Have you ever thought about how mold thickness might really affect your injection molding work?
The thickness of the mold greatly affects the injection molding process. It influences the opening of the mold, speed and pressure during molding. It also impacts the injection pressure, volume and the time needed to cool and hold the product. Adjustments to these settings based on the thickness are crucial. Product quality and efficient manufacturing depend on these adjustments.
Once, I was deep in a project and I realized how important understanding mold thickness really was. It’s not just about getting the measurements right. Anticipating necessary changes in the process is crucial. For example, mold opening stroke needs adjusting for the right mold thickness range. This adjustment allows smooth product release without any delays. Adjusting molding speed and pressure helps avoid costly mishaps like mold collision damage. Understanding these details saved my project. It also increased my respect for precision in manufacturing. By getting these adjustments right, I improved our production efficiency. Waste was reduced. It was a big success for any engineer.
Thicker molds require longer cooling time.True
Thicker molds have longer heat transfer paths, increasing cooling time.
Injection pressure is lower for thicker molds.False
Thicker molds need higher injection pressure due to increased cavity resistance.
How Do I Determine the Right Mold Opening Stroke for Different Thicknesses?
Picture setting the mold stroke perfectly – like tuning a guitar to get the best sound.
The best mold opening stroke balances mold thickness and cycle efficiency. Thin molds need a short stroke for fast ejection. Thick molds need a longer stroke to avoid damage. A longer stroke helps products release smoothly.

Understanding Mold Opening Stroke
I remember adjusting a mold’s opening stroke for the first time – it felt like solving a puzzle. In injection molding, the stroke decides how far the two mold halves move apart. This movement is important for the product to come out smoothly. It’s not just about separating them; it’s about doing it right. A short stroke might leave products stuck; a long stroke wastes time.
Impact of Mold Thickness
Mold thickness is very important. I’ve worked with thin molds that felt as fragile as paper – they needed only a small push to release the product. Thick molds, however, were like mountains. They need more space, so a longer stroke helps protect them and lets everything come out easily.
Adjusting Mold Opening Parameters
Setting these parameters is like custom-fitting a suit – one size never works for all. It relies on the mold’s thickness and the machine’s ability. With molds at the machine’s lower limit, I reduced the stroke to keep things smooth and avoid extra pressure on the machine. With thicker molds, raising the stroke really helped to eject products without problems, even with slightly longer cycle times.
Mold opening adjustments should also factor in molding speed and pressure1. Thicker molds, which have greater mass and inertia, might require slower speeds and higher pressures to close properly.
Role of Cooling Time and Pressure
Cooling time adds another layer to this task. Thick molds take more time to cool because they keep heat longer, affecting speed and product quality. Being patient here truly pays off, ensuring high-quality results without defects like shrink marks.
By understanding these factors, I’ve managed to refine processes for various mold thicknesses, reaching efficiency and quality in my products. Those wanting to improve their injection molding can explore injection pressure adjustments2 to find even more ways to get better.
Thicker molds require longer cooling times.True
Thicker molds have greater thermal resistance, needing 30%-50% more cooling time.
Mold thickness doesn't affect injection volume.False
Thicker molds may need increased injection volume due to larger cavity size.
How does mold thickness affect molding speed and pressure?
Have you ever thought about how mold thickness changes everything in injection molding? This balance is delicate. It very much affects product quality.
Mold thickness changes how fast and with what force molding happens. It does this by altering the mold’s opening stroke and injection settings. Thicker molds require stronger closing forces. These molds also need slower speeds. This prevents damage to the mold. Very thick molds require more injection force. More force guarantees that the mold fills completely.
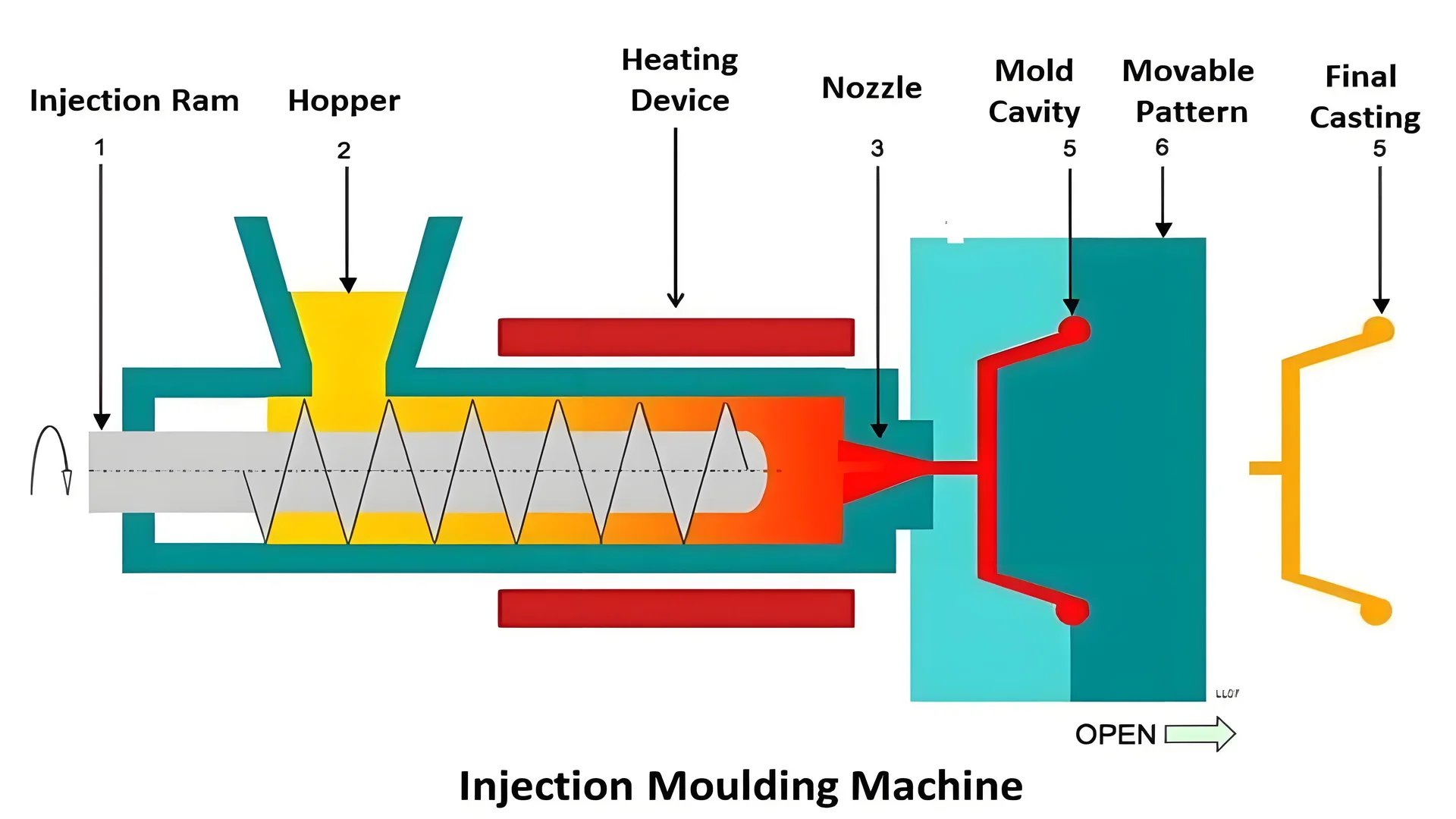
Mold Opening and Closing Parameters
Mold thickness surprised me when I started with injection molding. It really impacts the whole process. A mold’s thickness changes how products release. Thicker or thinner molds require exact opening strokes for smooth results. Thick molds need a longer opening stroke to prevent incomplete product release, whereas an excess stroke can unnecessarily prolong the molding cycle. Thickness truly matters.
Molding Speed and Pressure Dynamics
Pressure is not the only thing about thicker molds. Timing is important too. Imagine closing a heavy door too fast—damage can happen. Thick molds work the same way; moving too quickly causes damage. Slowing down carefully avoids problems. Mass and inertia create challenges, so speed and pressure must be just right for optimal mold performance3. Balance both for smooth operation.
Injection Pressure and Volume Considerations
Injection pressure needs careful adjustment as mold thickness varies within allowable limits. Thick molds raise the need for more force, requiring heightened injection pressure to ensure full cavity filling—sometimes 30% more pressure might be necessary compared to thinner molds. Volume matters as well; strong molds may need more material due to larger cavity volumes, impacting injection efficiency4. Watching the injection volume avoids shortages.
Cooling Time and Holding Time Adjustments
Cooling takes extra time with thick molds because they lose heat slowly, necessitating longer cooling periods—sometimes 50% more cooling time is needed compared to thinner molds. This extra time stops defects like shrink marks from appearing with careful timing during the holding stage, ensuring optimal product quality5.
Knowing these details made my process better. Small changes greatly improve product quality every time. Understanding these steps saved me from many problems—they are very important, truly significant.
Thicker molds require higher closing pressure.True
Thicker molds need more pressure to ensure complete closure.
Cooling time decreases with thicker molds.False
Thicker molds dissipate heat slowly, increasing cooling time.
Why Is Injection Pressure Crucial for Thick Molds?
Picture the excitement of seeing hot plastic turn into a flawless item. Precision is key. This is true especially with thick molds.
Injection pressure is vital for thick molds because it helps fill the mold correctly. Greater depth brings resistance. High pressure avoids flaws. It keeps quality very high.
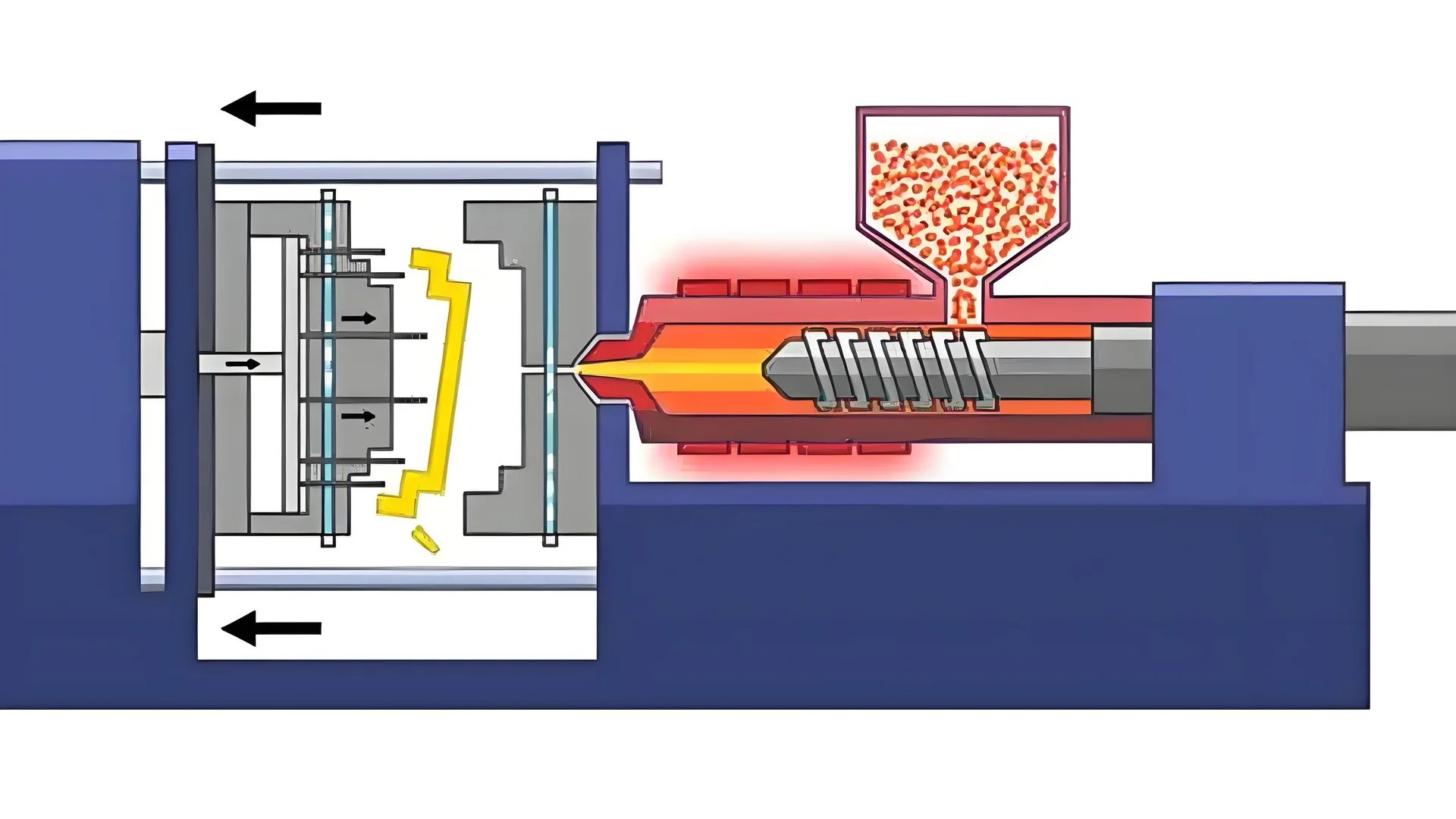
The Role of Injection Pressure in Mold Filling
I remember my first time working with thick molds. I felt both excited and nervous. Filling deep molds is really tough. It needs the right injection pressure. The deeper the mold, the harder it is for molten material to flow. This gives more resistance. Without enough pressure, you might face underfilling or warping problems. Enough pressure is very important. Really important.
Injection pressure is integral to filling mold cavities, especially in thick mold designs6. As the mold’s cavity depth increases, so does the resistance to the flow of molten material. Higher injection pressures are necessary to overcome this resistance, ensuring the material fills the cavity completely.
Impact on Injection Volume
There was a project where everything needed adjustments. Thick molds required tweaking the injection volume. The cavity depth meant needing a larger volume. I had to think about this a lot.
Thick molds often require adjustments in injection volume. The cavity’s increased volume demands more material to fill it adequately. If machines pushed beyond limits, we faced incomplete products or defects were common then.
Balancing Cooling and Pressure Holding Times
I remember waiting for a thick mold to cool. It felt like forever. Patience matters because thick molds lose heat slowly.
The cooling process is significantly influenced by mold thickness. Thicker molds dissipate heat more slowly, necessitating longer cooling times to prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage.
Holding the right pressure ensures the product keeps its shape and size.
During this cooling phase, holding pressure must be carefully managed to maintain product dimensions.
Finding just the right balance is essential.
Higher holding pressures might be required for thicker molds to ensure even solidification and avoid issues like sink marks.
Adjusting Mold Opening and Closing Parameters
Adjusting mold parameters is like solving a puzzle.
With thick molds, adjusting parameters makes working both hard and rewarding.
Understanding injection pressure details helps us succeed in making quality products consistently and effectively.
The mold opening stroke7 should be calibrated according to thickness; too little stroke means poor release while too much leads to long cycle times unnecessarily.
Moreover, controlling closing speed avoids damage from collision due to mass inertia of thicker molds.
Thicker molds require higher injection pressure.True
Thicker molds have greater cavity depth, increasing melt resistance.
Cooling time decreases with thicker molds.False
Thicker molds dissipate heat slowly, needing longer cooling times.
How Do Cooling Time and Holding Time Adjustments Impact Product Quality?
Have you ever thought about how a simple change in cooling and holding times affects your product’s quality? These small adjustments matter. These changes really shape the final outcome.
Changing cooling and holding times in injection molding greatly influences product quality. This adjustment gives parts better size stability and surface texture. It also improves their physical strength. Proper management stops defects. Warping and sink marks do not appear. Product output stays very high.
Cooling Time Considerations
I remember the first time I dealt with adjusting cooling times. It felt like finding the perfect mix between too firm and too soft when baking. Thicker molds held heat much longer. It was as if the heat was a guest who didn’t want to leave. I soon realized these molds needed extra cooling time adjustment8 – about 30% to 50% more than thinner ones. This extra time stopped warping and maintained the shape, like letting a pie rest to slice perfectly.
Impact of Holding Time Adjustments
Holding time was tricky, especially for thicker molds. I often stayed up late, adjusting bit by bit, like tuning a guitar for the right sound. Extending the holding time9 reduced shrink marks and filled every part of the mold well. Timing had to be perfect, like waiting to pour molten chocolate at the right moment.
Interplay with Mold Parameters
Adjustments don’t happen alone; they connect with details like mold opening stroke and injection pressure. I recall a project where the mold opening stroke wasn’t right—it felt like trying to open a glued book—nothing moved, slowing our process. We had to adjust the injection pressure10, ensuring it was strong enough to fill the molds completely.
Understanding these links is like solving a complex puzzle—every piece needs to fit. When they do, it’s very satisfying. Simple changes bring great improvements in quality and consistency. It’s all about finding that perfect balance where everything works well.
Thicker molds require longer cooling times.True
Thicker molds have longer heat transfer paths, slowing heat dissipation.
Mold thickness doesn't affect injection pressure.False
Thicker molds need higher injection pressure due to greater flow resistance.
Conclusion
Mold thickness significantly influences injection molding parameters, affecting mold opening stroke, injection pressure, cooling time, and product quality. Adjustments are crucial for efficient manufacturing and defect prevention.
-
Explore how speed and pressure settings affect mold quality. ↩
-
Discover optimal strategies for adjusting injection pressure. ↩
-
Explores the direct impact of thickness on mold operations. ↩
-
Guides on optimizing injection settings based on mold thickness. ↩
-
Details how mold thickness affects final product outcomes. ↩
-
Understand how high pressure aids in filling thick mold cavities. ↩
-
Learn techniques for optimizing mold opening stroke adjustments. ↩
-
Learn how cooling time adjustments influence final product quality. ↩
-
Discover why adjusting holding time is crucial for quality outcomes. ↩
-
Understand the role of injection pressure in achieving optimal results. ↩






