Picture producing items that are not only long-lasting but also adaptable – high-density polyethylene (HDPE) accomplishes exactly that!
HDPE is highly suitable for injection molding due to its excellent chemical resistance, strength, and cost-effectiveness. The process involves melting HDPE at 180°C-230°C, injecting it into a mold, and allowing it to cool, forming durable products.
This offers a quick look, but exploring deeper into the material’s traits, details of the molding process and its pros and cons probably helps you gain understanding to choose wisely in your production efforts.
HDPE is more flexible than polypropylene (PP).True
HDPE supplies more flexibility than PP, so it suits items requiring toughness and elasticity.
What Are the Advantages of Using HDPE in Injection Molding?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) remains popular in injection molding by virtue of its special features. Why is it so beneficial?
HDPE is advantageous for injection molding because of its excellent chemical resistance, high strength, low cost, and versatile processing capabilities. It is an opaque, durable material that performs well under various environmental conditions.

Chemical and Environmental Resistance
HDPE defends against many chemicals. It resists acids, bases, and solvents, showing strong stability. When harsh chemicals are present, HDPE stays reliable, giving it an edge over weaker materials.
Physical Qualities and Toughness
HDPE‘s toughness stands as a reason for its use in shaping by injection. It has more surface hardness and strength than low-density polyethylene (LDPE). It holds up well when hit or pressed. Items from HDPE keep their shape and stay firm over time.
Budget-Friendly and Flexible Use
HDPE appeals with its low price1. Its affordable nature does not lower its quality, making it good for large-scale output. This material adapts to different shaping ways like injection and blow molding, letting creators make various items from one material.
| Quality | Detail |
|---|---|
| Density | Higher than LDPE, adds to strength and long-lasting nature |
| Melting Point | 142°C, fitting for uses needing heat endurance |
| Process Temperature | 180°C-230°C, allows varied working conditions |
Downsides to Consider
HDPE has some downsides despite its many strengths. It lacks in strength compared to materials like polypropylene (PP), which might limit its use in very tough situations. HDPE ages and cracks under stress, especially without extras like stabilizers.
Environmentally Friendly Benefits
HDPE is non-toxic and lacks smell, posing fewer risks than materials like PVC. The ability to recycle it helps environmentally-friendly practices. Using HDPE can support companies aiming to lower their environmental impact.
HDPE offers excellent chemical resistance.True
HDPE resists acids, alkalis and solvents, providing stability.
HDPE is more costly than other plastics.False
HDPE is recognized for its low material price, increasing affordability.
How Does HDPE Compare to Other Materials Like LDPE and PP?
Deciding among HDPE, LDPE and PP might be difficult because they have different characteristics. Here is why HDPE is unique.
HDPE offers greater strength and rigidity than LDPE, with superior chemical resistance. It is more flexible than PP, though slightly less heat resistant. Its non-toxic nature makes it environmentally friendlier than some alternatives.

Material Properties Comparison
When selecting a plastic material for a project, understanding the nuanced differences between HDPE, LDPE, and PP is crucial.
-
Density and Strength: HDPE, known for its high density ranging from 0.941 to 0.960, provides greater strength and rigidity compared to LDPE2. This is particularly beneficial in applications requiring robust performance under stress.
-
Chemical Resistance: HDPE shines with its excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It maintains integrity in various chemical environments better than both LDPE and PP, making it ideal for packaging and piping systems.
-
Flexibility vs. Rigidity: While HDPE is tougher than LDPE, it also boasts greater flexibility than PP. This balance makes HDPE suitable for products needing both durability and flexibility, such as agricultural films3 and irrigation pipes.
-
Heat Resistance: Though HDPE offers good heat resistance, it slightly falls behind PP. PP‘s superior thermal properties make it a better choice for applications requiring exposure to higher temperatures.
Environmental Impact
HDPE is non-toxic and odourless, offering a more environmentally friendly profile than materials like PVC. Its ability to be recycled adds to its sustainability appeal, positioning it favorably against alternatives in eco-conscious industries.
Use Cases and Cost Efficiency
-
Applications: HDPE is utilized in manufacturing plastic bottles, geomembranes, and corrosion-resistant piping due to its advantageous properties. Its versatility extends to various sectors like packaging and construction.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Despite its higher density, HDPE remains cost-effective due to its longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs. This makes it a practical choice for many industrial applications.
For a clearer understanding of where each material excels, consider this table summarizing the key features:
| Property | HDPE | LDPE | PP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | High | Low | Medium |
| Strength | High | Low | Medium |
| Flexibility | Medium | High | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate | Low | High |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, recyclable | Recyclable | Recyclable |
In conclusion, while HDPE offers several advantages over LDPE and PP in terms of strength and chemical resistance, its choice should be guided by specific project requirements like heat tolerance4 and flexibility needs.
HDPE has greater chemical resistance than PP.True
HDPE resists acids, alkalis and solvents more effectively than PP.
PP is more flexible than HDPE.False
HDPE bends more easily than PP, allowing it to be used for many purposes.
What Are the Common Applications of HDPE Products?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) offers many uses in different sectors due to its special qualities.
HDPE is commonly used in packaging, pipes, and agricultural applications due to its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness.

Packaging Industry
One of the most prominent applications of HDPE is in the packaging industry5. HDPE‘s high strength-to-density ratio makes it ideal for creating robust and lightweight packaging materials. It is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic packaging. For instance, HDPE bottles are commonly found in households for storing milk, detergents, and shampoos.
Pipeline Industry
HDPE‘s resistance to chemicals and low moisture absorption make it suitable for the pipeline industry6. It is extensively used in manufacturing water supply pipes and gas pipelines. HDPE pipes are preferred due to their corrosion resistance and ability to withstand environmental stress.
Plastic Products
The plastic products industry7 benefits significantly from HDPE‘s versatility. It is used to produce bins, plastic boxes, and pallets that are durable and lightweight. These products are essential in various sectors, including logistics and storage.
Agricultural Field
In agriculture, HDPE is employed for making agricultural films8, irrigation pipes, and greenhouse coverings. Its toughness and weather resistance make it ideal for protecting crops and facilitating efficient irrigation systems.
Comparison with Other Materials
Compared to other materials like LDPE and PP, HDPE offers a unique combination of properties that make it highly desirable. While LDPE might provide better flexibility, HDPE excels in strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
HDPE is used in making milk bottles.True
HDPE's strength and toughness render it perfect for milk bottle creation.
HDPE pipes are unsuitable for gas pipelines.False
HDPE resists chemicals. It suits gas pipelines well.
How Should Molds Be Designed for Optimal HDPE Injection Molding?
Creating molds for HDPE needs careful planning and skill to achieve quality and efficiency in creating products.
Optimal mold design for HDPE injection molding involves careful planning of cooling systems, glue inlets, and ejection methods to prevent defects and ensure uniformity. Proper material selection and maintenance of mold temperature are crucial for achieving high-quality outcomes.
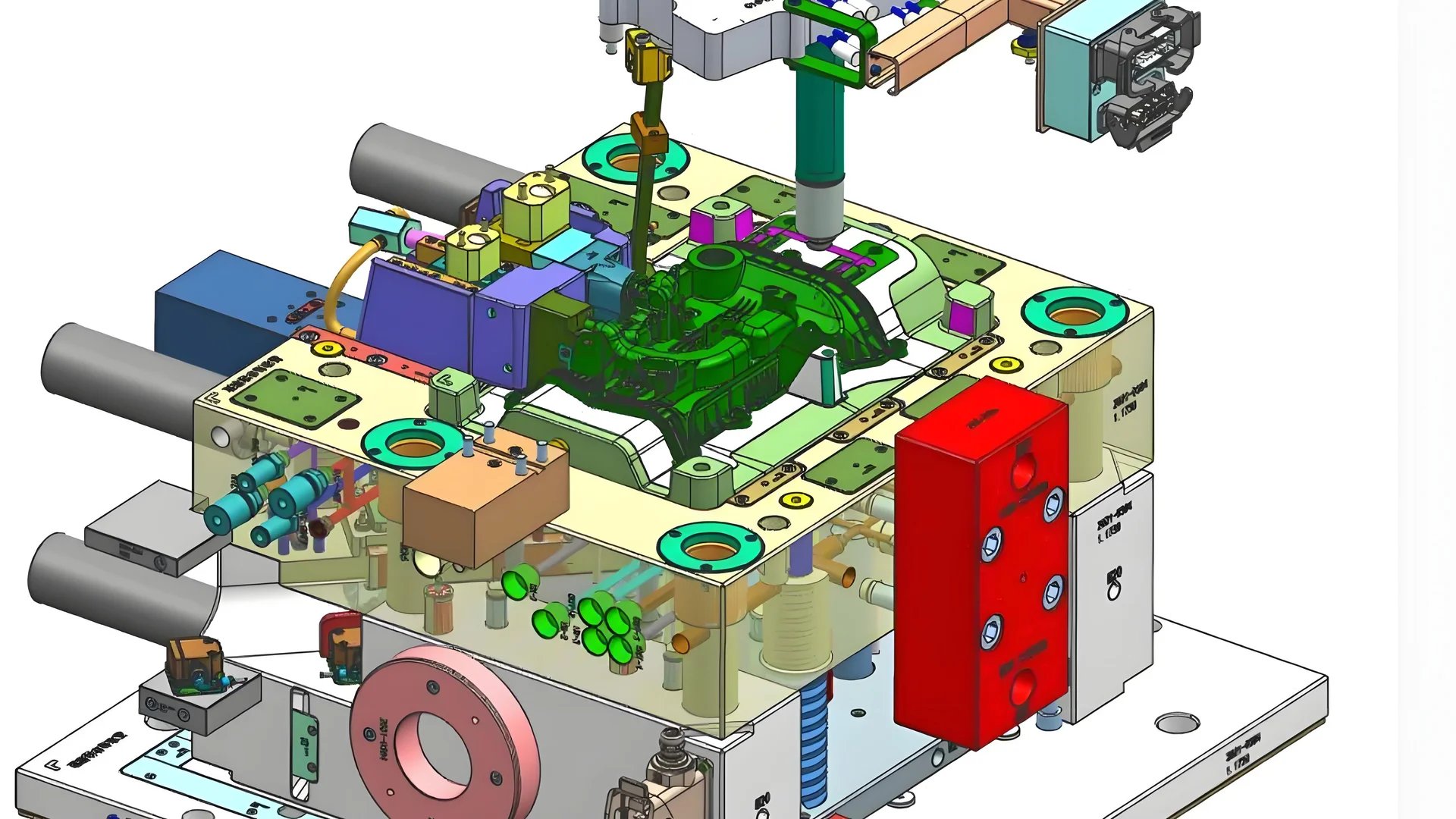
Understanding HDPE Properties
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is known for its robustness and versatility in injection molding applications. It is a lightweight, opaque white waxy material with a specific gravity ranging from 0.941 to 0.960. Notably tougher than LDPE, HDPE exhibits excellent chemical resistance, can withstand acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, and retains its toughness even at low temperatures. These characteristics make it highly sought-after in manufacturing a wide range of products.
Mould Material Selection
Selecting the right mold material is paramount to achieving optimal results in HDPE injection molding. Commonly used materials include P20 and 718H, known for their wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and superior processing performance. These materials meet the demanding requirements of HDPE injection molding, ensuring durability and longevity of the molds.
Cooling System Design
The design of the cooling system is a critical factor in mold design for HDPE. Cooling channels must be strategically placed to maintain uniform temperature across the mold, thereby improving product quality and reducing cycle time. The diameter and spacing of these channels should be customized based on the mold’s size and shape, keeping them at a safe distance from the mold’s surface to preserve its strength and lifespan.
Glue Inlet Design
Proper glue inlet design is essential to avoid common defects like flow marks and bubbles. The position of the glue inlet should be tailored according to the product’s size and shape to ensure even plastic distribution within the mold. Additionally, the size of the inlet must align with both the specifications of the injection molding machine and product requirements.
Ejector Mechanism Design
A well-designed ejector mechanism is vital for smooth demolding. The number and placement of ejectors should be strategically planned according to the product’s shape and dimensions to prevent defects like top white and top crack. Ensuring that products are ejected smoothly enhances efficiency and reduces production time.
Preparation and Material Handling
Prior to injection molding, HDPE materials should be properly prepared. Selecting high-quality HDPE materials is essential; they should be dried to remove moisture, typically at 80-90°C for 2-4 hours, achieving a moisture content below 0.05%. Proper storage in a dry, ventilated area also helps maintain material quality.
Ensuring a comprehensive understanding of HDPE properties9, along with strategic mold design and preparation techniques, can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of HDPE injection molding processes.
HDPE is tougher than LDPE in injection molding.True
HDPE shows greater toughness compared to LDPE, increasing strength.
Cooling channels should be close to the mold surface.False
Channels need safe distance to keep mold strong and lasting.
Conclusion
HDPE offers a strong balance of sturdiness, resistance to chemicals and low cost, making it a very good option for many injection molding uses. Think carefully about its qualities and process needs to fully utilize it in your projects.
-
Discover why HDPE offers economic advantages in production.: HDPE, the option of the future, the mere presence of HDPE as an option brings down project costs, thus enabling better control of costs. ↩
-
Understand the differences in density and strength between these materials.: HDPE has higher abrasion and tear resistance than LDPE, along with higher tensile and shear strength. If you’re going to bury your cables … ↩
-
Explore how HDPE’s flexibility benefits agricultural uses.: HDPE is a common material for irrigation pipes because of its high resistance to corrosion and exceptional weather tolerance. ↩
-
Learn why PP may be preferable for high-temperature applications.: Polypropylene and HDPE have overlapping uses. However, HDPE is generally more flexible, while polypropylene has better resistance to elevated temperatures. ↩
-
Explore how HDPE is used in diverse packaging solutions.: HDPE use is expected to rise in industries where hygiene and sanitation is becoming critical such as consumer packaged goods and home and personal care. ↩
-
Discover why HDPE is favored for pipeline manufacturing.: Learn why WL Plastics works with HDPE pipes. Between cost savings, its durability, corrosion resistance and flexibility – it’s well worth it. Learn more. ↩
-
Learn about HDPE’s role in producing durable plastic items.: HDPE is made under controlled conditions by applying intense heat to petroleum. This process, also known as “cracking,” helps create ethylene gas. ↩
-
Find out how HDPE supports agricultural innovation.: HDPE is a common material for irrigation pipes because of its high resistance to corrosion and exceptional weather tolerance. ↩
-
Explore detailed HDPE properties crucial for injection molding.: In general, HDPE provides excellent stiffness and is highly warp resistant. HDPE is typically lower in cost and has great chemical and impact resistance. Marlex … ↩