parts, where durability is key.
Cost Efficiency
Balancing material cost with performance is crucial. While high-performance materials might offer superior qualities, they may not be cost-effective for all projects.
| Material | Approximate Cost | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Low | Packaging, containers |
| Polycarbonate | High | Optical instruments, safety equipment |
| Phenolic Resin | Moderate | Electrical insulation parts |
Environmental Impact
Sustainability is increasingly important in material selection. Choosing recyclable materials like polyethylene can reduce environmental impact.
- Recyclability: Thermoplastics such as polypropylene are generally more recyclable compared to thermosetting plastics.
- Biodegradability: Newer biodegradable polymers are being developed to address environmental concerns.
By considering these factors, manufacturers can select materials that meet specific needs while balancing cost and sustainability considerations. This strategic approach not only enhances product quality but also aligns with modern environmental standards.
Polycarbonate is ideal for load-bearing applications.True
Polycarbonate's high tensile strength makes it suitable for such uses.
Thermosetting plastics are more recyclable than thermoplastics.False
Thermoplastics are generally more recyclable than thermosetting plastics.
Conclusion
By selecting the right injection moulding material, you can optimize manufacturing processes and enhance product quality. Reflect on your project needs to make the best choice.
-
Discover detailed benefits of using thermoplastics in manufacturing.: Thermoplastic injection molding process offers a flexible and efficient approach to manufacturing diverse plastic products with minimal cost and lead time. ↩
-
Learn why thermosetting plastics are chosen for durable applications.: Advantages of Thermosets: · High strength-to-weight ratio and performance · High dielectric strength · Low thermal conductivity and microwave transparency … ↩
-
Discover why polyethylene excels in injection moulding processes.: It is a lightweight thermoplastic material that has high chemical resistance, elasticity, and electrical insulating properties. ↩
-
Learn about the sustainability benefits of recycling polyethylene.: With an appropriate plastic recycling approach, businesses can reduce hazardous waste output, cut expenses on waste management, and generate profits. ↩
-
Discover how polyethylene’s properties benefit various industrial applications.: What are the properties of HDPE? · HDPE Melting point: 120-140°C · Density of HDPE: 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm · Chemical resistance of HDPE: · Continuous temperature: -50°C … ↩
-
Learn how polypropylene meets automotive industry demands.: Manufacturers can, therefore, use PP to decrease a car’s weight, making them more environmentally and economically appealing. ↩
-
Explore PVC’s versatility in construction and other fields.: Electrical Properties: PVC is a good insulation material. · Durability: PVC is resistant to weathering, chemical rotting, corrosion, shock, and abrasion. · Flame … ↩
-
Uncover why ABS is a preferred choice in electronics.: ABS can be easily moulded, sanded and shaped, while its glossy surface finish is highly compatible with a wider range of paints and glues. ABS plastics takes … ↩
-
See how phenolic plastics are used in various industries.: Countertops and scientific or industrial work surfaces · Printed circuit boards (PCBs) and terminal boards · High-temperature, high-speed, and high-wear … ↩
-
Explore why polycarbonate’s tensile strength makes it a top choice.: Polycarbonate is an extremely durable and strong alternative to acrylic and plastics. Learn more about its tensile strength and why it’s so strong. ↩






