When I first explored the world of injection molding, I was very surprised by how this method shifts raw materials into complex parts. It feels like a magic trick that needs talent and accuracy.
The essential elements of injection molding include preparation of raw materials, the injection process itself, and post-processing. These steps ensure the quality and precision of molded parts by controlling temperature, pressure, and timing.
You already saw a glimpse into these important steps. Now, explore each one more closely. Discover how every section of the method connects with technical details that guarantee the end result is perfect.
Preparation affects injection molding quality.True
Thorough planning produces flawless items by handling materials carefully and adjusting tools correctly.
How Does Preparation Before Molding Affect Quality?
Getting ready before shaping is important for reaching high-quality and flawless products in injection molding. It lays the groundwork for a smooth and efficient production process.
Preparation before molding impacts quality by ensuring raw materials are adequately treated and equipment is set up correctly. This includes drying plastics to specific moisture levels, preheating inserts, cleaning machinery, and selecting appropriate release agents.
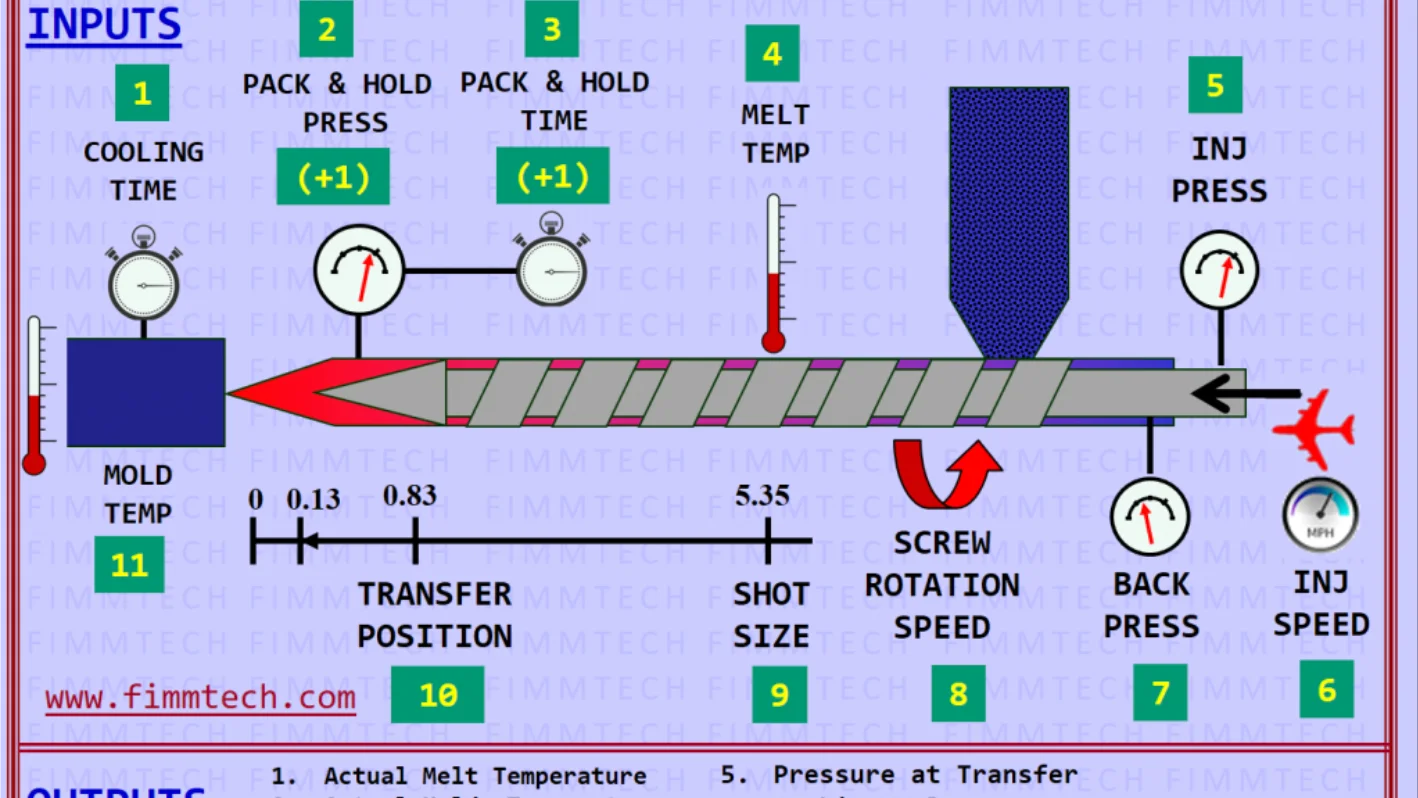
Raw Material Preparation
Good preparation starts with the materials. Treating these materials is crucial to reduce issues in the final product. Plastics like ABS or polycarbonate require specific moisture levels before shaping. Using a vacuum drying oven1 helps dry these plastics to needed standards, such as below 0.2% for polycarbonate, to avoid problems from moisture. Adding color may involve certain agents or color additives.
Preheating Inserts
Including metal parts needs preheating. This lessens the stress inside due to different shrinking between metal and plastic. Picking metals with high heat expansion and warming them helps lower stress and lead to a uniform connection with the plastic around.
Equipment Preparation
Cleaning the injection machine’s chamber is an important step not to miss. New machines or those changing materials or products need a thorough clean. Using recycled materials or low-density polyethylene helps in cleaning without harming sensitive parts.
Selecting Release Agents
Choosing the right release agent matters a lot. Zinc stearate suits general plastics, while liquid paraffin works better with polyamides. It’s important to apply the right amount to keep product looks and color intact.
Table: Common Plastics and Their Pre-treatment Needs
| Plastic Type | Moisture Content Need | Suitable Drying Method |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Below 0.2% | Vacuum Drying Oven |
| PA (Nylon) | Below 0.1% | Hot Air Circulation |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | Below 0.03%-0.05% | Vacuum Drying Oven |
These steps prepare the injection molding process for smooth operation and quality products free from usual problems like voids or warping. Knowing these steps helps manufacturers keep their production steady and precise.
Preheating metal inserts reduces internal stress.True
Warming up matches shrinkage levels, lowering tension in molded pieces.
Zinc stearate is ideal for all plastic types.False
Various plastics need particular release agents for the best outcomes.
What Happens During the Injection Process?
The injection method is the main part of injection molding. Raw materials change into final pieces. Knowing every step is important for good production.
During the injection process, plasticized material is injected into a mold cavity, undergoing phases like charging, plasticization, injection, cooling, and demolding. Each phase requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and timing to ensure high-quality products.
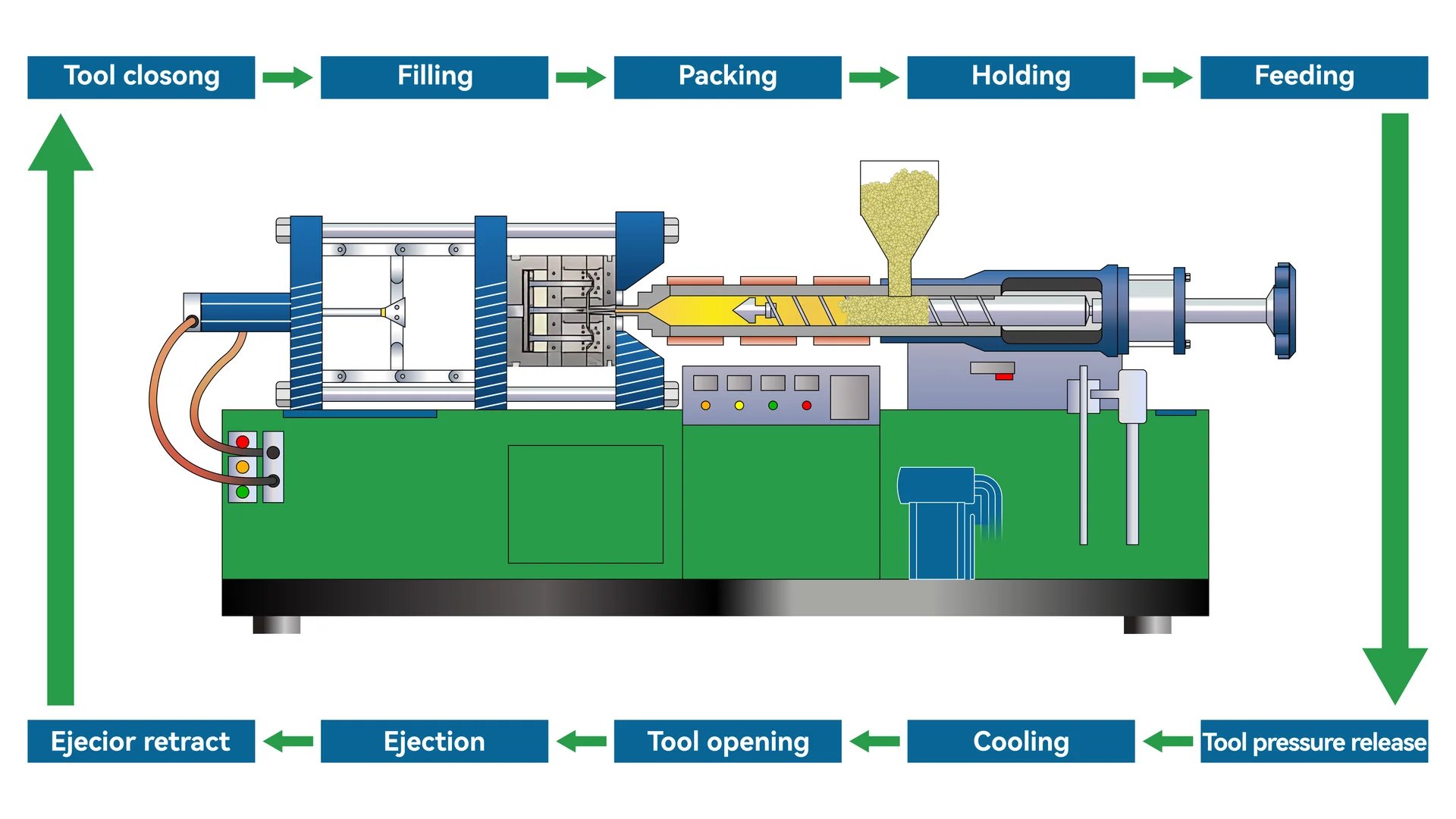
Charging: Material Balance
In this phase, the machine needs a specific amount of material for smooth working. Using too much or too little can cause problems like shrinkage or incomplete shapes. Selecting the correct amount based on product details and machine capacity is important.
Plasticization: Creating a Uniform Melt
Plasticization turns solid polymer pieces into a smooth melt through heat and mixing. This step is important for evenness and product quality. Settings like cylinder warmth, screw speed, and back pressure must be carefully managed to keep the melt consistent. For example, some plastics need temperatures above a certain point for proper melting.
Injection: Filling the Mold
The molten plastic enters the mold at high pressure during this phase. It divides into steps like flow filling, holding, and backflow. In flow filling, materials move quickly into the mold, adjusting for speed and thickness. Holding pressure ensures that the mold fills completely, which really helps with strength and density.
Cooling: Keeping Shape and Size
After filling, the mold cools with a special medium, hardening the plastic and fixing its final shape and features. Cooling time changes based on size and material. Proper cooling is key to maintaining shape and preventing warping.
Demoulding: Removing Parts
When cooled enough, the part leaves the mold using a pushing tool. This step must be done with care to avoid harm or sticking. Well-made ejector systems and release agents really help in smooth removal.
These steps show how each part of the injection process2 helps in quality and exactness. By managing warmth, force, and time effectively, factories probably produce steady and trustworthy parts. Learn more about injection molding settings3 to deepen your knowledge of this complicated process.
Charging phase determines material quantity.True
The charging step guarantees the correct quantity of material for excellent plastic melting.
Cooling affects the part's final dimensions.True
Chilling hardens the plastic, deciding the part's size and features.
Why Is Post-Processing Crucial for Injection Molding?
Post-processing in injection molding guarantees that the last product achieves quality and performance rules. It removes flaws and improves material characteristics.
Post-processing is vital for injection molding because it reduces residual stresses, improves dimensional stability, and enhances surface finish. Techniques like annealing and moisturizing are crucial to achieving these outcomes.

The Role of Annealing in Cutting Down Residual Stress
During the injection molding process, materials often deal with uneven melting, hardening, shaping, and cooling inside the mold. Additionally, metal parts or improper extra processing can introduce stress inside the molded pieces. To address these issues, annealing is often used afterward.
Annealing involves placing the molded pieces in a warm oven or liquid for a set time. This allows parts inside the plastic to relax, reducing leftover stresses. Usually, the oven temperature is set 10-20°C above how hot the plastic parts normally get used or 10-20°C below their heat deformation temperature. Care is needed to avoid warping by preventing excessively high temperatures.
The time needed for annealing varies based on factors such as the type of plastic, heating medium temperature, shape, and thickness of the pieces. For example, thicker pieces or those with very precise requirements may require longer times.
Moisturizing for Stable Shapes and Strength
Moisturizing is important later on, especially for materials like polyamide. Freshly molded pieces are immersed in hot water to keep them away from air exposure. This prevents oxidation and helps them absorb moisture faster, maintaining their shape stability and strengthening them.
Typically, this process occurs at temperatures between 100°C and 120°C. For plastics that bend at higher temperatures, the upper limit is preferred. Moisturizing time depends on plastic type, piece shape, wall thickness, and how parts are packed inside.
With quick water soaking, molded pieces become tougher and stronger. This treatment not only keeps pieces air-free but also enhances their performance characteristics.
Importance of Right Post-Processing Steps
How post-processing steps are executed greatly affects the final quality of injection molded items. Poor annealing might leave residual stresses that weaken them over time. Similarly, insufficient moisturizing can lead to dimensional changes and reduced strength.
By implementing comprehensive post-processing plans effectively, manufacturers can address these issues well. Steps like annealing and moisturizing improve product performance while meeting design needs.
Post-processing is key to successful injection molding. By using the right steps, manufacturers increase product strength, accuracy, and quality—making them useful in industries ranging from automotive to electronics. To learn more about injection molding details and explore further improvements in results through advanced post-processing techniques4.
Annealing reduces residual stresses in molded parts.True
Annealing soothes macromolecules, lowering leftover tension.
Moisturizing is unnecessary for polyamide parts.False
Adding moisture balances size and strengthens polyamide.
How Do Temperature and Pressure Impact Injection Molding?
Temperature and pressure are important aspects that directly affect the quality and success of injection molding. Knowing their impact probably leads to finer product results.
Temperature and pressure in injection molding impact material flow, product quality, and efficiency. Proper control ensures optimal plasticization, reduces defects, and influences cooling rates.
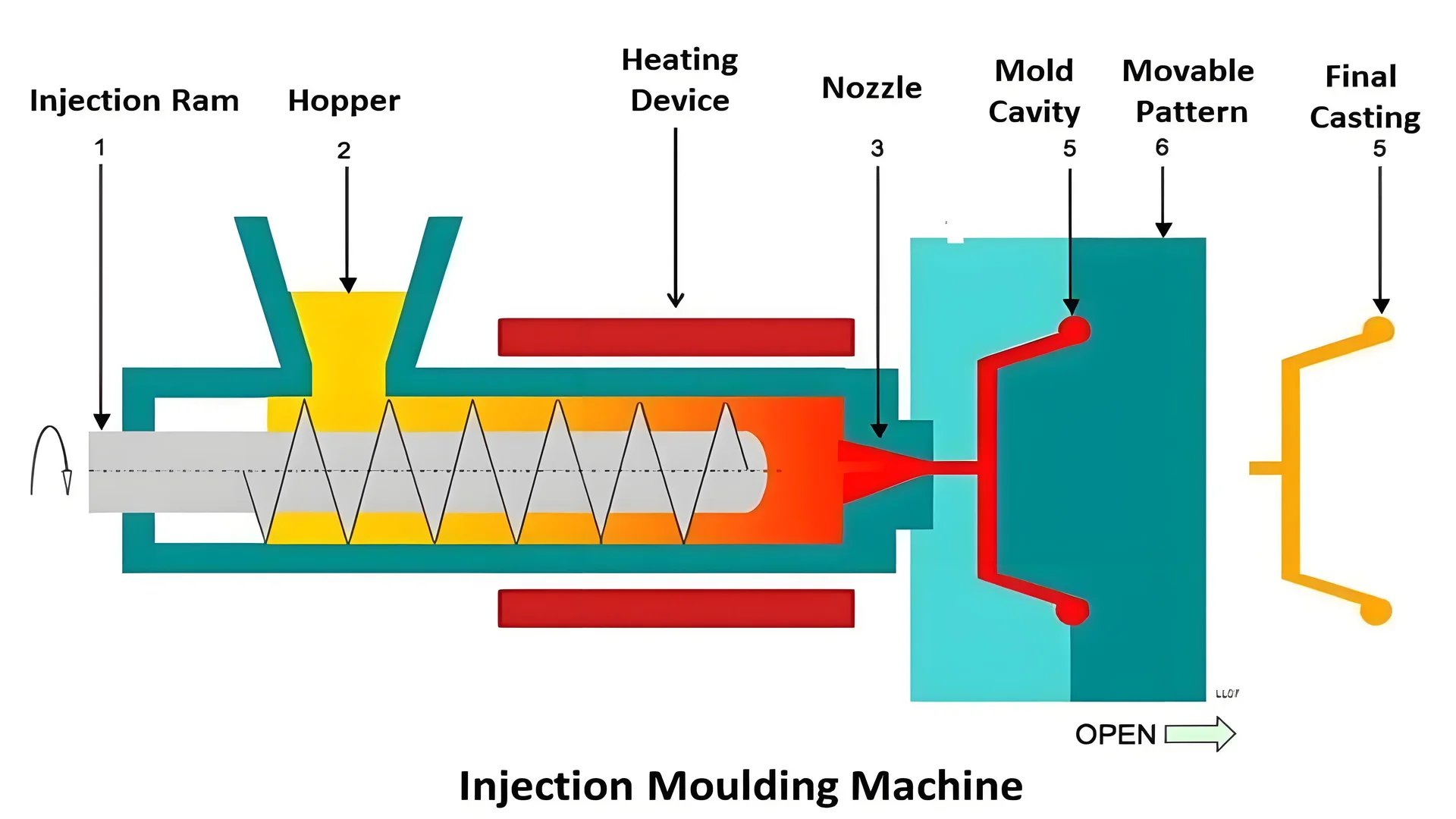
Using Temperature’s Role in Injection Molding
Temperature is very important in injection molding. It affects how well the plastic moves and its final quality. Two key temperatures are considered: material temperature and mold temperature.
-
Material Temperature: The machine’s barrel controls this. The heat should be high so the plastic flows well without breaking down. For example, polycarbonate5 needs a barrel temperature between 260°C and 300°C to stay stable.
- Example: When making thin products like mobile phone covers, the barrel temperature for ABS plastics might be raised to help the plastic fill the mold fully.
-
Mold Temperature: This is managed by cooling systems, usually with water. It affects how fast the melt cools, which impacts surface appearance, work speed, and shrinkage. If the mold temperature increases, it might help crystallize certain plastics like polyamide6, resulting in better density and strength.
Pressure Dynamics in Injection Molding
Pressure is important for the quality of the molded item by influencing melt heat and movement. Key pressures are plasticizing pressure, injection pressure, and cavity pressure.
-
Plasticizing Pressure: Also known as back pressure, controls the melt’s mix within the barrel. More pressure can raise melt heat and help plasticize but might slow down flow if too high.
- Example: For materials like polyethylene (PE), altering plasticizing pressure greatly affects melt quality.
-
Injection Pressure: Important for filling the mold space. It must balance with material temperature to stop issues like overflow or not filling enough.
- Example: For car parts, the right injection pressure is key to reach needed accuracy.
-
Cavity Pressure: The final pressure after losses through openings affects product quality. Control is crucial for precise parts.
Temperature and Pressure Interaction
Both these factors connect; changes in one may need tweaks in the other. For instance, higher material temperatures drop required injection pressures but must be watched closely to avoid damage.
Knowing these links is crucial for perfecting injection molding, ensuring good products with few flaws. Producers should adjust these elements based on material traits and product needs for best outcomes.
Higher mold temperature enhances crystallization in polyamide.True
Increasing the mold temperature supports better crystallization, boosting density and strength.
Increasing plasticizing pressure reduces melt temperature.False
Increased plasticizing pressure raises melt temperature, enhancing plasticization.
Conclusion
Knowing these elements improves your injection molding skills, bringing precision and quality in production. Think about these learnings to better your manufacturing processes.
-
Vacuum drying ovens ensure optimal moisture levels, preventing defects.: Significantly reduced process times … Digitally controlled vacuum cycles, in which the working chamber is vented at short intervals, … ↩
-
Explore detailed phases to enhance understanding of injection molding stages.: The Injection Molding Process Steps · 1. Clamping · 2. Injection · 3. Dwelling · 4. Cooling · 5. Mold Opening · 6. Ejection. ↩
-
Understand key parameters for optimizing injection molding quality.: A case can be made for multiple variables—fill balance, fill time, injection pressure, cavity pressure—as most important. ↩
-
Discover methods to optimize injection molded product quality.: Popular Post-Processing Options for Injection Molding · Mold-Tech Textures · Pad Printing · Silk Screening · Heat Stake Inserts · Ultrasonic Welding. ↩
-
Learn how polycarbonate’s thermal properties affect its processing.: A polycarbonate can maintain its toughness in temperatures up to 140°C, which means polycarbonate parts can withstand repeated sterilization. ↩
-
Discover how mold temperature influences polyamide’s crystallization.: The mold temperature should be between 55 and 80 degrees Celsius for PA6 injection molding and PA66 injection molding, which is the acceptable temperature range … ↩