Picture a world where the materials we employ change easily to very tough situations.
Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCPs) are ideal for injection molding due to their excellent thermal stability, high mechanical strength, and superior fluidity. These properties enable precise molding of complex shapes while ensuring durability and performance under extreme conditions.
LCPs offer clear benefits. Looking closely at their qualities shows why they perform better than many other materials in tough conditions. LCPs remain a better pick when stacked against other options.
LCPs have high thermal resistance in injection molding.True
LCPs endure temperatures ranging from 250°C to 350°C, suitable for applications with significant heat.
How Do LCP‘s Mechanical Properties Enhance Injection Molding?
Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCPs) appear like a revolution in injection molding due to their outstanding mechanical traits. Learn how these traits bring actual benefits for producers.
LCP‘s high tensile strength, impact resistance, and low shrinkage make it ideal for precise injection molding. These properties minimize defects and ensure consistent product quality.

Understanding LCP‘s Mechanical Ability
The mechanical traits of Liquid Crystal Polymer1 support the improvement of the injection molding method. Especially, LCPs show strong tensile power from 150MPa to 250MPa and bending ability between 200MPa to 300MPa. These strong qualities help create parts that handle high mechanical pressures without bending, helpful for uses needing strength, like car parts and electronic connectors.
Also, LCP‘s impact ability, usually from 10kJ/m² to 20kJ/m², helps molded parts resist sudden hits or bumps without breaking. This feature is important for making top-quality parts in tough places where physical strength is very important.
Dimensional Accuracy and Stability
A key feature of LCP is its very low shrinkage rate, often between 0.1% and 0.5%. This low shrinkage supports exact copying of detailed mold designs, lowering the risk of size errors and keeping strict tolerances. This quality partners with LCP‘s very low water absorption rate (under 0.02%), helping it stay stable even in wet conditions.
| Property | Value Range |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 150MPa – 250MPa |
| Bending Strength | 200MPa – 300MPa |
| Impact Strength | 10kJ/m² – 20kJ/m² |
| Shrinkage | 0.1% – 0.5% |
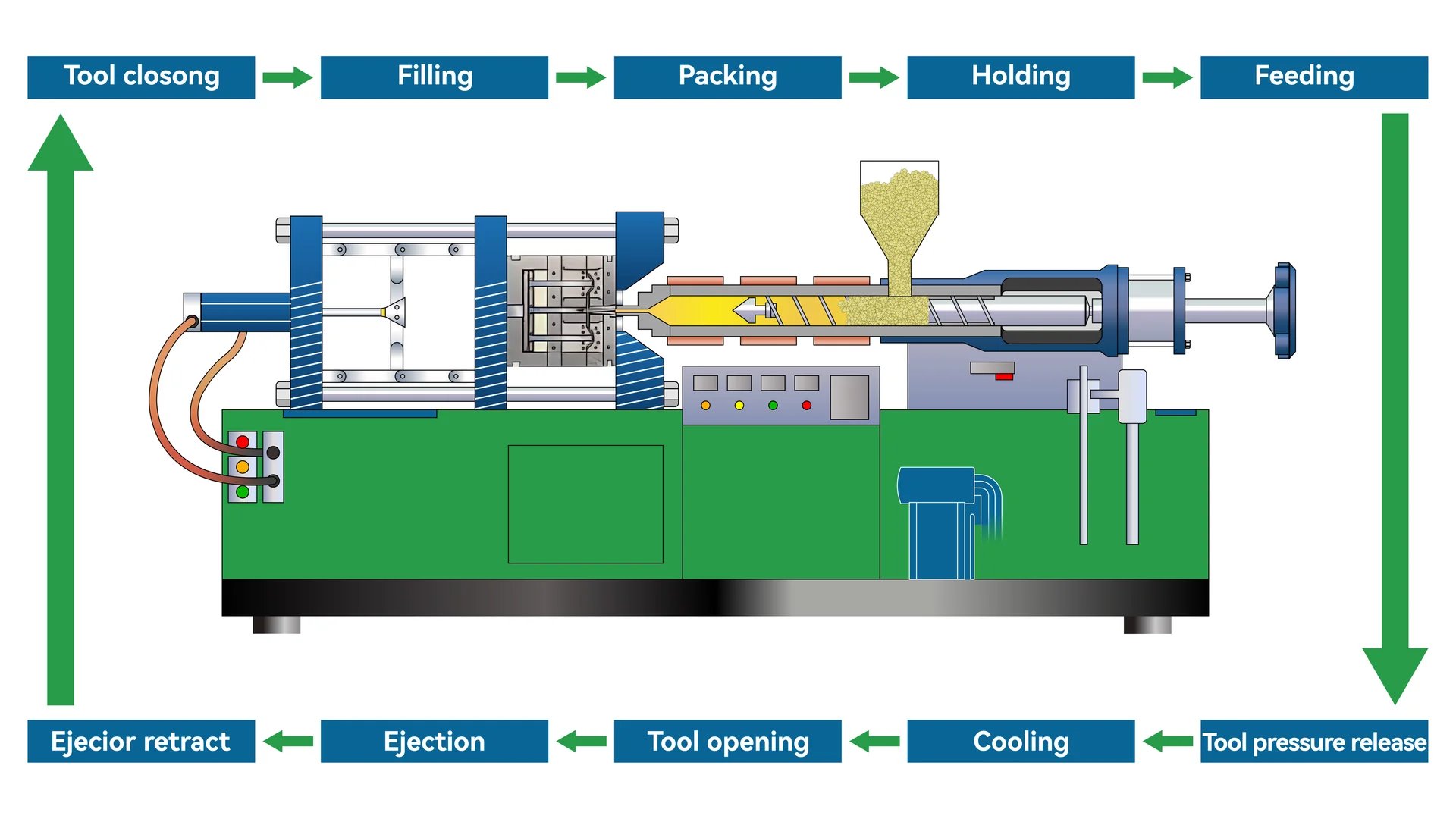
Improving Molding Process
LCP‘s mechanical traits allow a better injection molding process. Its high flow and low melt viscosity mean it gets injected at lower pressures than other plastics. This reduces mold part wear and extends their life, saving money for producers.
Moreover, LCP‘s fast curing time leads to shorter molding cycles, greatly raising production speed. Fast shaping of complex forms without losing quality makes LCP appealing for sectors needing quick production.
In electronics production, where parts should be created quickly without losing accuracy, LCP provides a helpful edge. Its ability to keep mechanical strength at high heat makes it suitable for parts used in very hot conditions.
Real-Life Uses Showing Mechanical Benefits
In real-life scenarios, LCPs find roles in car fuel side parts2, needing strong stress resistance. Use in electrical connectors highlights the importance of their mechanical traits, giving reliable support under mechanical force.
By using these mechanical strengths, companies achieve better product results and benefit from efficient production ways.
LCPs have tensile strength up to 250MPa.True
LCPs show tensile strength between 150MPa and 250MPa.
LCPs have a high shrinkage rate of 5%.False
LCPs possess a tiny shrinkage rate ranging from 0.1% to 0.5%.
What Are the Thermal Advantages of Using LCP in Molding Processes?
Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCPs) provide excellent heat benefits in molding, including high heat resistance and sustained use temperatures.
The thermal advantages of using Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) in molding processes include its high heat distortion temperature, ranging from 250°C to 350°C, and its ability to maintain structural integrity at continuous use temperatures between 200°C and 250°C. These properties make LCPs ideal for high-temperature applications, ensuring stability and performance.
Understanding Thermal Properties of LCPs
LCPs stand out in the world of injection molding primarily because of their exceptional thermal properties3. With a heat distortion temperature generally between 250°C and 350°C, LCPs can withstand significant thermal stress without deforming. This is a vital feature for applications requiring sustained performance at high temperatures, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries.
Furthermore, the continuous use temperature of LCPs, typically ranging from 200°C to 250°C, supports their use in demanding environments where other polymers might fail. These thermal characteristics ensure that parts molded from LCPs maintain their structural integrity and performance even when exposed to prolonged heat.
High Heat Resistance and Stability
The high heat resistance of LCPs is attributed to their unique molecular structure. In the molten state, they exhibit liquid crystal properties, allowing them to align in a highly ordered manner. This results in a polymer matrix that is not only thermally stable but also exhibits excellent dimensional stability. As a result, components molded from LCPs maintain precise dimensions even after repeated thermal cycling.
Comparing LCPs to Other Polymers
When compared to traditional polymers such as polyethylene or polypropylene, LCPs offer significant thermal advantages4. For instance, while typical thermoplastics might begin to soften or deform at lower temperatures, LCPs retain their mechanical properties and do not suffer from shrinkage or warping.
| Property | LCP | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distortion Temperature | 250°C – 350°C | 100°C – 120°C |
| Continuous Use Temperature | 200°C – 250°C | 85°C – 100°C |
Applications Benefiting from Thermal Advantages
The superior thermal properties of LCPs make them indispensable in industries where high thermal stability is crucial. For instance, in electronic applications, they are used in the manufacture of connectors and sockets which need to operate reliably under continuous thermal stress. Similarly, in automotive applications, LCPs are employed in fuel system components where they must resist the combined effects of heat and chemical exposure.
In conclusion, the thermal advantages of Liquid Crystal Polymers make them an ideal choice for injection molding processes where high heat resistance and stability are required. By choosing LCPs, manufacturers can ensure their products meet stringent performance standards in the most demanding environments.
LCPs have a heat distortion temperature of 100°C.False
LCPs probably have a heat distortion temperature from 250°C to 350°C.
LCPs maintain integrity at 200°C continuous use.True
LCPs tolerate regular usage temperatures from 200°C to 250°C.
How Does LCP Compare to Other Materials in Injection Molding?
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) represents a high-quality substance in injection molding, presenting special benefits compared to regular plastics.
LCP outperforms many injection molding materials with its high thermal resistance, excellent mechanical properties, and exceptional fluidity. These characteristics make LCP ideal for precision components requiring stability and strength.

Mechanical Performance: LCP vs. Traditional Plastics
LCP plastic material stands out for its strong mechanical properties. Tensile strength ranges from 150MPa to 250MPa and bending strength is between 200MPa and 300MPa. Common plastics used in injection molding processes5 often have lower strength, limiting their use in high-stress situations.
Impact strength of LCP is usually between 10kJ/m² and 20kJ/m², showing its quality. This fits well for products needing to handle big stresses without losing structure.
Thermal Properties: Standing Up to Heat
LCP‘s thermal features set it apart. With heat distortion temperature from 250℃ to 350℃, it is better than many other plastics that soften at much lower heat. This lets LCP keep its shape and strength even in high heat, important for automotive and electronics industries6.
Continuous use temperature range of 200°C to 250°C lets LCP perform well where long exposure to heat is a concern.
Fluidity and Dimensional Stability
LCP shows great fluidity, making molding easy and lowering production expenses. Its low melt viscosity allows for smaller injection pressures, usually between 15MPa and 45MPa, compared to other thermoplastics. This high fluidity allows for molding of complex designs, a need in high-precision components7.
LCP‘s small shrinkage rate, generally from 0.1% to 0.5%, provides excellent dimensional stability, good for tasks that need tight measurements.
Electrical Properties: Insulation Superiority
In cases where electrical properties are crucial, LCP‘s low dielectric constant (2.5 to 3.5) and minimal dielectric loss (0.001 to 0.005) help. This makes LCP a good option for electronic parts where electrical insulation and stability are important.
Comparative Analysis: LCP vs. Alternative Materials
| Property | LCP | Traditional Plastics |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 150-250 MPa | Varies, typically lower |
| Heat Distortion Temp | 250-350℃ | Often <200℃ |
| Shrinkage | 0.1% – 0.5% | Higher, varies |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.5 – 3.5 | Higher, varies |
In conclusion, when comparing LCP with other materials in injection molding, its strong mechanical, thermal and electrical properties make it suitable for tough tasks.
LCP has higher tensile strength than traditional plastics.True
LCP's tensile strength spans from 150MPa to 250MPa, much above numerous plastics.
LCP softens at temperatures below 200°C.False
LCP tolerates warmth with a bending temperature from 250℃ to 350℃.
What Are the Common Applications of LCP in Industry?
Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCPs) stand as a foundation in many fields because of their excellent qualities. These qualities include strong durability, heat stability and resistance to chemicals. Explore the fields using these advantages.
LCPs are commonly used in the electronics, automotive, and medical industries. Their applications include connectors, sensors, fuel system components, and surgical instruments due to their robustness and precision molding capabilities.

Electronics Industry: The Heart of Miniaturization
LCPs have outstanding dielectric qualities, perfect for electronic parts like connectors, switches, and sockets. As gadgets get smaller but more powerful, LCPs give the needed dimensional stability8 for exact production. Their low dielectric rate leads to little signal disturbance, essential for high-frequency uses.
Automotive Sector: Fuel System Parts
Car makers use LCPs for various parts under the hood. Due to great heat resistance and strong build, LCPs fit well in fuel system pieces like pumps and valves. These parts need to endure tough settings, facing fuels and high temperatures, making LCPs a very good choice for keeping them dependable and long-lasting.
Medical Devices: Assuring Safety and Strength
In healthcare, LCPs are found in surgical tools and other medical devices. Their resistance to chemicals and ability to handle cleaning processes without breaking down suits them for repeated use. Plus, the precision needed in medical tools is possible due to LCPs’ great flow9 during the molding process.
Packaging and Containers: Heat Endurance
LCPs also see use in making containers and packing goods that need to resist high heat. For example, electronic oven containers benefit from LCPs’ skill to handle long exposure to heat without changing shape or melting. This trait helps a lot in factories where heat plays a crucial role.
Conclusion: A Flexible Material
These examples show key uses of LCPs, but their flexibility reaches other fields like telecommunications and aerospace. By providing a mix of strength, stability, and dependability, LCPs grow their reach in many areas, opening doors to new uses.
LCPs are used in electronic furnace containers.True
LCPs resist high temperatures. These traits suit them for furnace containers.
LCPs have low chemical resistance in medical devices.False
LCPs are selected for medical equipment because of their strong chemical resistance.
Conclusion
LCPs have unique features for injection molding tasks, providing very strong and accurate results. Choose LCPs for top-quality tasks to tap into their full capabilities and promise products that last.
-
Explore diverse applications of LCPs in modern manufacturing.: What Are the Uses of Liquid-Crystal Polymers? · Electrical connectors: LCP plastic can be used to manufacture conductive electrical connectors. ↩
-
Learn about LCP’s role in enhancing automotive components.: Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP), a high performance engineering plastic and offers outstanding mechanical properties at high temperatures, excellent chemical … ↩
-
Discover detailed benefits of LCP’s thermal properties.: These very high thermal properties, combined with excellent flowability, make LAPEROS suited for thin wall devices that undergo high-temperature … ↩
-
Explore how LCP compares to other polymers in thermal performance.: The manufacturing of LCP raw material makes use of dangerous chemicals but once that is complete, LCPs become inert, much like other polymers. ↩
-
Explore comparative tensile strength data across various plastics.: In addition, it has the highest melting temperature and can have the highest tensile strength. The properties of LCP include three common … ↩
-
Learn about LCP’s thermal benefits in automotive settings.: Film grade LCP is mainly used to produce high-performance films with good heat resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical stability. The … ↩
-
Understand how LCP’s fluidity aids precision molding tasks.: Injection grade LCP material is mainly used for injection molding to form complex geometries through fluidity at high temperatures. · Film grade … ↩
-
Learn how LCP’s dimensional stability enhances electronics miniaturization.: LCP films offer excellent dimensional stability, high strength, and excellent resistance to temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for a … ↩
-
Understand why LCP’s fluidity is crucial for precision medical devices.: Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) materials have high temperature capability and flow easily. It is especially well-suited to applications that require very thin … ↩






