Ever felt curious about how polypropylene products get created? I really have!
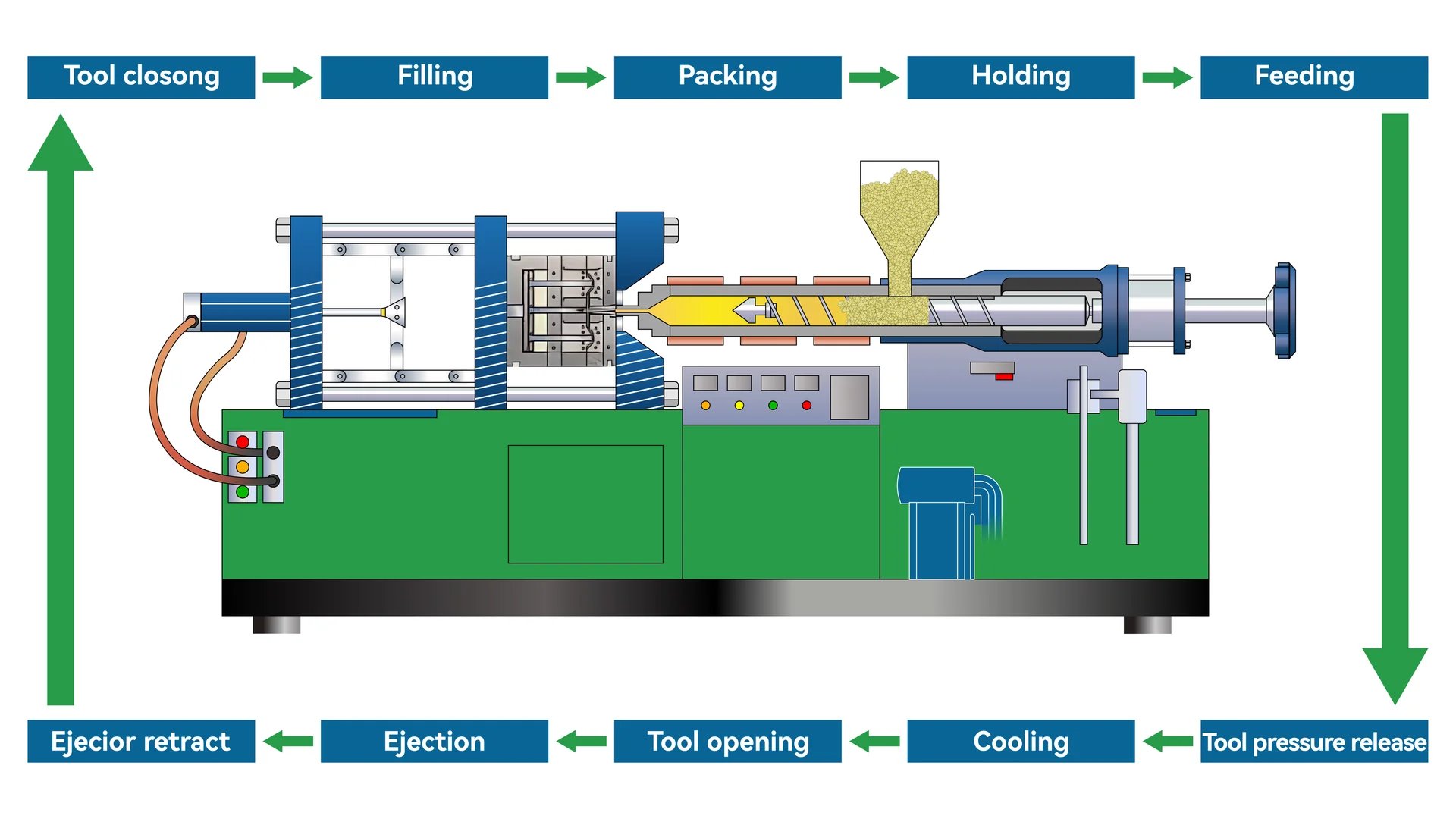
The PP injection molding process involves feeding polypropylene pellets into a heated barrel, where they are melted and injected into a mold cavity. The material cools and solidifies, forming the desired shape before being ejected. This process is valued for its efficiency and versatility in producing complex parts.
This short summary shows the simple parts. Learning PP injection molding involves exploring interesting details of material traits, mold shape and processing situations. Stay and explore each piece and find how to improve your injection molding practices.
PP injection molding uses polypropylene pellets.True
Polypropylene pellets usually go through melting and then injection into a mold.
What Are the Stages of PP Injection Molding?
Learn about the details of polypropylene injection molding, an important method in current production.
PP injection molding consists of several stages: material preparation, melting, injection, cooling, and ejection. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the quality and precision of the final product, from selecting the right material to designing an efficient mold.
Material Preparation: Beginning the Process
The initial step1 in PP injection molding involves preparing the materials. First, select the correct polypropylene resin based on the product needs. The chosen resin must be clean and free from unwanted materials. It must also be dried properly to avoid moisture issues during molding. Usually, PP resin needs drying at temperatures between 80 and 100°C for 2-4 hours, with moisture levels kept below 0.05%.
Melting: Reaching the Right Thickness
Prepared resin goes into the injection molding machine’s heated barrel. Here, temperatures between 160 to 250°C melt the resin. The right melting temperature is necessary to keep the resin fluid and prevent it from breaking down, which might weaken the product.
Injection: Filling the Shape
Molten resin is injected into a specially designed mold cavity under high pressure, typically 50 – 120 MPa2. The speed and pressure need careful control to ensure full filling without creating defects like flow marks or fusion lines.
Cooling: Hardening the Product
After injecting, the material cools and hardens inside the mold. This is a crucial phase as it defines the product’s final shape and size. A good cooling system, often with water channels inside the mold, allows for even temperature distribution and reduces shrinking and bending.
Ejection: Removing the Product
In the last step, the cooled product3 is taken out of the mold. This must be done carefully to avoid any damage. Different ejector types are used depending on the product shape, such as ejector pins or plates.
Each stage plays a vital part in PP injection molding. Paying close attention to details in each step leads to high-quality products. Choosing strong mold materials like P20 or 718 steel and adjusting injection settings like pressure and speed are important choices that affect both look and function.
PP resin requires drying at 80-100°C for 2-4 hours.True
Drying the resin blocks moisture problems. This supports quality molding.
Injection pressure in PP molding is always below 50 MPa.False
Injection force usually ranges from 50 to 120 MPa for PP molding.
How Do Material Properties Affect the Molding Process?
Grasping material traits is vital for successful molding results.
Material properties significantly influence the molding process by affecting flow, temperature resistance, and final product quality. Key properties include thermal stability, viscosity, and mechanical strength, which determine the efficiency of the molding cycle and the structural integrity of the molded parts.

Importance of Heat Stability
In the molding process4, heat stability is very important. It affects how the material acts when it gets hot. Polypropylene (PP), for example, starts to melt between 160 – 170°C. This feature makes it good for many uses. Its strong heat resistance helps it stay strong in warm places like car interiors or electrical parts.
Materials that lack heat stability may break down or burn when molded. This can cause problems like color changes or weak spots. Thus, picking materials with enough heat resistance is necessary for quality and long life.
Effects of Thickness on Flow
Thickness or viscosity affects how easily a material slides into molds. PP flows well and helps fill complex mold shapes without too much force. But if a material is too thick, it might not fill the mold’s small areas right, causing incomplete pieces.
On the other hand, very thin materials might cause issues like extra material or too much shrinking. So, adjusting thickness with additives or mixing with other plastics can improve flow.
Strength and Item Durability
A material’s strength, like how much it can stretch or bend, is important for the final product’s use. For instance, PP has a stretch strength of 20 – 30 MPa and bend strength of 25 – 40 MPa. These strengths give enough toughness to create long-lasting items like consumer goods or car parts.
Moreover, PP resists impacts better than some other plastics like polystyrene. This makes PP perfect for uses that need high strength and less brittleness. It is also safe for food wrapping because it is not toxic.
Chemical Resistance and Use
PP resists chemicals like acids, bases, and solvents. This increases its applications in areas like food packaging and appliances. This ability keeps the product safe and strong when it meets different chemicals during use or cleaning.
Choosing materials based on how they resist chemicals is very important in industries where products often meet harsh substances.
Final Thoughts on Material Traits
Each material trait helps the success of the molding process in a special way. By knowing and adjusting these traits—heat stability, thickness, strength, and chemical resistance—makers probably improve quality and usefulness across different uses.
Polypropylene has a melting point of 160 - 170°C.True
Polypropylene melts at a high temperature, permitting it to endure intense heat.
High viscosity materials flow easily into mold cavities.False
Thick liquid resists movement, so it becomes difficult to fill mold details.
What Role Does Mold Design Play in Product Quality?
Curious about how mold design affects your products’ quality? Let’s find out!
Mold design is crucial in determining the quality of injection-molded products. It influences aspects such as dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and structural integrity. Proper mold design ensures efficient cooling, smooth ejection, and minimal defects, directly affecting the final product’s reliability and aesthetics.
Importance of Mold Material Selection
Picking the correct mold material is crucial to handle the high pressure and temperature in the injection molding process. Materials like P20 and 718 steel are popular for their hardness, strength, and resistance to wear. For example, P20 steel5 offers great processing performance at a lower cost, which makes it ideal for general PP injection molding.
Cooling System Design
A good cooling system is needed for even mold temperature, which is essential for consistent product quality. Generally, water cooling is used with channels arranged inside the mold. The width of these pathways often ranges from 8-12 mm, with space based on the product’s wall thickness and shape, typically between 20-50 mm.
The cooling system design6 must ensure that the inlet and outlet are symmetrically positioned to guarantee uniform water flow, optimizing the cooling effect and reducing cycle times.
Parting Surface and Release Mechanism
The parting line should be placed where it does not harm the product’s look or function. The mechanism for releasing must be designed per the product’s shape and structure to enable easy removal without damage or bending.
Different ejector designs7 are selected based on needs, like ejector pins for general uses or push plate ejectors for larger products needing even force distribution.
Glue Feed System
Selecting a glue feed method impacts product quality. Options include direct gluing for faster filling but more visible marks or side gate gluing for bigger products with fewer visible marks. Spot gate gluing is best for items needing a high-quality surface finish.
Impact on Product Design
Even wall thickness is crucial to prevent problems like uneven shrinking and internal stress, which can cause warping. For products with tricky shapes, a slow change in wall thickness helps lower stress concentration. Typically, a thickness of 1-3 mm is suggested depending on usage.
Improving Product Look and Function
Good mold design not only improves the look but also the function of the final product. By getting the cooling and gate systems right, creators achieve better surface finishes and structural strength, making sure products meet top-quality standards consistently.
Overall, careful mold design is key in improving both the visual appeal and working of injection-molded products, therefore securing customer happiness and staying competitive.
Mold design affects product surface finish.True
Careful mold creation brings smooth surfaces by reducing faults.
Uniform wall thickness prevents warping in products.True
Uniform wall thickness lessens tension and contraction problems.
How Can You Optimize Injection Molding Parameters?
Want to improve your injection molding technique for better outcomes? Here’s how!
To optimize injection molding parameters, focus on adjusting injection pressure, speed, and screw rotation. Each parameter should be fine-tuned based on product size, shape, and material properties to minimize defects and improve quality.

Understanding Key Parameters
Injection molding parameters are critical in defining the quality and productivity of creating items. Important parameters include injection pressure, speed, and screw rotation.
-
Injection Pressure: This typically lies between 50 – 120 MPa. Thinner products often need higher pressure for proper filling, while thicker items may use less pressure to avoid stress inside.
-
Injection Speed: Commonly ranges from 50 – 150 mm/sec. Adjust these based on how complex the item is and what appearance you need. Faster speeds fill complex molds better, but slower speeds provide high-quality surfaces.
-
Screw Speed: Usually between 30 – 100 rpm. Higher speeds raise production rates but might cause overheating and harm the material.
Fixing Common Defects
Injection molding might result in defects like incomplete filling, shrink marks, and flow marks. Solutions for these are:
| Defect | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete Filling | Low pressure or low speed | Raise pressure and speed, change mold temperature |
| Shrink Marks | Too much shrinking | Lengthen holding time, lengthen cooling time |
| Flow Marks | Too fast speed | Slow down speed, increase mold temperature |
Adjusting Parameters for Various Products
The design of products8 affects parameter settings too. For example, a product with even walls requires different parameters than one with uneven walls.
Exploiting the perks of polypropylene (PP), such as its strong resistance to chemicals and low price, probably results in affordable solutions9.
Balancing Efficiency and Quality
Setting these parameters right not only improves quality but also increases production efficiency. Regular checking and tweaks result in less waste and lower costs.
Understanding the details of injection molding parameters helps creators balance speed and detail, leading to really good product quality.
Higher injection pressure prevents internal stress in thick walls.False
Increased pressure probably leads to internal tension in thick-walled items.
Fast screw speed can degrade resin quality in injection molding.True
Quick screw rotations may result in high temperatures, damaging the resin.
Conclusion
Understand the details of PP injection molding to improve efficiency and quality. These ideas improve design and process adjustment.
-
Gain insights into optimizing PP resin preparation for quality production.: 1) Make sure you have the proper molding equipment · 2) Consider pre-drying ONLY if you are using certain polypropylene resins · 3) Use a melt … ↩
-
Explore advanced techniques to enhance your injection molding process.: This blog introduces the types, properties and injection molding process of engineering plastics PP, the selection of equipment, product modeling and mold … ↩
-
Discover innovative ejector designs for seamless product removal.: To reduce the force necessary for ejection, the design for injection molding incorporates increased draft angles and may introduce a smoother polish on the core … ↩
-
Learn how material properties dictate molding outcomes and efficiencies.: Lower melt flow rate values are associated with materials of higher average molecular weight. Higher molecular weight, in turn, provides for improved properties … ↩
-
Explore P20 steel’s properties suitable for PP injection molds.: P20 Mold Steel is a versatile, low-alloy tool steel that is characterized by good toughness at moderate strength levels. The steel is commonly used for plastic … ↩
-
Learn about designing optimal cooling systems for molds.: Make sure the cooling line diameter is large enough to overcome the convection of the plastic material temperature into the surrounding steel. … ↩
-
Discover various ejector mechanisms for smooth demolding.: Types of Ejection System in Injection Molding · Pins and Blades Ejection · Ejector Sleeves · Valve Ejectors · Stripper Ring Ejection · Air Ejection · Things to … ↩
-
Learn why uniform wall thickness is crucial for stress reduction.: Proper wall thickness will reduce the risk of cosmetic defects in plastic parts. Walls in any plastic-molded part should be no less than 40 to 60 percent that … ↩
-
Discover why PP is favored in various industries.: Advantages of Using PP Injection Molding · Polypropylene is readily available and affordable. · It is resistant to moisture, fatigue, and impact. · PP has a … ↩






