Do you ever think about how everyday plastic items are formed? Let’s go on a journey to see the fascinating process of plastic creation!
Plastic products are manufactured through a detailed process involving product design, material selection, mold creation, and molding techniques like injection and extrusion molding, ensuring the final product meets performance and aesthetic standards.
As I explore the complex world of plastic production, I remember the moment when I watched a plastic bottle transform from raw materials to a finished item. The process involves more than just melting and shaping. It requires creativity, precision and maybe a touch of magic. Each stage, from designing the item to choosing the right materials and molding methods, has a crucial function. These steps help the final product to look attractive and work well. The process definitely resembles an art form!
Plastic manufacturing involves multiple detailed steps.True
The process includes design, material selection, mold creation, and molding techniques.
Injection molding is the only technique used in plastic production.False
While injection molding is common, other techniques like extrusion are also used.
- 1. What are the key stages in plastic product design?
- 2. How do I choose the right plastic materials?
- 3. What factors influence mold design and manufacturing?
- 4. What are the differences between injection molding and extrusion molding?
- 5. What does quality control look like in plastic manufacturing?
- 6. What advancements are shaping the future of plastic production?
- 7. Conclusion
What are the key stages in plastic product design?
Have you ever thought about how those everyday plastic products are created? Let’s explore the amazing world of plastic product design. We will discover the important steps that bring these items into existence.
Key stages in plastic product design include defining the product, selecting materials, designing molds, processing with molding techniques, applying finishes, and conducting thorough quality inspections.
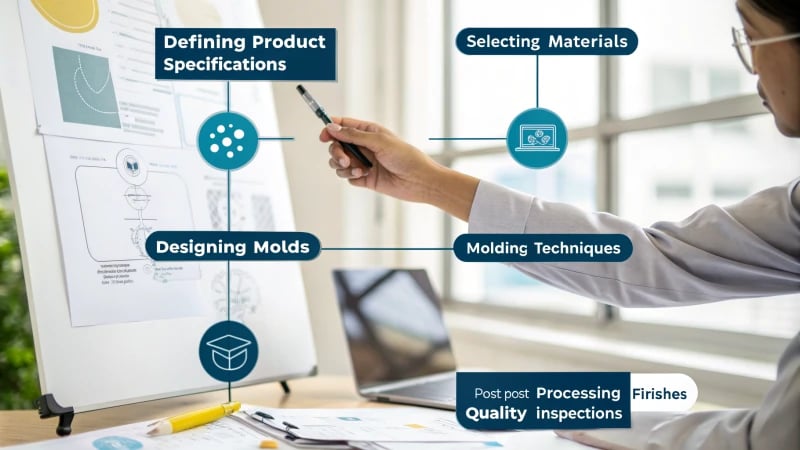
Understanding Key Stages in Plastic Product Design
My journey in product design taught me that crafting plastic products is like telling a story with materials. Each stage in the design process shapes the final narrative. We must create items that function well and connect with users. Let’s explore these steps together:
-
Product Design
The core of every great product is its design. I remember my first project on food packaging. Understanding how the container performs was crucial, especially for sealing and hygiene.- Determine Product Functions and Specifications:
I delved into market demands. What do consumers need? When designing containers, I thought about how they would hold various foods and withstand heat. - Design Product Shape and Structure:
I used CAD software to model my ideas in 3D. Balancing aesthetics and practicality was both exciting and challenging. Avoiding complicated structures often made the molding process easier, especially for plastic toys.
- Determine Product Functions and Specifications:
-
Select Plastic Materials
Choosing the right materials is like picking the right characters for a story. They are critical to success.- Consider Product Performance Requirements:
Nylon is excellent for strength. Plexiglass is ideal when transparency matters. Each choice demands careful thought to meet functional needs. - Consider Processing Performance and Cost:
It’s a balancing act! Polyethylene is affordable but high-performance plastics are sometimes necessary despite their cost.
- Consider Product Performance Requirements:
-
Mold Design and Manufacturing
This stage feels like sculpting a masterpiece.- Mold Design:
I remember sketching molds with attention to cooling systems and ejector mechanisms. Precision in mold design affects final product quality. - Mold Manufacturing:
Watching CNC machines in action during mold production was amazing! Dimensional accuracy and surface quality are vital for flawless results.
- Mold Design:
-
Plastic Molding Processing
Shaping raw materials into real products is exciting:- Injection Molding:
I witnessed the transformation of raw materials into finished products – they turned beautiful under pressure. - Extrusion Molding:
Watching molten plastic form continuous profiles or sheets was fascinating. It created everyday items like pipes and films.
- Injection Molding:
-
Post-Processing
Finishing touches can make products great:- Removal of Flash and Gate Marks:
Trimming excess material felt like a final polish before releasing products to the world. - Surface Treatment:
Experimenting with treatments elevated aesthetics and functionality. Painting vehicle parts to match interiors was particularly satisfying! - Assembly and Packaging:
Combining components into a complete product felt rewarding. It was the last step before packaging for delivery.
- Removal of Flash and Gate Marks:
-
Quality Inspection and Control
The last stage verifies the quality of our efforts:- Appearance Inspection:
Careful examination for defects is nerve-racking yet crucial. - Dimensional Accuracy Inspection:
Measuring dimensions with calipers confirms we meet perfection. - Performance Test:
Testing strength and durability reassures me of the product’s reliability.
- Appearance Inspection:
If you want to explore more about plastic product design, think about examining advanced techniques1 or material selection criteria Each stage plays a big role in creating products that meet market needs and last over time.
Plastic product design starts with defining specifications.True
The initial stage of plastic product design is crucial for establishing the product's purpose and specifications based on market demands.
Injection molding is the only method for shaping plastics.False
While injection molding is a common technique, other methods like extrusion molding are also used in plastic processing.
How do I choose the right plastic materials?
Exploring plastic materials often feels daunting. Success depends on choosing the right plastic. Here is my journey with valuable insights. These insights really help in choosing wisely.
Choose the right plastic materials by evaluating product specifications, performance, processing behavior, and costs. Design suitable molds and conduct thorough quality control for optimal material selection.
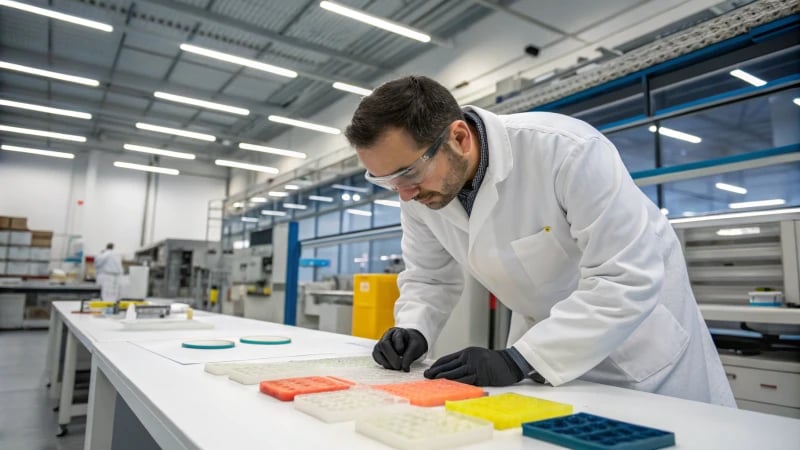

Understanding Product Functions and Specifications
Choosing the correct plastic materials goes beyond a technical choice. It involves knowing your product’s essence and the practical needs it involves. I recall my first project needing unique plastic for food packaging. It wasn’t only about picking a material. Safety and functionality were essential, and it had to satisfy customers. This experience confirmed the value of this process in my mind.
Selecting Appropriate Plastic Materials
Once you have clarity on product requirements, the next step is to select suitable plastic materials. You should assess both the performance requirements and processing characteristics of the plastics available.
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polyamide (PA) | High strength, wear resistance | Automotive parts, industrial components |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Cost-effective, versatile | Packaging, automotive interiors |
| Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | High transparency | Optical lenses, signage |
For instance, if your application requires higher strength and wear resistance, polyamide may be the right choice. Alternatively, for applications requiring high transparency, PMMA would be more suitable.
Consideration of Processing Performance and Cost
Processing performance and cost are crucial factors in material selection. Different plastics come with varying processing properties such as fluidity and shrinkage. While general plastics like polyethylene (PE) are cost-effective, specialized materials may incur higher costs. The goal is to meet performance requirements while keeping costs manageable. Therefore, it is advisable to evaluate various materials based on their processing characteristics and overall cost-effectiveness.
Mold Design Considerations
The design of the mold is intrinsically linked to the type of plastic used. It involves several key aspects:
- Shape and size of the product: Must align with material characteristics.
- Cooling system design: Essential for large products to ensure uniform cooling.
For instance, a well-designed cooling system can prevent defects due to uneven cooling rates which could affect product quality. This requires careful consideration during the design phase.
The Molding Process
Understanding the molding processes can also guide your material choice. Common methods include:
- Injection Molding: Used for producing complex shapes with high precision.
- Extrusion Molding: Ideal for continuous profiles like pipes or sheets.
Each method has specific material requirements that need to be adhered to ensure successful production.
Post-Processing Techniques
After molding, certain post-processing techniques may be required:
- Flash Removal: Trimming any excess material from edges.
- Surface Treatment: Enhancing appearance through painting or electroplating.
These steps can affect the final properties of the product and should be factored into the initial material selection process.
Quality Inspection and Control
Finally, rigorous quality inspection is necessary to ensure that the final product meets all specifications. This includes:
- Appearance Inspection: Check for defects like scratches or bubbles.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Use tools like calipers to measure key dimensions.
- Performance Testing: Conduct tests based on functional requirements.
By incorporating these quality control measures, you can ensure that the selected plastic materials perform as intended under real-world conditions.
Understanding product specifications is essential for material choice.True
Identifying performance indicators like strength and heat resistance is crucial in selecting the right plastic materials for specific applications.
Post-processing techniques do not affect final product quality.False
Post-processing steps such as flash removal and surface treatment significantly influence the final properties and quality of molded products.
What factors influence mold design and manufacturing?
Have you ever thought about what happens in the art and science of designing and creating molds? This journey is really fascinating. It combines creativity and exactness. Let’s explore the important factors that form this world.
Mold design and manufacturing are influenced by product design, material choice, mold structure, processing methods, post-processing steps, and quality control, all crucial for efficient and high-quality production.
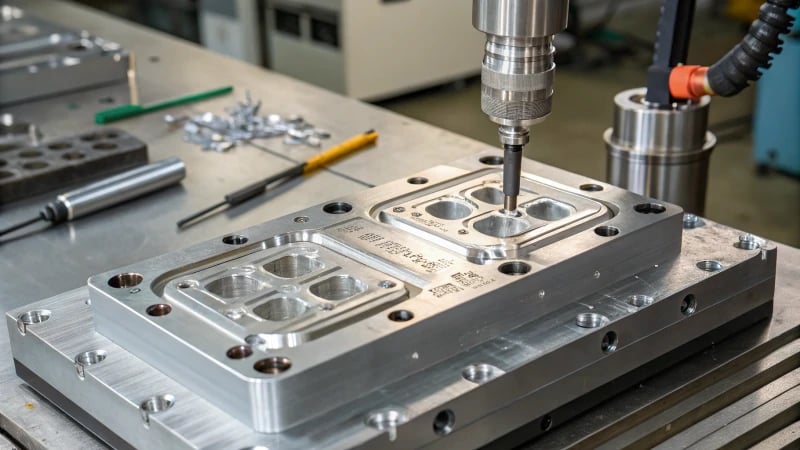

Product Design
Product design is very important in mold manufacturing. It guides how the mold is crafted based on what the product needs. For instance, when designing plastic containers for food packaging, it’s crucial to consider sealing and hygiene standards. Meeting market demands is essential.
Additionally, using CAD software2 to create product shapes in 3D helped me a lot. It was like a game changer. I learned early on to avoid complex shapes that complicate the process. Managing wall thickness was another important lesson. Too thick creates uneven shrinkage, while too thin affects durability.
Material Selection
Choosing the right material sometimes feels overwhelming. Picking the right plastic is crucial for the product’s performance. If I wanted a strong product, polyamide (PA) was the go-to choice. For clear items, like plastic lenses, polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) was perfect.
| Performance Requirement | Recommended Material |
|---|---|
| High strength | Polyamide (PA) |
| High transparency | Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) |
Balancing performance with cost is also very important. At first, I picked high-performance plastics without considering the budget. Now, I try to find materials that meet performance needs while being cost-effective. It’s about finding a perfect balance.
Mold Design and Manufacturing
Mold structure is vital since it determines how the product forms. Details like cavity shapes and gate locations impact the manufacturing process. Large products require efficient cooling systems to guarantee uniform cooling.
Manufacturing uses precise methods like CNC machining and EDM processes. Initially, I underestimated these mechanical techniques. Now, I understand that maintaining dimensional accuracy is essential for high-quality results.
Plastic Molding Processing
Knowing the plastic molding process is really important. I remember my first experience with injection molding:
- Feeding: Plastic granules enter the machine’s barrel.
- Plasticization: Heat turns granules into a molten form.
- Injection: Watching molten plastic enter molds was mesmerizing.
- Pressure Holding: This step compensates for shrinkage.
- Cooling: Allowing plastic to solidify created great anticipation.
- Mold Opening and Ejection: Seeing the final product emerge was very rewarding.
For extrusion processes, stages like these happen, focusing on forming continuous profiles or sheets which adds extra complexity.
Post-Processing Steps
After forming products, post-processing comes in. My early years involved lots of trimming excess material; it’s a tedious but essential task for a polished look.
Surface treatments like painting or electroplating became my favorite as they transformed simple plastic items into visually stunning pieces. Assembly and packaging reminded me to protect creations during their journey to customers.
Quality Inspection and Control
Finally, quality inspection feels like the finishing touch before products go out; checking for defects and ensuring dimensional precision is now second nature for me! Performance testing showed me that designs met all functional criteria.
Product design specifications impact mold manufacturing.True
The specifications guide the mold's structure and function, ensuring products meet market demands and performance requirements.
Material selection does not affect mold design efficiency.False
Choosing the right material is crucial as it influences performance, cost, and overall manufacturing efficiency in mold design.
What are the differences between injection molding and extrusion molding?
Have you ever been in a discussion about the details of manufacturing methods? I have! Let’s explore the interesting world of injection molding and extrusion molding. Every detail holds importance. These details probably shape the final look of your designs.
Injection molding creates complex shapes using a mold, while extrusion molding forms continuous profiles. Each method has unique benefits, drawbacks, and cost implications influencing product design decisions.
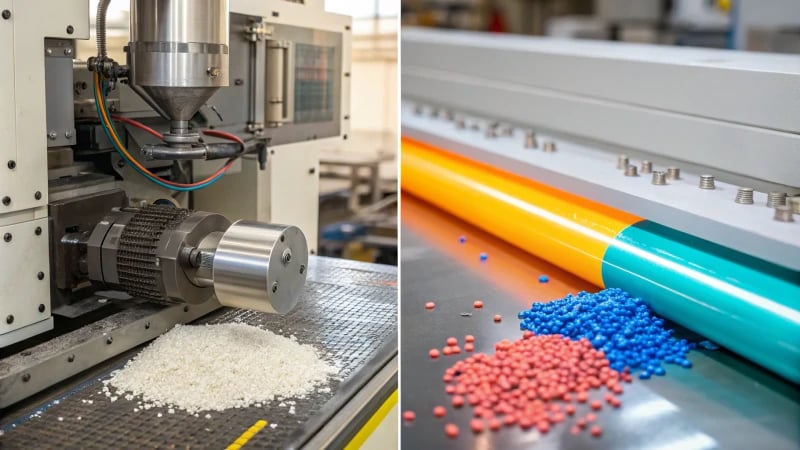

Overview of Injection Molding and Extrusion Molding
Injection molding and extrusion molding are two of the most widely used processes in the manufacturing of plastic products. While both methods involve the shaping of plastic materials, their techniques, applications, and efficiency vary significantly.
Key Differences in Process
Injection Molding involves:
- Feeding: Plastic granules are loaded into a barrel where they are heated until molten.
- Plasticization: The molten plastic is mixed and pressurized using a screw mechanism.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity at high speed.
- Cooling: The product is cooled within the mold until solidified.
- Ejection: The solid plastic part is ejected from the mold.
It’s like watching a newborn ready to meet the world.
In contrast, Extrusion Molding follows a different approach:
- Feeding and Plasticization: Similar to injection molding, but the plastic is continuously melted as it is pushed through a barrel.
- Extrusion: The molten plastic is forced through a die to create continuous shapes, such as pipes or sheets.
It feels almost like creative flow.
Applications
| Aspect | Injection Molding | Extrusion Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Products | Toys, containers, automotive parts | Pipes, sheets, films |
| Production Volume | Suitable for high-volume production | Ideal for continuous production |
| Complexity of Shapes | Can create intricate shapes and designs | Generally limited to simpler shapes |
| Material Usage | Less waste; precise material use | More waste during cutting and trimming |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Injection Molding Advantages:
- High precision and repeatability ensure quality.
- Ability to produce complex geometries becomes achievable with this method.
- Reduced waste due to precise molding benefits budget and environment.
- Fast production cycle times excite those who love quick results.
Injection Molding Disadvantages:
- Higher initial mold costs may discourage use.
- Limited to specific materials that can be injected; not every plastic fits!
Extrusion Molding Advantages:
- Lower cost favors larger runs of simpler products; great for bulk production.
- Continuous process allows for longer production runs, saving time.
- Versatile in terms of materials used helps find affordable options easily.
Extrusion Molding Disadvantages:
- Limited to simpler shapes compared to injection molding can frustrate perfectionists.
- Waste produced during cutting and finishing processes can be an issue.
Cost Considerations
When comparing costs between these two methods, several factors come into play:
- Initial Investment: Injection molds demand more money due to complexity, while extrusion dies often cost less.
- Production Costs: Injection molding may have a higher cost per part for low volumes but becomes more economical at larger volumes. Conversely, extrusion may have lower costs initially but can incur higher costs for varied product shapes.
- Material Costs: Both methods require specific types of plastic affecting overall production costs based on material choice and availability. Wise choice plays a key role!
For more insights on optimizing your product design and manufacturing processes, check out design considerations3.
Reflecting on these processes brings gratitude for the opportunities they provide. Understanding differences helps make better choices daily. Each method holds unique power in shaping creations. They matter.
Injection molding allows for intricate shapes and designs.True
Injection molding can produce complex geometries, making it suitable for detailed products like toys and automotive parts.
Extrusion molding is ideal for high-volume production of complex items.False
Extrusion molding is better suited for continuous production of simpler shapes, not complex items.
What does quality control look like in plastic manufacturing?
Join me as I explore the detailed process of quality control in plastic manufacturing. Each step checks that products meet standards and impact lives. Let’s discover more together!
Quality control in plastic manufacturing involves product design, material selection, mold designing, processing, and inspections, ensuring products meet industry standards and consumer expectations through specific checks at each stage.
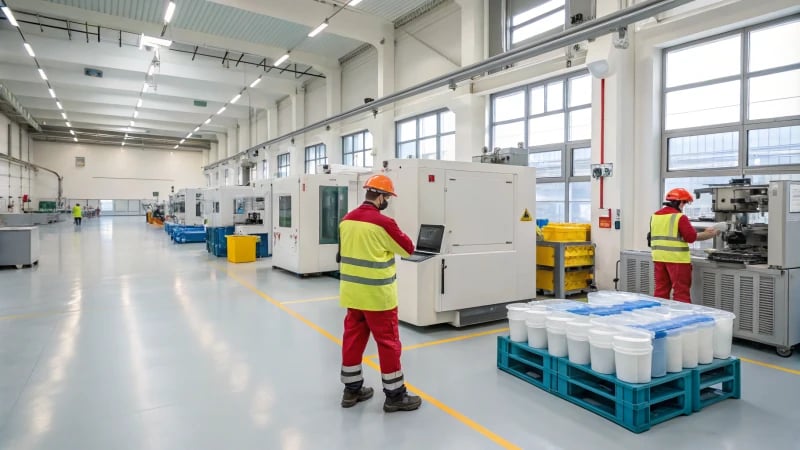

Understanding Quality Control in Plastic Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) acts as a hidden champion in plastic manufacturing. It quietly watches over products to keep them safe, effective, and high-quality. I remember my first encounter with QC in this field. I had to design a simple plastic container and was surprised by the many precise steps involved. Each detail must be checked from start to finish. Everything needs to be just right.
Key Stages of Quality Control
-
Product Design
The process starts with product design. Here, I discovered the need to clearly state product functions and specifications. While developing a series of plastic containers4 for food packaging, hygiene standards became key. Adapting to various food types was also necessary. It opened my eyes to the importance of using CAD software for design. Simplifying shapes avoids defects during manufacturing. -
Material Selection
Selecting the right plastic material feels like choosing a dance partner. Each material must match the needs of the product. High strength and wear resistance may require polyamide (PA), while high transparency might need polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). I clearly remember having to balance performance with budget limits.
| Material | Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| PA | High strength and wear resistance | Moderate |
| PMMA | High transparency | Higher |
| PE | General use, low cost | Low |
-
Mold Design and Manufacturing
Mold design combines creativity and precision. Molds must meet product requirements, and effective cooling systems ensure uniform results. I was amazed by the CNC machining process, which offers great accuracy in creating molds. -
Plastic Molding Processing
The injection molding process marks the moment of truth where all planning comes together:- Injection Parameters: Temperature, pressure, and speed control during injection can save the product from defects like short shots or sink marks.
- Cooling Time: Proper cooling prevents warping or size errors.
-
Post-Processing
After molding finishes, products receive final touches that are vital for quality assurance:- Surface Treatment: Treatments like painting or polishing should be checked for uniformity and adherence to specifications.
- Assembly: Proper assembly requires each component to fit perfectly, demanding patience and attention.
-
Final Quality Inspection
The last stage is comprehensive quality inspection:- Appearance Inspection: Checking for surface defects such as bubbles or scratches helps maintain aesthetic quality.
- Dimensional Accuracy Inspection: Tools like calipers or micrometers help verify dimensional accuracy.
- Performance Testing: Tests such as tensile strength or heat resistance confirm that products meet functional needs.
Quality control measures in plastic manufacturing do more than improve product quality; they build customer trust. Reflecting on my journey through these processes helps me remember why I love this work—it’s about crafting products that probably enhance lives while maintaining high standards. For more on applying these QC methods, explore best practices in QC5.
Quality control starts at the product design phase.True
The quality control process in plastic manufacturing initiates with defining product specifications during the design phase, ensuring adherence to standards from the outset.
Final inspections are unnecessary in plastic manufacturing.False
Comprehensive final inspections are crucial in plastic manufacturing to ensure products meet appearance, dimensional accuracy, and performance standards before delivery.
What advancements are shaping the future of plastic production?
Do you ever think about how plastics are changing? This world is full of new ideas. People show a big dedication to sustainability. This really inspires me.
Advancements in product design, material selection, mold engineering, and molding processes are shaping plastic production by improving sustainability and performance, with post-processing techniques and quality inspection methods playing crucial roles.
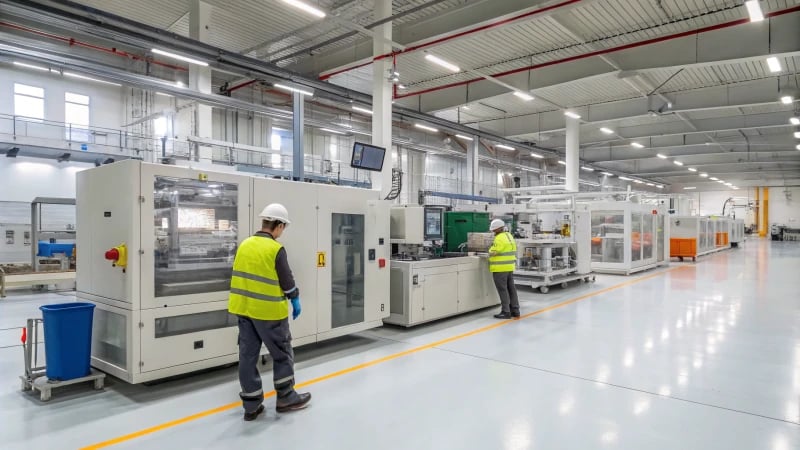

Innovations in Product Design
Advancements in plastic production begin with innovative product design. Modern methodologies require designers to clarify product functions and specifications based on market demand.
For instance, when creating plastic containers for food packaging, it is crucial to ensure they meet hygiene standards and are adaptable to various food types. I spent a lot of time discussing its details, function and even how it looks.
Using CAD software allows for precise three-dimensional modeling, optimizing both shape and structure while considering molding feasibility. Witnessing ideas become detailed 3D models was amazing. For example, when designing plastic toys, safety and assembly methods must be prioritized. It was really fulfilling.
Material Selection Revolution
Selecting the right plastic materials is another key advancement. Material selection must align with product performance requirements.
| Material | Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Polyamide (Nylon) | High strength & wear resistance | Moderate |
| PMMA (Plexiglass) | High transparency | Moderate to High |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Low cost & versatile | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Good processing & durability | Low |
Materials are chosen not just for their mechanical properties but also for cost efficiency. I clearly remember deciding between polyamide (Nylon) for its strength and PMMA for its transparency when working on plastic lenses. Choosing affordable materials like polyethylene (PE) was crucial to staying within budget while meeting requirements.
Advanced Mold Design Techniques
Mold design is critical in shaping plastic products. The design process involves creating structures that accommodate product specifications and material characteristics.
For example, in molds for large products, the cooling system must be designed meticulously to ensure even cooling, preventing defects. Designing molds for larger items required careful detail; it’s like creating art; every shape must be perfect to guarantee a flawless final product.
Efficient Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic molding has evolved significantly, particularly in injection molding. Here’s a brief overview of the steps:
- Feeding: Introduce raw plastic granules into the injection machine.
- Plasticization: The screw melts and mixes the plastic perfectly.
- Injection: Molten plastic injects rapidly into the mold cavity.
- Cooling: It cools and hardens inside the mold – patience is key here!
- Ejection: Finished products eject beautifully.
This process not only improves efficiency but also enhances the quality of molded products. Witnessing everything work smoothly is very satisfying.
Post-Processing Improvements
Post-processing techniques have also seen advancements, allowing for better finishing of plastic products. Surface treatment processes like painting and electroplating enhance both aesthetics and functionality. A project for car interiors comes to mind where we painted parts to match vehicle styles – it was really eye-catching!
Quality Inspection Innovations
With advancements in technology, quality inspection processes have become more rigorous and automated. This includes:
- Appearance inspections: Identifying surface defects using advanced imaging technology – it feels like having extra eyes!
- Dimensional accuracy checks: Utilizing precision measuring tools to ensure product specifications meet design requirements.
- Performance testing: Conducting thorough tests such as tensile strength gives peace of mind knowing products are safe and reliable.
Implementing these quality controls ensures that products not only meet market demands but also comply with safety standards, which is essential for maintaining consumer trust and brand reputation.
Modern CAD software is essential for plastic product design.True
CAD software enables precise modeling, optimizing shapes and structures for effective plastic production and ensuring product specifications meet market demands.
Injection molding has not evolved in recent years.False
Injection molding processes have significantly improved, enhancing efficiency and product quality through advanced techniques and technology integration.
Conclusion
Explore the detailed process of plastic product manufacturing, covering design, material selection, molding techniques, post-processing, and quality control for optimal performance and sustainability.
-
Discovering comprehensive guides on plastic product design can enhance your understanding and improve your skills in this area. ↩
-
Discover essential insights into mold design principles that can enhance your manufacturing efficiency. ↩
-
Explore detailed insights into the differences between these two molding techniques and understand their applications better. ↩
-
Discovering these resources can enhance your understanding of QC methods tailored for plastic manufacturing, providing practical insights for implementation. ↩
-
These articles offer valuable insights into specific techniques and technologies used in QC processes within the plastic industry. ↩





