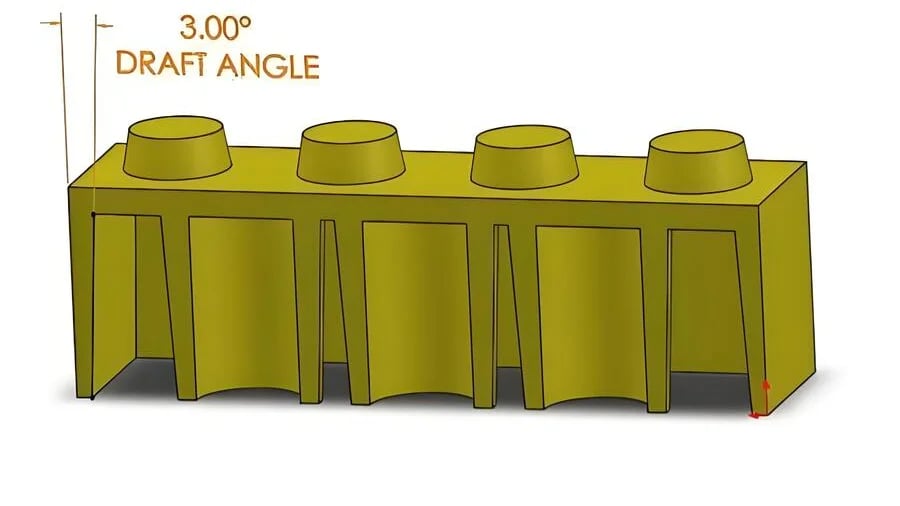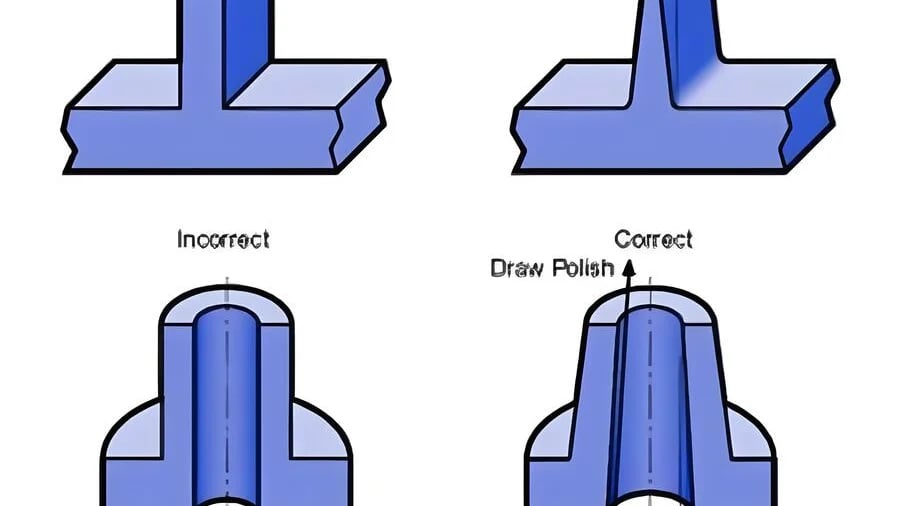
Understanding the standard specifications for injection mold draft angle is essential for any manufacturing process involving injection molding.
Injection mold pullout slopes, or draft angles, are essential for smooth demolding in injection molding processes. Industry standards like ISO recommend a 0.5°-1.5° slope for outer surfaces and 1°-3° for inner surfaces, while automotive standards require 1°-2° for outer and 2°-4° for inner surfaces. These angles ensure quality and precision.
While understanding these basic specifications is crucial, it’s equally important to dive deeper into how different industries and enterprises tailor these standards to fit their unique requirements. Keep reading to uncover how these variations impact product performance and manufacturing efficiency.
ISO standards recommend a 0.5°-1.5° slope for outer surfaces.True
ISO standards suggest these slopes for easier demolding of plastic products.
Large enterprises often ignore industry standards in mold design.False
Large enterprises develop internal standards based on industry norms and experiences.
How Do Industry Standards Vary Across Different Sectors?
Industry standards ensure quality and safety across sectors but differ based on specific needs and challenges. Understanding these variations can enhance compliance and innovation.
Industry standards vary across sectors to address unique requirements. In the plastics industry, ISO standards dictate mold draft angles, while automotive standards focus on precision for interior parts. Enterprises develop internal standards, with large firms setting stricter guidelines than SMEs, adapting industry norms to their resources and goals.
Understanding Industry Standard Norms
Industry standards serve as essential benchmarks that guide production and quality assurance across various sectors. They are crucial in ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency. For instance, in the plastics industry1, standards set by the ISO determine specific guidelines like mold draft angles, ranging from 0.5° to 1.5° for outer surfaces and 1° to 3° for inner surfaces. This variation accounts for differences in demolding difficulty between surfaces.
Sector-Specific Standards in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry showcases a stringent application of standards, particularly in injection molding for interior parts. According to the VDA, the German Federation of Automotive Industries, the mold draft angle for automotive interior parts ranges from 1° to 2° on the outer surface and 2° to 4° on the inner surface. These specifications ensure high-quality appearance and assembly precision, crucial for automotive safety and performance.
Enterprise Internal Standard Specification
Large enterprises often develop their own internal standards tailored to specific product characteristics. For example, a major home appliance company might set a minimum outer surface mold pull-out slope of 1°, with rigorous checks during the design review stage. This approach ensures that production aligns with corporate quality objectives.
Conversely, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) typically adapt industry standards to fit their capabilities. SMEs might follow a mold draft angle range of 0.5° to 1° for outer surfaces and 1° to 2.5° for inner surfaces, adjusting based on equipment capabilities2 and material fluidity. This flexibility allows them to maintain quality while optimizing resources.
The Role of Global Standards Organizations
Organizations like the ISO play a pivotal role in harmonizing standards internationally. However, sectors like technology or pharmaceuticals3 may have additional or differing guidelines due to rapid innovation cycles or regulatory requirements. Understanding how global standards interact with local regulations is vital for companies operating in multiple regions.
Implications of Industry Standards on Business Strategy
Adhering to industry standards not only ensures compliance but also affects a company’s strategic positioning. Firms that excel in meeting stringent standards can leverage this as a competitive advantage in markets where quality is paramount. Conversely, companies must also weigh the costs associated with stringent compliance against potential benefits such as brand reputation or market access. This balance is critical in sectors like electronics or aerospace4, where innovation must align with robust safety and quality criteria.
ISO recommends 0.5°-1.5° slope for outer plastic surfaces.True
The ISO standard suggests this slope for easier demolding.
VDA standard requires 2°-4° slope for automotive inner surfaces.True
This ensures high quality and precision in automotive parts.
What Role Do Enterprise Internal Standards Play in Mold Design?
Explore how enterprise internal standards shape the precision and efficiency of mold design processes.
Enterprise internal standards in mold design ensure consistency, quality, and compliance with industry norms. These standards guide the specific parameters for mold creation, including mold draft angles, which are crucial for efficient production and product quality.
The Intersection of Industry and Internal Standards
In the realm of mold design, enterprise internal standards are pivotal. They bridge the gap between broader industry standard norms5 and the unique demands of specific companies. For instance, the plastics industry adheres to ISO guidelines for mold draft angles. However, individual enterprises customize these standards based on their specific production needs.
Large enterprises might establish stringent standards due to their extensive production scales and diverse product lines. For example, a major home appliance company may mandate a minimum mold pull-out slope of 1° for outer surfaces to ensure product durability and aesthetic appeal. This customization allows them to maintain high quality while accommodating the complex internal structures6 inherent in advanced products.
Tailoring Standards for Competitive Advantage
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), on the other hand, often adapt these industry standards to fit their capabilities. They might set more flexible mold draft angles, such as 0.5° to 1° for outer surfaces, allowing them to remain agile and responsive to market demands.
The flexibility in internal standards allows SMEs to cater to niche markets where precision and customization are valued over mass production. For instance, by adapting their standards based on the plastic material fluidity7, they can optimize their production processes to meet specific customer requirements efficiently.
Impact on Quality Control and Efficiency
Internal standards significantly impact quality control measures within an enterprise. By establishing clear guidelines for mold design, companies can prevent defects and improve product consistency. This is especially crucial in industries like automotive, where precision is paramount.
For automotive injection molded parts, internal standards might dictate a mold draft angle of 2° – 4° for inner surfaces, aligning with VDA standards to prevent surface strain. This alignment not only enhances product quality but also streamlines the assembly process8 by reducing variability and defects.
Balancing Innovation with Standardization
While adherence to internal standards is essential, it’s equally important for companies to foster innovation. Standards should evolve with technological advancements and changing market needs. By reviewing and updating internal guidelines, enterprises can ensure they remain competitive while adhering to necessary quality benchmarks.
By balancing these aspects, companies can harness the full potential of their mold design processes, ensuring both innovation and compliance with industry expectations.
ISO recommends 0.5°-1.5° mold slope for outer surfaces.True
ISO standards suggest this range for general injection-molded plastic products.
VDA standards require 3°-5° slope for automotive interiors.False
VDA standards specify a 2°-4° slope for inner surfaces, not 3°-5°.
Why Is the Draft Angle Critical in Injection Molding Processes?
Understanding the draft angle is essential for optimizing injection molding, ensuring product quality and efficient production.
The pullout slope, or draft angle, is vital in injection molding as it facilitates easy removal of parts from molds, preventing damage and ensuring production efficiency. Industry standards recommend slopes between 0.5° to 3°, varying by material and part complexity.
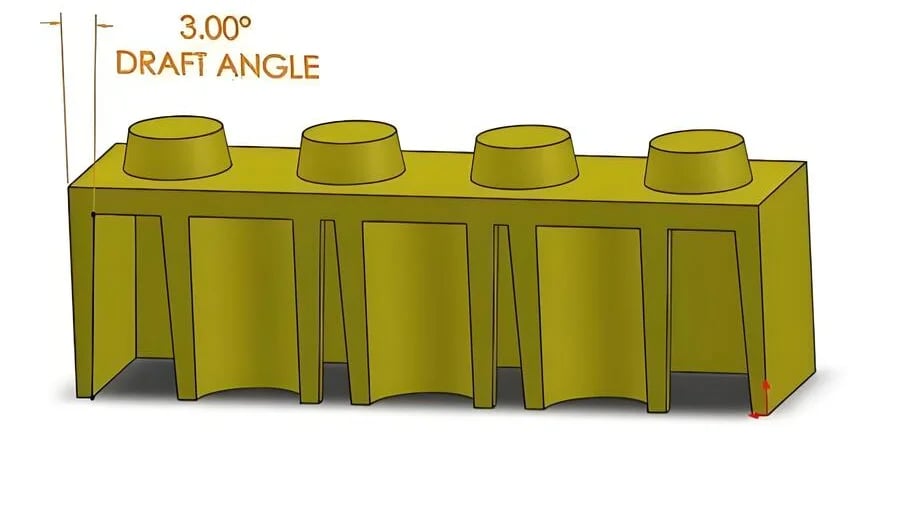
Importance of Draft Angle in Injection Molding
In injection molding, the pullout slope, also known as the draft angle, is crucial for ensuring that parts are smoothly ejected from the mold without causing damage. This angle allows the mold to separate from the part with minimal friction, reducing the chances of deformation or surface defects. The significance of the pullout slope becomes apparent when considering industry standards and internal specifications adopted by companies.
Industry Standards for Pullout Slope
Various industry standards set benchmarks for draft angles to ensure high-quality outcomes. For instance, the Plastics Industry9 standards suggest a draft angle of 0.5° to 1.5° for outer surfaces and 1° to 3° for inner surfaces in general injection-molded plastic products. These standards are crucial as they guide manufacturers in designing molds that ensure smooth demolding.
In the automotive sector, standards are even more stringent due to the demand for precision and quality. The German Federation of Automotive Industries (VDA) prescribes a 1° to 2° slope for outer surfaces and 2° to 4° for inner surfaces of automotive interior parts. This precision helps prevent surface strain10 and assembly issues, which are critical for maintaining product integrity.
Internal Specifications in Enterprises
Large enterprises often develop internal standards tailored to their specific product lines and manufacturing experiences. For example, a major home appliance company might require a minimum draft angle of 1° for outer surfaces of appliance shells, ensuring thorough reviews during mold design stages.
Smaller companies might adopt a more flexible approach, adapting industry standards to fit their equipment capabilities and production conditions. For instance, they might set the mold draft angle taper at 0.5° – 1° for outer surfaces and 1° – 2.5° for inner surfaces, adjusting based on factors like mold processing accuracy and plastic material fluidity11.
Key Considerations for Draft Angle Design
When designing molds, several factors must be considered to determine the appropriate draft angle:
- Material Type: Different plastics have unique flow characteristics, affecting the necessary draft angle.
- Part Complexity: More intricate designs may require greater draft angles to ensure easy release from molds.
- Production Scale: Large-scale production might necessitate stricter adherence to standards to maintain consistency.
These considerations highlight the necessity of understanding how draft angles impact mold design and overall production efficiency.
ISO standards require a 1°-3° slope for inner surfaces.True
ISO standards recommend a 1°-3° slope for inner surfaces to aid demolding.
Small factories set mold taper at 2°-3° for outer surfaces.False
Small factories typically set mold taper at 0.5°-1° for outer surfaces.
How Can Variations in Standards Affect Product Quality?
Exploring how differing standards can influence the quality and reliability of products across industries.
Variations in standards can significantly impact product quality by affecting consistency, performance, and reliability. In industries like plastics and automotive, standards define critical parameters such as mold slope angles, directly influencing the ease of manufacturing and final product attributes. Adhering to consistent standards ensures uniformity and high quality across products.

The Role of Industry Standard Norms
Industry standards are established to ensure products meet specific safety, reliability, and performance criteria. In the plastics industry12, for instance, standards dictate mold pull-out slopes to optimize demolding processes. The ISO standard suggests different slopes for inner and outer surfaces to cater to varying demolding difficulties. Similarly, the automotive sector has stringent requirements, such as those from the German Federation of Automotive Industries (VDA), ensuring interior parts not only fit but also maintain high aesthetic quality.
Standards impact product quality directly by providing a baseline that manufacturers must meet or exceed. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining customer trust and ensuring that parts from different production batches are interchangeable. Deviations from these norms can lead to inconsistencies that might affect product performance or even cause defects. Hence, strict adherence to industry norms is vital for maintaining product integrity.
Enterprise Internal Standard Specification
Beyond industry standards, many companies develop their own internal standards tailored to their specific production needs. Large enterprises often have robust guidelines based on their extensive experience with certain product types. For example, a home appliance company might have internal standards dictating minimum mold slopes to ensure product durability and appearance. These company-specific standards13 are crafted to align with unique product characteristics and operational capabilities.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may adapt broader industry standards to suit their particular equipment and materials. These adaptations are necessary to accommodate the nuances of their processes while still aiming to produce high-quality products. However, variations in these standards can pose challenges, especially when parts need to interface with components made under different specifications.
Implications of Standard Variations on Product Quality
When standards vary significantly across regions or companies, it can lead to challenges in product quality assurance. Inconsistencies in standards mean that similar products might not perform uniformly when produced by different manufacturers or even different facilities within the same organization. These variations can lead to issues such as product recalls14, increased waste due to defective parts, and higher costs associated with reworking components.
To mitigate these risks, companies often implement rigorous quality control measures and invest in training programs to ensure that all employees understand and adhere to the required standards. By doing so, they can ensure consistency and reliability in their products despite inherent variations in the standards they follow.
ISO standards set mold slope at 0.5°-1.5° outer surface.True
ISO recommends these slopes for easier demolding of plastic products.
VDA standards require 3° slope for outer automotive parts.False
VDA sets the slope for outer surfaces between 1°-2°, not 3°.
Conclusion
Injection mold draft angles, essential for demolding, vary by industry standards: ISO recommends 0.5°-1.5° for outer surfaces and VDA specifies 1°-2° for automotive parts.
-
Explore ISO standards for plastic mold designs to ensure compliance. ↩
-
Discover how SMEs adjust standards based on equipment limitations. ↩
-
Learn how technology industry standards adapt to regulatory needs. ↩
-
Understand compliance in electronics and aerospace for safety and innovation. ↩
-
Learn about ISO’s recommended standards for mold design slopes. ↩
-
Explore how complex designs influence appliance mold standards. ↩
-
Understand how fluidity affects mold design choices. ↩
-
Discover how precision in molds enhances assembly efficiency. ↩
-
Explore industry guidelines that ensure quality in molded products. ↩
-
Learn how proper slopes avoid defects and ensure smooth demolding. ↩
-
Understand material characteristics affecting draft angle requirements. ↩
-
Learn how mold slope angles affect plastic product quality. ↩
-
Discover how companies tailor standards to enhance product quality. ↩
-
Understand challenges posed by varied manufacturing standards. ↩