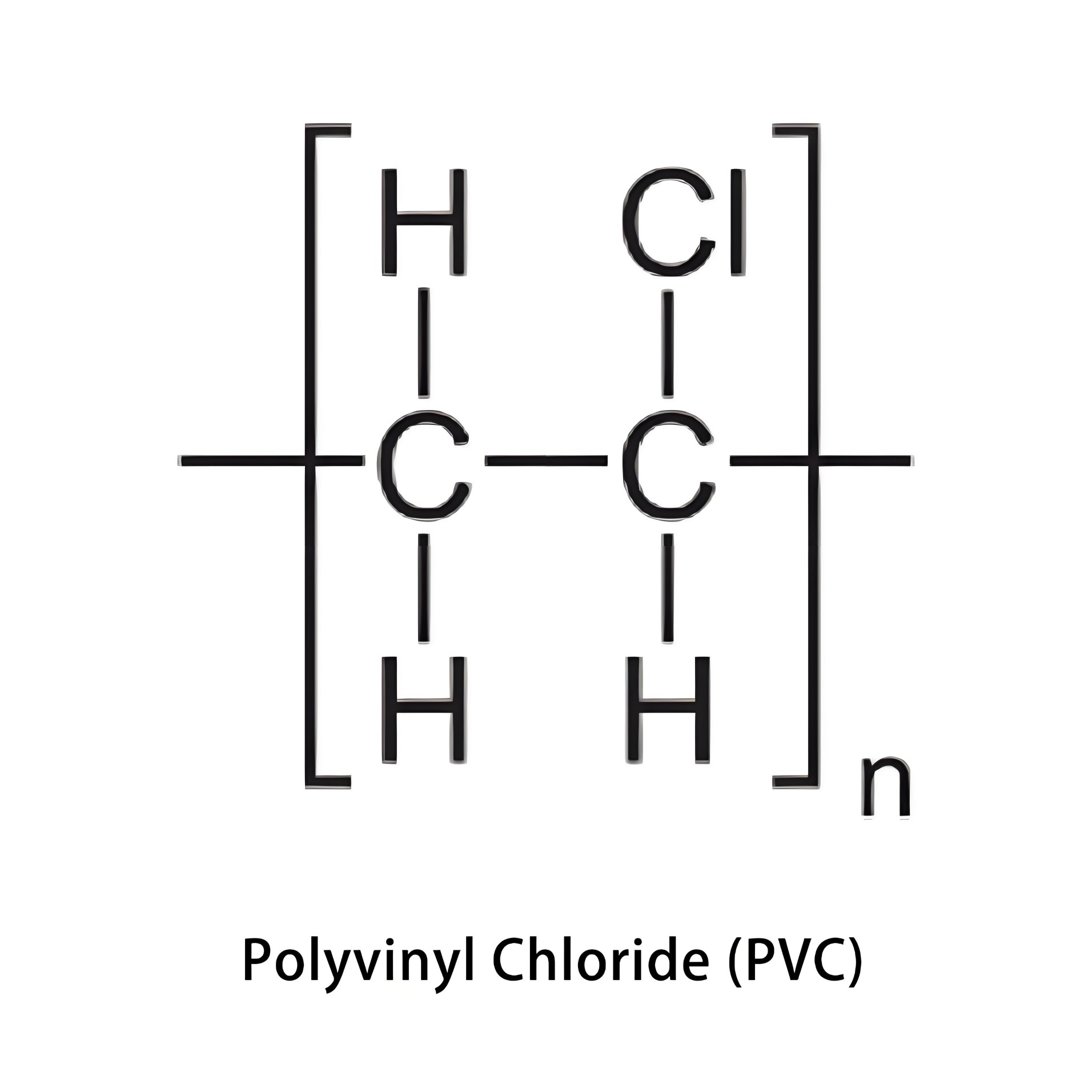
Have you ever thought about how those strong PVC pipes or medical tubes are created?
PVC injection molding involves heating polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to a molten state and injecting it into a mold to form desired shapes. This process is precise, allowing for mass production of uniform components used in various industries, such as construction and medicine.
However, more lies beneath the surface. Delve deeper into how various steps, from choosing materials to controlling temperature, connect closely to form high-quality PVC items.
PVC decomposes at temperatures above 200°C.True
PVC starts to break down at temperatures over 200°C, releasing harmful gases.
What Are the Key Stages in the PVC Injection Molding Process?
PVC injection molding stands as an important method in shaping strong and flexible plastic objects.
The key stages in PVC injection molding include material preparation, melting, injecting, cooling, and ejection. Each step must be precisely controlled to produce high-quality components.
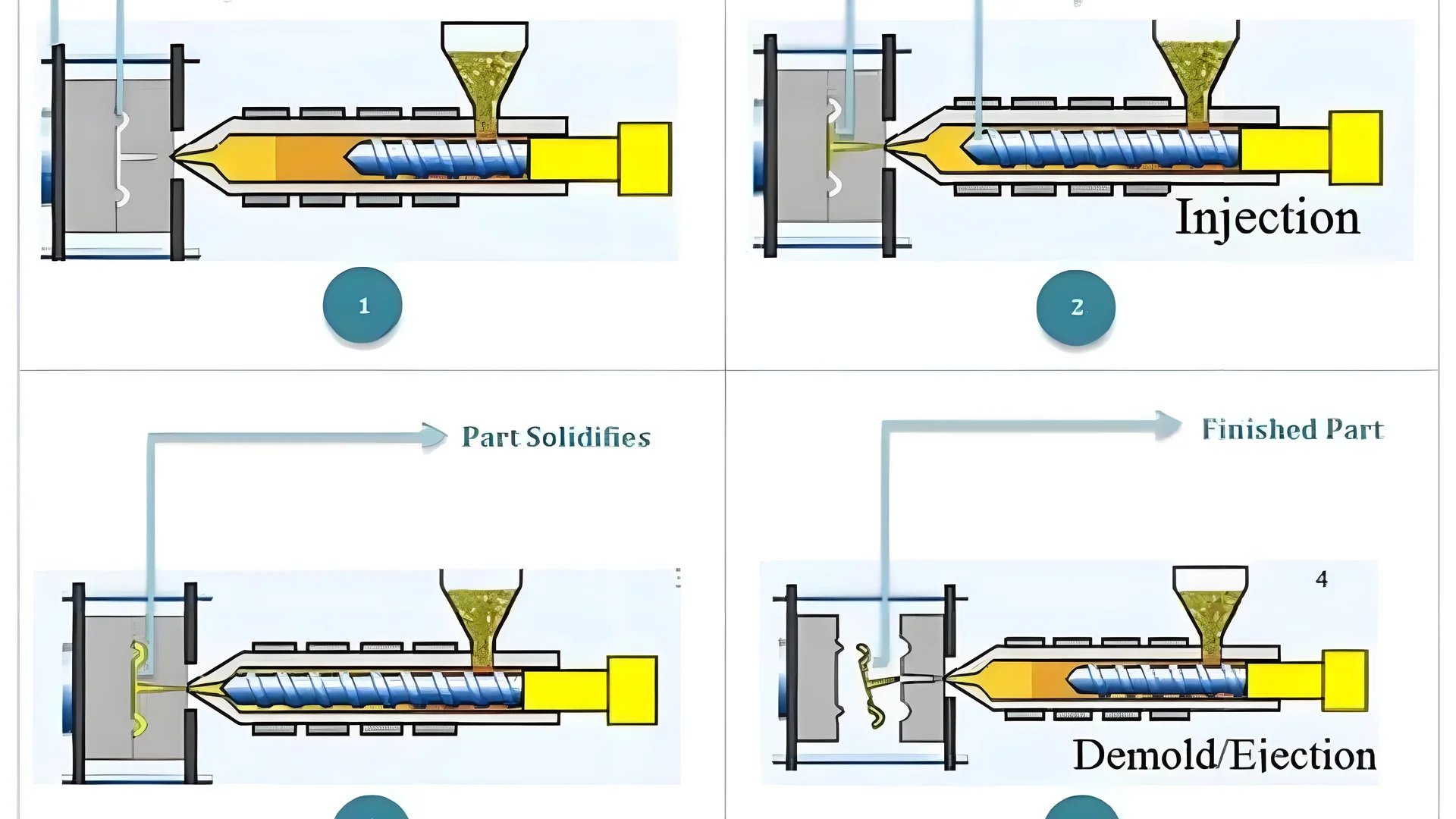
Material Preparation
In PVC injection molding, selecting the appropriate PVC material1 is crucial. Depending on the application, you can choose from rigid PVC (UPVC), chlorinated PVC (CPVC), or soft PVC. The material should be stored in a dry environment and dried at 60-80°C for 2-4 hours to reduce moisture content below 0.1%.
Melting and Injection
Before processing, preheat PVC powder to enhance plasticizing and avoid air bubbles. The melting process involves heating PVC to 160-190°C. It’s vital to control the temperature closely due to PVC’s narrow processing range and its tendency to decompose above 200°C.
Using a screw-type injection machine with a large-diameter nozzle minimizes stagnant material. Stainless steel screws are preferred to prevent corrosion from decomposed PVC.
Cooling
Cooling is a pivotal stage in ensuring the quality and appearance of the product. The mold should be cooled efficiently, maintaining a temperature of 30-60°C. The mold’s design should allow for large inlets to facilitate proper flow and cooling.
Ejection
Once the PVC has solidified in the mold, the component is ejected. This requires careful attention to mold design to prevent damage to the product. The use of durable materials like stainless steel can mitigate wear and tear during this stage.
Each phase in the PVC injection molding process2 must be meticulously managed. Ensuring optimal temperature control, choosing suitable materials, and designing molds with precision are all essential for producing superior PVC products.
PVC must be heated above 200°C for injection molding.False
PVC breaks down above 200°C, so it is warmed to 160-190°C.
Cooling stage affects PVC product's appearance.True
Correct cooling keeps the product's quality and look.
How Do Material Properties Affect PVC Injection Molding?
Material properties greatly affect the success and standard of PVC injection shaping.
Material properties such as thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength are critical in PVC injection molding. These properties influence mold selection, temperature settings, and the overall durability of the final product. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing production and ensuring high-quality results.
Understanding PVC Types
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) splits into three main types: hard PVC (UPVC), chlorinated PVC (CPVC), and soft PVC. Every type has special traits, useful for different things. For instance, hard PVC is strong, so builders prefer it. Soft PVC bends easily, so it’s good for things like tubes.
Important Material Traits for Injection Molding
Heat Stability
An important part of PVC injection molding is how it handles heat. PVC breaks down at high heat, releasing gases like hydrogen chloride, which harm metals. Keeping temperatures between 160-190°C is necessary. Using stainless steel parts in machines helps avoid damage from these gases.
Resistance to Corrosion
PVC does not corrode easily in places with chemicals or water. During injection molding, using molds that withstand PVC’s harmful byproducts is essential. Stainless steel or materials like S136 quenching work well to make molds last longer.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Stability | Breaks down above 190°C, releases harmful gases. |
| Resistance to Corrosion | Resists chemicals but needs strong mold materials. |
Strength and Design Factors
The strength of PVC relies on its structure and added substances. Fillers or softeners change its strength and flexibility, altering the molding process. More fillers might lower strength but increase flexibility. Balancing these additions is key to keeping a solid structure.
Mold Planning and Material Setup
Choosing the right mold and getting materials ready is crucial for successful PVC injection molding. Warming PVC powder beforehand improves molding and stops air pockets, ensuring smooth results. Also, molds should cool well with temperatures from 30-60°C for good product precision and look.
Real-World Effects
Knowing how these properties affect molding helps producers improve their factories. By picking the right materials and keeping close watch on conditions, companies create top-quality PVC items that follow industry rules.
In short, grasping how material traits impact PVC injection molding is critical for crafting reliable and long-lasting items in fields like building, electrical, and health industries.
Thermal stability is crucial for PVC injection molding.True
PVC breaks down at high heat, reducing molding efficiency.
Soft PVC is primarily used in construction applications.False
Hard PVC, not flexible PVC, finds use in building because of its durability.
What Are Common Challenges in PVC Injection Molding?
PVC injection molding has special difficulties. It requires exact management of material and process factors.
Common challenges in PVC injection molding include material decomposition, corrosion of molds, and precise temperature control. PVC’s narrow processing temperature range requires stringent monitoring to avoid degradation. Mold material must resist corrosion from PVC’s acidic decomposition products, while maintaining adequate hardness to withstand wear.
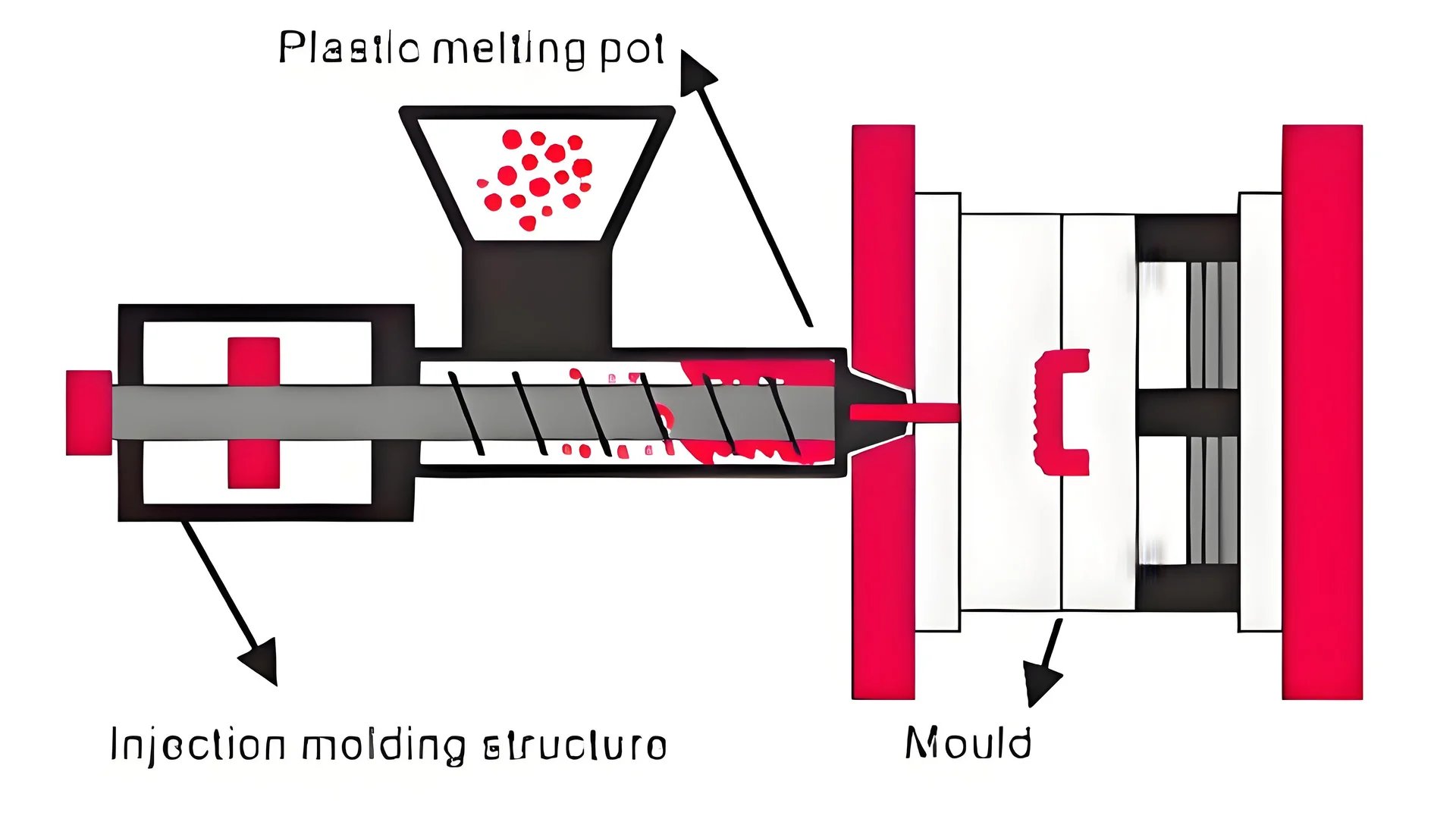
Material Breakdown
A big problem in PVC injection molding3 is material breakdown. PVC starts breaking down at temperatures as low as 140°C, letting out hydrogen chloride gas, which may harm machinery and molds. To stop this, keep the material temperature between 160-190°C during injection.
Preventive Steps:
- Warm up PVC powder to take out moisture and improve plastic effects.
- Choose stainless steel screws to lower corrosion.
- Use a screw-type injection machine with a big nozzle to cut dead space and stuck material.
Mold Damage and Wear
PVC’s breakdown products are acidic and can harm molds. Molds should use materials like stainless steel or have nitride hardening to fight corrosion.
Material Tips:
- For more than 500,000 cycles, opt for S136 steel, treated to 48-52 HRC hardness.
- Mold materials should be harder than HRC30 to resist wear.
Heat Management
Heat plays an important role in the quality of molded PVC parts. The narrow processing temperature needs sharp control to stop issues like bubbles or bad surface finish.
Temperature Rules:
- Keep mold temperatures between 30-60°C.
- Control material temperature within the 160-190°C range to stop breakdown and get good flow.
Process Improvement
To reach a high-quality level, knowing how different material properties4 influence the molding process is vital. For example, adding plasticizers improves flexibility but lowers strength. Find the right balance of these properties based on use.
| Material Comparison: | Property | PVC | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Strength | High | Moderate | Low |
| Heat Tolerance | Moderate | High | High |
| Bendability | Low | High | Moderate |
Grasping these difficulties and using smart fixes really increases the efficiency and grade of PVC injection molding. Think about how to tweak mold design, pick the right materials and manage heat5 to solve problems and improve production results.
PVC decomposes at 140°C during injection molding.True
PVC starts to break down at temperatures as low as 140°C, releasing hydrogen chloride gas.
Stainless steel molds are unnecessary for PVC molding.False
Stainless steel is suggested to withstand damage from PVC's acidic breakdown byproducts.
How Does Temperature Control Impact Product Quality?
Temperature control is vital in PVC injection molding. It directly impacts product quality and consistency.
Proper temperature control ensures optimal material properties and reduces defects during PVC injection molding. Maintaining precise temperatures helps prevent issues like decomposition, warping, and inconsistent product dimensions, thereby ensuring the durability and reliability of the finished products.
Why Temperature Matters in PVC Molding
PVC injection molding depends on temperature for good quality products. PVC is a thermoplastic and needs careful warming to become soft for molding. But too much heat can break it down, releasing harmful gases like HCl, which hurt the mold and the product.
Maintaining the right temperature range is key. Material temperature should usually stay between 160-190°C and mold temperature between 30-60°C for optimal results6. Going beyond these levels can harm the product’s strength and appearance.
Temperature Changes and Their Effects
Changing temperatures bring problems in molding. If too cold, PVC might not melt well, causing incomplete mold filling. Too hot, and it breaks down fast, hurting strength and appearance.
Higher temperatures also risk PVC sticking to molds, interrupting production and raising maintenance costs through cleaning and fixing molds.
Ways to Control Temperature Well
- Preheat: Preheating PVC powder removes wetness, which helps to avoid air bubbles and product differences.
- Consistent Checking: Use modern checking tools to watch material and mold temperatures for steady production.
- Material Care: Store and dry PVC correctly. Dry at 60-80°C for 2-4 hours to keep moisture below 0.1%.
- Mold Planning: Add cooling paths in molds for even temperature distribution to prevent warping or bending.
Good Temperature Control Benefits
With proper temperature control, producers get:
- Stronger and longer-lasting PVC products.
- Lesser risk of warping or bubbles.
- Better looks and uniformity in production.
- Faster production cycles and more efficiency.
Controlling temperature well not only stops flaws; it also affects how PVC products perform and last. Producers focusing on exact temperature control give better products, meeting both industry needs and customer expectations.
Proper temperature prevents PVC decomposition.True
Keeping the right temperatures prevents too much heat, which leads to PVC breaking down.
High mold temperature reduces product defects.False
High mold temperature might lead to issues such as warping, not lessen them.
Conclusion
Learning PVC injection molding improves production speed and product excellence. Explore material choice and temperature regulation to create new ideas in your area.
-
Learn about various PVC types for different applications.: However, there are four types of PVC; UPVC, PVC, PVC-O, and PVC-C. These types have their strengths and weaknesses, so knowing their properties … ↩
-
Understand each phase of the PVC injection molding process.: PVC plastic begins as a pellet or powder. The pellet is then melted into a moldable state. The optimum PVC molding temperature is generally 345° … ↩
-
Explore effective strategies to prevent PVC decomposition during injection molding.: This review summarized various chemical recycling methods for PVC, such as pyrolysis, catalytic dechlorination and hydrothermal treatment ↩
-
Learn how different PVC properties influence the injection molding process.: Flexible PVC can experience a significant reduction in material properties over time. Rigid PVC that lacks resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light … ↩
-
Understand the importance of precise temperature management for quality outcomes.: When manufacturing injection-moulded parts from plastics, the mould temperature has a decisive influence on the quality of the parts and the cycle time. ↩
-
Learn the best temperature settings for efficient PVC molding.: Mold Temperature: The appropriate temperature range for the molds is from 70oF to 130oF. The importance of mold temperature is the effect it has … ↩






