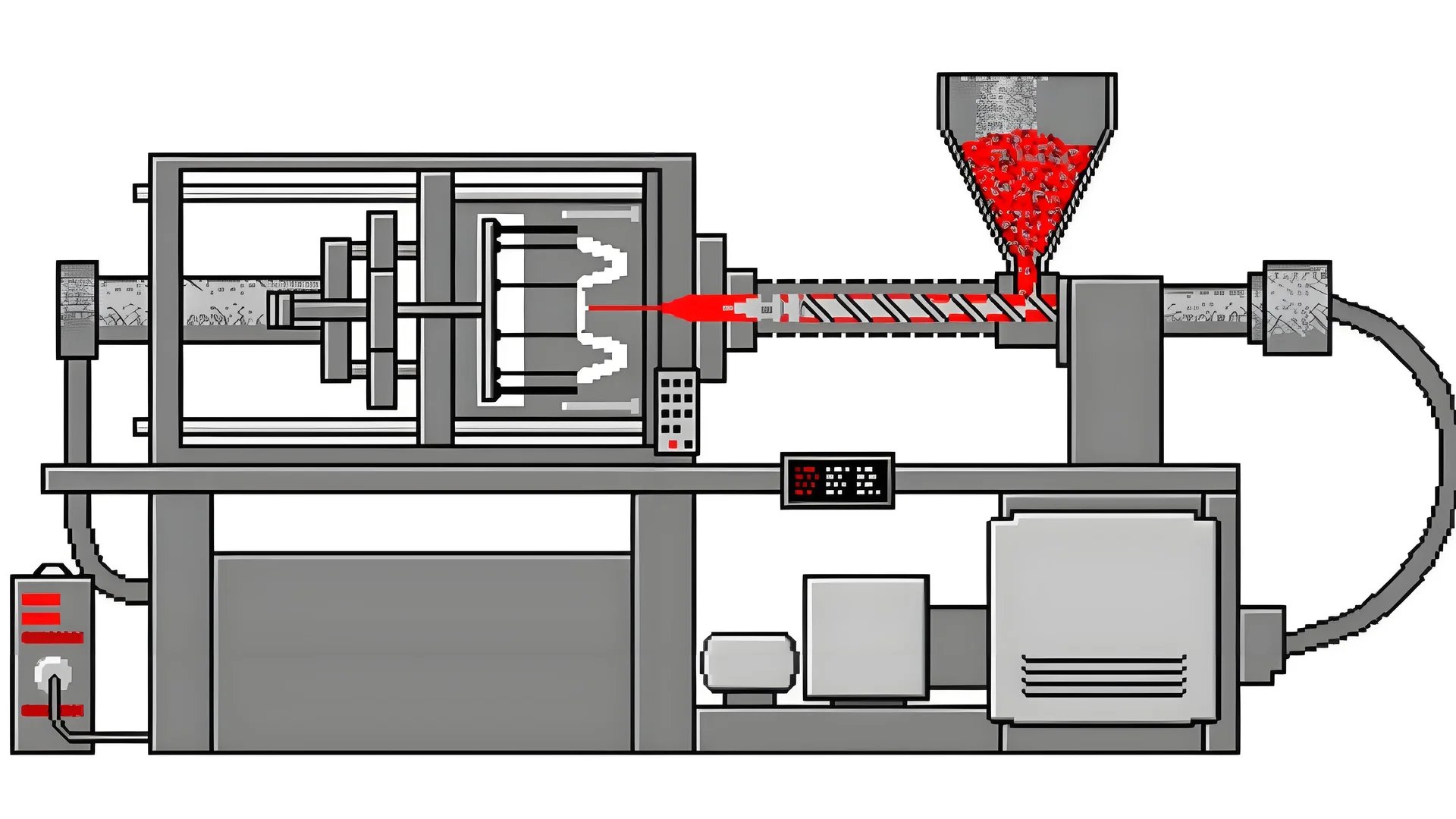
Picture shaping a wonderful creation from plastic – a task as careful as drawing a picture.
The ideal temperature for molding plastic varies with the type of plastic. Thermoplastics typically range from 180°C to 250°C, while thermosetting plastics require 200°C to 280°C. Factors like plastic type, mold material, and environment affect these settings.
You now possess a quick view of the temperatures required. Knowing the details of each element helps change your way of thinking about plastic molding. Let us travel further into the temperature world and observe how each detail may influence your work.
Thermoplastics mold at 180°C to 250°C.True
Thermoplastics soften under heat and become moldable at these temperatures.
- 1. How Do Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics Differ in Molding Temperature?
- 2. What Factors Influence the Optimal Temperature for Plastic Molding?
- 3. Why is Mold Material Important in Determining Molding Temperature?
- 4. How Does the Production Environment Affect Plastic Molding Temperatures?
- 5. Conclusion
How Do Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics Differ in Molding Temperature?
Knowing the differences in molding temperatures for thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics is very important for creating quality products quickly.
Thermoplastics are typically molded at 180°C to 250°C, whereas thermosetting plastics require higher temperatures, usually between 200°C and 280°C, to properly cure and set.

The Science Behind Molding Temperatures
Thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics have distinct properties that dictate their molding temperatures. Thermoplastics1 soften when heated and can be reshaped, making them versatile for various applications. Their molding temperatures generally fall between 180°C and 250°C due to their lower melting points. This temperature range allows thermoplastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) to be molded efficiently, ensuring high productivity without compromising the material’s integrity.
In contrast, thermosetting plastics undergo a chemical change when heated, forming a rigid structure that cannot be remolded. This process requires a higher temperature range of 200°C to 280°C to ensure complete curing. For instance, phenolic plastics and amino resins need these elevated temperatures to achieve their final hardened state.
| Plastic Type | Molding Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | 180°C – 250°C |
| Thermosetting Plastics | 200°C – 280°C |
Factors Influencing Molding Temperature
Several factors influence the optimal molding temperature for both types of plastics. These include:
- Material Properties: Each type of plastic has unique melting points and thermal stability levels.
- Mold Material: Molds made from materials with high thermal conductivity can transfer heat more effectively, enhancing productivity.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature and humidity in the production environment can affect how heat is managed during the molding process.
Practical Applications
Knowing the right molding temperature for each plastic type is essential in manufacturing settings. For example, Polystyrene2 used in household items benefits from a moderate mold temperature of 40℃ – 70℃, balancing cooling speed and surface finish.
Conversely, high-viscosity plastics like polycarbonate (PC) require higher mold temperatures to ensure reduced internal stress and improved dimensional accuracy. Adjusting the mold temperature based on these requirements ensures the production of high-quality plastic parts.
By understanding these critical differences in temperature requirements, manufacturers can optimize their processes, leading to efficient production cycles and superior product quality.
Thermoplastics mold at 180°C to 250°C.True
Thermoplastics form shapes at this temperature range because they have lower melting points.
Thermosetting plastics can be remolded after curing.False
After hardening, thermosetting plastics develop a firm shape that cannot be altered.
What Factors Influence the Optimal Temperature for Plastic Molding?
Heat holds a vital role in the quality of molded plastic items. Comprehending elements that affect it is important.
The optimal temperature for plastic molding is influenced by the type of plastic, mold material, and production environment. Thermoplastics generally range from 180°C to 250°C, while thermosetting plastics need 200°C to 280°C. Factors such as mold design and environmental conditions also play a crucial role in determining the ideal temperature.

Understanding Plastic Types and Characteristics
Different types of plastics have distinct properties that significantly influence their molding temperatures. For example, thermoplastics like polyethylene and polypropylene typically require lower temperatures, between 180°C and 250°C. This is due to their lower melting points and thermal stability. In contrast, thermosetting plastics, such as polycarbonate and phenolic plastics, demand higher temperatures ranging from 200°C to 280°C for proper curing and hardening.
| Plastic Type | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | 180°C – 250°C |
| Thermosetting | 200°C – 280°C |
Moreover, the choice of specific plastic3 affects the molding temperature due to its unique characteristics, including viscosity and crystallinity. For instance, high-viscosity plastics like polycarbonate require higher temperatures to ensure adequate fluidity and reduce internal stress.
The Role of Mold Material and Structure
The material and structure of the mold are pivotal in determining the optimal temperature for molding. Molds made from materials with excellent thermal conductivity can transfer heat more efficiently, thereby increasing productivity. Additionally, the structure of the mold impacts its resistance to high temperatures; larger molds may require a reinforced design to prevent deformation.
Examining mold materials4 shows that metals like aluminum or steel are commonly used due to their superior heat resistance and durability, ensuring consistent mold quality across various temperatures.
Impact of the Production Environment
The environment in which plastic molding occurs can also affect optimal temperature settings. High ambient temperatures or humidity levels may limit the working temperature range of molds. For instance, excessive humidity might lead to condensation on the mold surface, affecting the quality of the final product.
Therefore, controlling environmental variables is essential for maintaining optimal molding conditions and achieving the desired product quality.
Balancing Part Quality with Productivity
In practical applications, finding the right balance between part quality and productivity is crucial. Lower mold temperatures can speed up cooling rates, thereby enhancing productivity but potentially compromising surface quality. On the other hand, higher temperatures can improve surface finish and dimensional stability but might slow down production rates.
A comprehensive analysis5 of these factors enables manufacturers to fine-tune temperature settings to achieve an optimal balance, thus ensuring high-quality outputs without sacrificing efficiency.
Thermoplastics require 200°C to 250°C for molding.False
Thermoplastics require 180°C to 250°C because they possess lower melting temperatures.
Mold material affects the optimal temperature for molding.True
Materials with high thermal conductivity efficiently move heat.
Why is Mold Material Important in Determining Molding Temperature?
Mold material selection greatly affects the temperature necessary for successful plastic shaping. This alters product quality and production speed.
Mold material determines the heat transfer rate and structural stability at high temperatures. Materials with high thermal conductivity reduce cycle time and enhance productivity, whereas poor choices may lead to deformation and defects.
The Role of Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is an important feature of mold materials that influences temperature during molding. Copper alloys and aluminum allow quick heat movement, which shortens cycle times. This really increases productivity and part quality by keeping the temperature even across the mold.
On the other hand, materials like stainless steel with low conductivity need more time to cool, which lowers efficiency. Still, they often give more strength and resist rust, so they are good for some uses despite possible longer cycles.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Alloys | 200-400 | High conductivity, strong |
| Aluminum | 150-250 | Lightweight, medium strength |
| Stainless Steel | 15-25 | Rust-resistant, durable |
Impact on Structural Integrity
Mold materials need to handle heat pressure without bending. Materials with high heat resistance keep their shape when hot. Beryllium copper molds have great thermal conductivity and strength, fitting for big or complex designs that might expand with heat.
Weaker materials could bend or break under frequent heating and cooling, causing faults in the molded pieces.
Considerations for Choosing Mold Material
When picking mold materials, think about:
- The plastic type used: Different plastics need different heat levels (plastic heat requirements6).
- Mold design: Complicated shapes might need stronger materials to stop bending.
- Cost: High-quality materials like beryllium copper cost more but might save money over time by being more efficient and lowering mistakes.
The choice of mold material balances cost, efficiency, and quality. Knowing these factors may lead to better decisions and outcomes in plastic molding.
Copper alloys reduce cycle time due to high conductivity.True
Copper alloys possess high thermal conductivity, improving heat movement.
Stainless steel molds require shorter cooling times than aluminum.False
Stainless steel conducts heat less efficiently than aluminum, requiring extra time to cool down.
How Does the Production Environment Affect Plastic Molding Temperatures?
The place where plastic molding happens probably affects the temperatures needed for good results. Elements such as room temperature and moisture very much change the material’s qualities and influence production results.
Production environment factors, such as temperature and humidity, directly influence plastic molding temperatures by affecting material behavior and mold performance. Managing these conditions ensures precision and quality in molded products.

The Role of Ambient Temperature
The ambient temperature of a production facility can alter the thermal dynamics within the molding process. High ambient temperatures may lead to increased mold temperatures, potentially causing material degradation or deformation of the finished product. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures can slow down the cycle time, affecting productivity. This necessitates precise control of the environmental conditions to maintain the desired mold temperature range7.
Impact of Humidity
Humidity levels in a molding environment can also play a critical role. High humidity may lead to condensation on the mold surfaces, impacting material flow and resulting in defects like blistering or voids. On the other hand, extremely low humidity might cause static build-up, attracting dust and contaminants that can affect surface finish quality. Therefore, maintaining an optimal humidity level is essential for achieving consistent results8.
Production Environment Control Strategies
To address these environmental factors, many facilities implement climate control systems. These systems help in maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels, thus reducing variability in the molding process. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems can provide feedback for adjustments, ensuring that the environmental conditions remain stable9. Some advanced setups even incorporate automated adjustments to respond to any detected changes promptly.
Case Study: Real-World Application
A manufacturing plant producing polypropylene components observed defects during high summer temperatures. By installing a climate-controlled enclosure around their molding machines, they managed to stabilize mold temperatures and reduce defects significantly, showcasing the importance of environment management in molding10.
High ambient temperatures increase mold temperature.True
Warmer air heats the mold more, changing how the material behaves.
Low humidity prevents condensation on mold surfaces.True
Less moisture in the air lowers the chance of water droplets forming and problems occurring.
Conclusion
Learning about molding temperatures raises quality and efficiency. Use these ideas to improve your plastic processing.
-
Discover the fundamental differences between thermoplastics and thermosets.: In a nutshell, thermosets generally have greater physical properties than thermoplastics; however they cannot be remoulded and recycled. ↩
-
Learn the specific temperature settings for molding polystyrene efficiently.: The melting temperature of the product is 150~180℃, the thermal decomposition temperature is 300℃, the thermal deformation temperature is 70~100 … ↩
-
Understand specific plastic characteristics affecting molding temperatures.: Plastic Material Melt and Mold Temperatures Table ; POLYCARBONATE, 280-320 ; POLYESTER PBT, 240-275 ; PET (SEMI-CRYSTALLINE), 260-280 ; PET (AMORPHOUS), 260-280. ↩
-
Discover materials that enhance mold efficiency and temperature stability.: Polyethylene is the most commonly used plastic in the world and is a commercial polymer that can be selected according to its density. High-density polyethylene … ↩
-
Explore strategies for optimizing both product quality and production speed.: The key to increasing productivity lies in getting more good parts using the machines, the materials and the people you have available to you. ↩
-
Learn how different plastics influence mold material selection.: Properties such as melting point, shrinkage rate, and moldability of the chosen plastic should all be taken into consideration when selecting … ↩
-
Learn how ambient temperature alters mold performance and material behavior.: Good Answer: From years of experience, the ambient temperature has very little to do with finished product size from the moulding process. ↩
-
Discover how humidity levels influence material flow and product quality.: More humid areas will absorb more moisture. Colder areas may cause barrels to be lest efficient, or if someone leaves a door open you might have … ↩
-
Explore strategies for managing production environment conditions effectively.: Ambient room temperature matters only to the extent of the bulk expansion coefficient for the plastics involved, and also has an effect on the … ↩
-
Understand real-world applications of environment control in reducing defects.: This paper studies the environmental impact of the injection molding process by carrying out a life cycle assessment. ↩






