Ever wondered how everyday items like plastic cups or phone cases are made? Enter the fascinating world of injection molding.
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce a wide range of products, including daily necessities, electronic product shells, automotive parts, toys, and medical supplies. It allows for high precision, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in production.
While injection molding is commonly associated with plastic products, its versatility extends far beyond. Join me as we delve deeper into the specific items made using this innovative process and understand why it’s a cornerstone in modern manufacturing.
Injection molding is only used for plastic products.False
Injection molding is also used for metals and ceramics, not just plastics.
How Does Injection Molding Work?
Understanding the mechanics of injection molding reveals how plastic transforms into useful products like toys and gadgets.
Injection molding involves melting plastic pellets, injecting the molten plastic into a mold cavity, cooling it to solidify, and then ejecting the finished product. This process allows for the precise creation of complex shapes and is integral to manufacturing a variety of items efficiently.
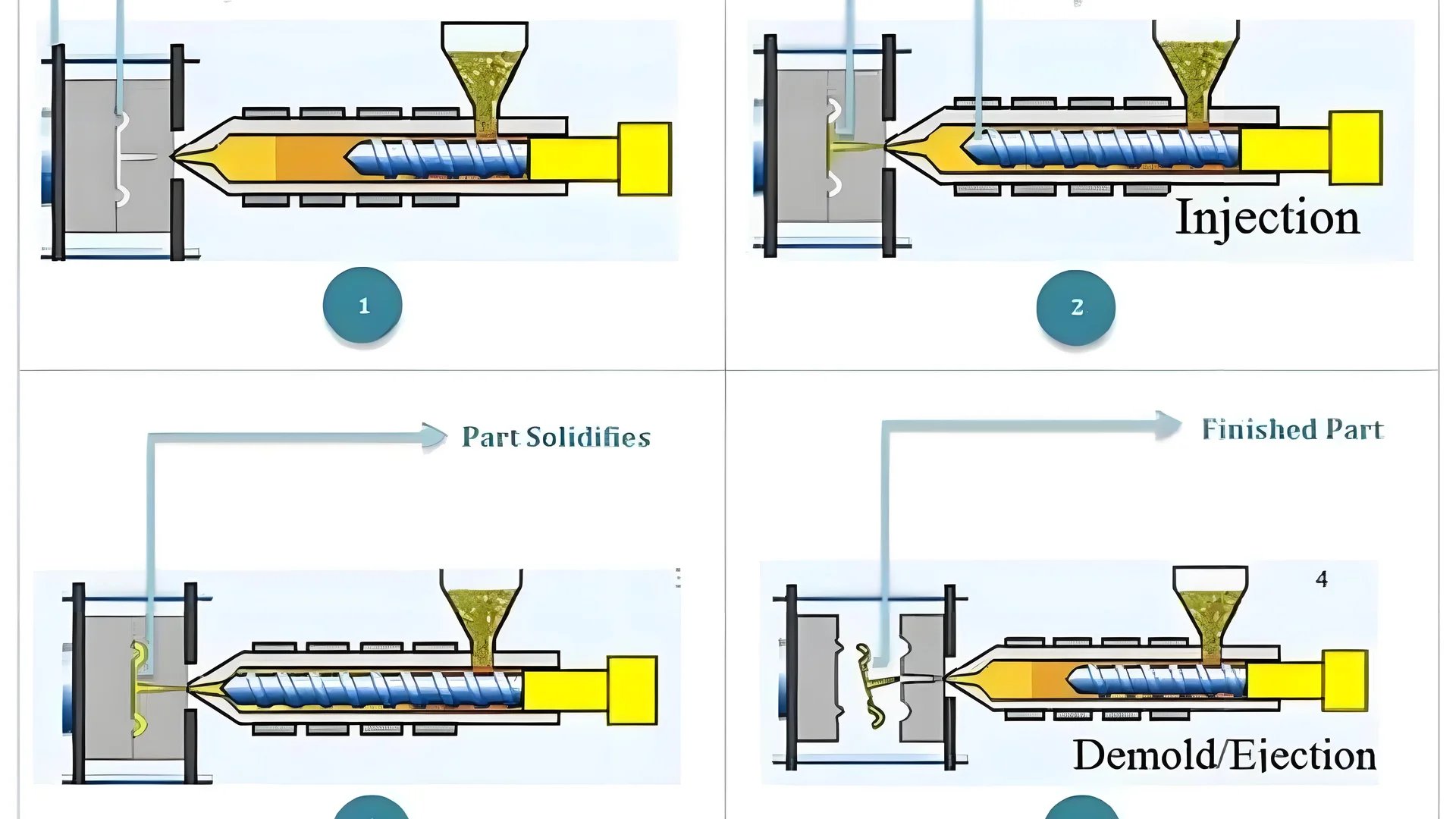
The Injection Molding Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
Injection molding is a method that brings precision and efficiency to manufacturing, making it invaluable across industries. Here’s how it works:
-
Material Preparation:
The process begins with feeding plastic pellets into the injection molding machine. These pellets are typically made from polymers like polypropylene and polycarbonate1, chosen for their durability and flexibility.
-
Melting and Injection:
The plastic pellets are heated in a barrel where they melt into a viscous liquid. This molten plastic is then injected into a steel mold cavity under high pressure using an injection unit.
-
Cooling and Solidification:
Once inside the mold, the plastic cools and solidifies, taking on the shape of the cavity. Cooling time varies based on material type and product complexity.
-
Ejection:
After cooling, the mold opens, and ejector pins push the finished product out of the mold. This cycle can repeat rapidly for mass production.
Applications Across Industries
Daily Necessities
- Plastic Tableware: Injection molding is vital for creating durable, food-safe tableware like plates and bowls.
- Water Cups and Storage Solutions: Molded with precision to ensure strength and longevity, making them ideal for everyday use.
Electronics
- Phone Cases and Keyboard Shells: The technique allows for intricate designs, ensuring a snug fit and aesthetic appeal.
Automotive
- Interior Panels and Bumpers: Engineered to provide safety and comfort, with materials that withstand wear and tear.
Injection molding’s versatility makes it indispensable, offering solutions from robust automotive parts to delicate medical supplies. This ability to cater to diverse needs highlights its role in advancing manufacturing technology.
Injection molding uses steel molds for shaping products.True
Steel molds are commonly used due to their durability and precision.
Plastic pellets are cooled before being injected into the mold.False
Plastic pellets are melted before injection, not cooled.
What Materials Are Used in Injection Molding?
Delving into the world of injection molding reveals a variety of materials, each serving unique purposes in crafting everyday objects.
Injection molding utilizes various materials, primarily thermoplastics like polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), and polycarbonate (PC). These materials offer durability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for diverse applications from household items to automotive parts.

The Role of Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the backbone of injection molding due to their versatility and ease of use. These materials can be repeatedly melted and reformed, which is crucial for high-volume manufacturing. Common thermoplastics include polypropylene (PP)2, known for its toughness and resistance to chemicals, making it perfect for food containers and automotive components.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is another popular choice, prized for its impact resistance and toughness. ABS is extensively used in electronic housings, such as computer keyboard shells3, and automotive parts.
Polycarbonate (PC) offers excellent transparency and heat resistance, often used in making plastic water cups4 and lenses for headlights.
Engineering Resins
When products demand enhanced properties like higher strength or better thermal resistance, engineering resins come into play. Materials such as polyamides (nylon) and polyesters are engineered to withstand more rigorous conditions. For instance, nylon is frequently used in manufacturing automotive interior parts5 due to its durability and strength.
Specialty Polymers
Specialty polymers, including thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and liquid silicone rubbers (LSR), cater to niche applications requiring flexibility or medical-grade standards. TPEs are often utilized in making soft-touch grips or flexible seals found in consumer electronics.
Environmental Considerations
Increasingly, the injection molding industry is turning towards sustainable options like biodegradable polymers and recycled plastics. Biodegradable options offer a promising solution to reduce environmental impact, particularly in single-use products like disposable syringes6.
By choosing the right material, manufacturers can achieve the desired balance between product performance and cost-efficiency, solidifying injection molding’s role in various sectors.
Polypropylene is used in food containers.True
Polypropylene's toughness and chemical resistance make it ideal for food containers.
ABS is unsuitable for electronic housings.False
ABS's impact resistance and toughness make it ideal for electronic housings.
Why Choose Injection Molding Over Other Manufacturing Methods?
Considering different manufacturing methods for your product? Here’s why injection molding might be your best bet.
Injection molding offers unparalleled precision, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to other manufacturing methods. It’s ideal for producing complex shapes with consistent quality, making it a preferred choice for industries ranging from electronics to automotive and medical supplies.
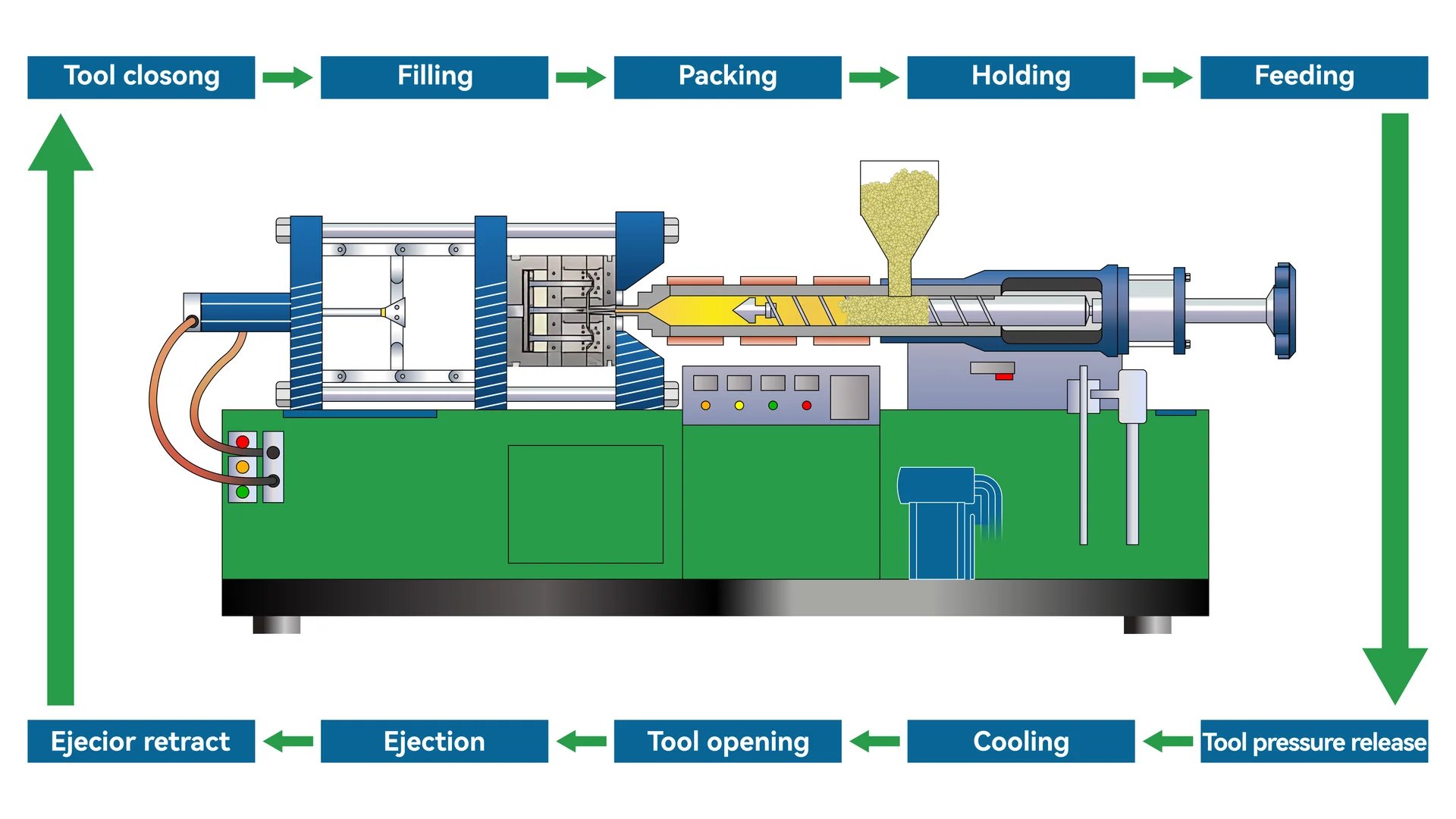
Precision and Complexity
One of the standout benefits of injection molding7 is its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. Unlike other methods, injection molding allows for intricate designs such as the textured surfaces of mobile phone shells or the complex interlocking parts of plastic building blocks. The mold design8 plays a crucial role here, enabling tight tolerances that ensure components fit perfectly without post-processing.
Scalability and Speed
When it comes to large-scale production, injection molding excels. The process is highly automated, which minimizes human error and speeds up production. For example, plastic tableware like plates and bowls can be produced in large quantities with consistent quality, meeting the high demand efficiently.
Material Versatility
Injection molding supports a wide range of materials, from food-grade plastics used in plastic water cups to high-strength plastics for automotive bumpers. This versatility makes it suitable for diverse applications across various industries, ensuring that products like headphone shells maintain durability without compromising on aesthetics.
| Material | Common Products | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Water cups, storage boxes | Lightweight, durable |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Electronic shells | High impact resistance |
| Engineering Plastics | Automotive parts | Heat resistant, strong |
Cost-Effectiveness
Despite the initial cost of mold creation, the long-term savings in production make injection molding cost-effective. Once the mold is made, the per-unit cost decreases significantly as production volumes increase. This is particularly advantageous for medical supplies like syringes and infusion sets, where high-volume production is essential.
In summary, injection molding stands out due to its unique combination of precision, efficiency, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re producing everyday items like plastic trash cans or sophisticated components like computer keyboard shells, injection molding offers a compelling solution for modern manufacturing challenges.
Injection molding is ideal for small-scale production.False
Injection molding excels in large-scale production due to automation.
Injection molding can produce complex shapes with high precision.True
It allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances without post-processing.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Injection Molding?
Injection molding has revolutionized manufacturing but raises questions about its environmental footprint.
Injection molding impacts the environment through energy consumption, material waste, and emissions. Despite its efficiency in mass production, the process relies heavily on non-renewable resources, generates significant waste, and contributes to pollution if not managed properly.

Energy Consumption in Injection Molding
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with injection molding is its energy consumption9. The process involves melting plastic pellets, which requires substantial amounts of electricity. Most injection molding machines operate on electricity generated from fossil fuels, leading to greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and transitioning to renewable energy sources can mitigate this impact.
Material Waste and Recycling Challenges
Injection molding generates waste in various forms, including rejected parts, excess sprue material, and leftover resins. Although some of this waste can be recycled, the recycling process itself can be resource-intensive. Innovative approaches like using biodegradable plastics or optimizing mold designs to reduce waste are essential strategies for minimizing the environmental impact.
Emissions and Pollution
The process can also contribute to air and water pollution. During production, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants may be released into the atmosphere. Additionally, improper disposal of waste materials can lead to contamination of water bodies. Adopting stringent emission controls and improving waste management practices are crucial steps in reducing pollution.
The Role of Sustainable Materials
The choice of materials significantly influences the environmental impact of injection molding. Opting for sustainable materials10, such as bio-based or recycled plastics, can lessen dependency on fossil fuels and reduce carbon footprints. Furthermore, these materials often require less energy to process, thereby lowering overall emissions.
Innovations in Green Manufacturing
Advancements in technology offer promising solutions for more sustainable injection molding. For instance, implementing closed-loop systems that recycle heat or utilizing advanced robotics to optimize production processes can substantially decrease energy consumption and waste. Encouraging innovation in green technologies will be vital for minimizing the ecological footprint of injection molding.
By understanding these environmental impacts and exploring innovative solutions, we can make injection molding a more sustainable manufacturing method.
Injection molding uses renewable energy sources.False
Most machines rely on fossil fuels, not renewables.
Biodegradable plastics reduce waste in injection molding.True
They offer a sustainable alternative, lowering environmental impact.
Conclusion
Injection molding remains an essential process across various industries, offering unmatched precision and efficiency. Consider exploring this technology further for your next project or business venture.
-
Explore their properties that make them ideal for various applications.: Injection molding polypropylene parts known for its heat and chemical resistance, is widely used in creating durable household items like kitchenware and … ↩
-
Discover polypropylene’s role in diverse industrial applications.: Polypropylene Uses · Children’s toys · Sporting goods · Caps · Closures · Automotive applications · Food trays · Cups and to-go containers · Household goods and … ↩
-
Understand why ABS is ideal for electronic casings.: PBT: Generally more expensive. ABS keycaps are generally more affordable due to lower material and manufacturing costs, making them a popular … ↩
-
Explore why polycarbonate is preferred for water cups.: Polycarbonate plastic is widely used for its transparency and impact-resistance, making it a great lightweight choice for key industries. ↩
-
Learn how nylon enhances automotive part durability.: NYCOSIX Nylon 6 and NYCO66 Nylon 66 reinforced grades are used to manufacture under the hood components, such as engine covers, fan shrouds, radiator components … ↩
-
See the advantages of biodegradable options in healthcare.: Applications are wide ranging with degradable polymers being used clinically as surgical sutures and implants. ↩
-
Learn how injection molding achieves exceptional precision in product manufacturing.: What are the advantages of injection molding? · 1. Efficient high production · 2. Low cost per part · 3. Repeatability · 4. Large material choice · 5 … ↩
-
Understand the critical role of mold design in injection molding success.: The quality and make of the mold allows injection molders to ensure high tolerance, identify defects, maintain precision, choose the right raw materials, as … ↩
-
Explore how energy-efficient technologies can reduce environmental impact.: Injection Molding facilitates tend to consume 0.9 – 1.6 kWh/kg to process plastics, depending on their processing efficiency. ↩
-
Discover eco-friendly material options that minimize environmental harm.: Sulapac Universal Flex 35 is a sustainable, beautiful, and functional injection molding material which contains 87% USDA certified bio-based content. The … ↩






