Ever felt the thrill of molding perfection with your own hands?
Design effective thin-wall injection molding molds by optimizing material flow, precise temperature control, and suitable material selection to ensure consistent wall thickness and reduce defects like warping or shrinkage for high-quality, large-scale production.
I remember the first time I tackled thin-wall injection molding. It felt like trying to sculpt a masterpiece with a blindfold on. There’s something exhilarating about pushing the limits of material and design. But I soon learned that understanding the basics is just the start. Embracing advanced techniques and learning from seasoned experts transformed my approach. In this journey, every tip and strategy was a stepping stone toward achieving manufacturing excellence. Dive deeper with me to uncover these invaluable insights that can refine your process and elevate your results.
Precise temperature control reduces warping in thin-wall molding.True
Maintaining precise temperature control ensures uniform cooling, reducing warping.
Material flow optimization is irrelevant to mold design.False
Optimizing material flow is crucial for uniform wall thickness in molds.
- 1. What Are the Key Design Principles for Thin-Wall Molding?
- 2. How Does Material Selection Impact Mold Performance?
- 3. What Are the Best Cooling Techniques for Thin-Wall Molds?
- 4. What Are Common Defects in Thin-Wall Molding and How to Prevent Them?
- 5. Why Is Uniform Wall Thickness Crucial in Thin-Wall Molding?
- 6. Conclusion
What Are the Key Design Principles for Thin-Wall Molding?
Mastering thin-wall molding is like crafting the perfect recipe—it’s all about understanding the ingredients and the process.
Key design principles for thin-wall molding include optimizing wall thickness, ensuring uniformity, selecting suitable materials, and using proper draft angles to improve manufacturability, minimize defects, and enhance product structural integrity.

Understanding Wall Thickness Optimization
I remember my first project involving thin-wall molding. I was a bit anxious because it felt like walking a tightrope—balancing structural integrity while trimming every unnecessary gram of material. Wall thickness typically ranges from 0.5mm to 2mm for thin-wall molding1. Reducing it can save on material costs but may require fine-tuning pressure and cooling times, much like adjusting the oven temperature for a delicate soufflé.
Ensuring Uniform Wall Distribution
Uniformity is key; it reminds me of when I tried my hand at baking bread. If the dough isn’t evenly kneaded, you’ll end up with an uneven loaf. The same principle applies here—uniform wall thickness helps prevent warping and sinking during cooling. Designers must employ consistent thickness to minimize stress concentrations. Using CAD software is like having a reliable recipe book—it helps simulate and adjust wall distribution efficiently, avoiding stress concentrations with simulation tools2.
Selecting Appropriate Materials
Choosing the right material for thin-wall molding feels like picking the right ingredients for your favorite dish. For example, polycarbonate and ABS are often my go-to choices due to their strength and flexibility. They remind me of using high-quality chocolate in baking—essential for the best results. When selecting materials, I always consider thermal expansion and shrinkage rates to ensure dimensional stability.
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | High impact resistance | Electrical components |
| ABS | Good strength & rigidity | Automotive parts |
Incorporating Proper Draft Angles
Draft angles are like greasing a cake pan—they ensure that parts come out smoothly from molds. A typical draft angle ranges between 1 to 2 degrees. Without it, you might face surface defects or increased mold wear, much like a stubborn cake that won’t leave the tin.
Managing Cooling Times and Techniques
Efficient cooling techniques are vital, akin to letting a cake cool before frosting. Rapid cooling systems and conformal cooling channels help prevent deformation, reducing cycle times while maintaining quality. Optimizing cooling channel design3 is crucial for efficiency.
Utilizing Advanced Mold Design Techniques
Advanced mold design techniques, such as hot runners and precision machining, remind me of using top-tier kitchen tools—they give you better control over material flow and temperature, reducing defects and improving part quality.
Understanding these principles has been pivotal for me. It’s like mastering a complex dish—once you know the techniques, you can create reliable, cost-effective thin-walled components that look great and work even better.
Optimal wall thickness is between 0.5mm to 2mm.True
Thin-wall molding typically requires wall thickness within this range.
Polycarbonate is unsuitable for thin-wall molding.False
Polycarbonate is commonly used due to its strength and flexibility.
How Does Material Selection Impact Mold Performance?
Ever wondered how a simple choice of material can make or break your mold’s performance?
Material selection affects mold performance by impacting thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and final part quality. Choosing the right materials enhances mold longevity and efficiency, crucial for successful injection molding.

Understanding Material Properties
I remember when I first started working with molds, the sheer variety of materials was overwhelming. It felt like each one had its own personality quirks. Take thermal conductivity4, for example. It’s crucial for getting those cycle times down because materials that conduct heat well can cool faster. This not only speeds up production but also helps cut down on energy use.
Wear resistance is another biggie. I learned the hard way that using the wrong material could mean frequent mold replacements—a costly mistake. That’s why I lean towards hardened steel or titanium; they withstand the pressure without wearing out quickly.
Balancing Cost and Performance
Of course, it’s not just about finding the toughest material out there. Budget constraints are a reality I face every day. There’s always this juggling act between cost and performance. While high-end materials can seem like a dream come true, their price tags often tell another story. So, a good old cost-benefit analysis5 is my go-to strategy. It helps me figure out if splurging now will save me money later.
| Material Type | Thermal Conductivity | Wear Resistance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Hardened Steel | Moderate | High | High |
| Titanium | Moderate | Very High | Very High |
Application-Specific Considerations
Then there’s the matter of application-specific needs. Designing for automotive parts versus consumer electronics is like comparing apples to oranges. Automotive components need materials that can handle high temperatures and pressures, whereas consumer electronics often require materials that allow for intricate detailing and a sleek finish.
I try to stay on top of industry trends and material science breakthroughs. It’s like this endless treasure hunt for new materials with better performance specs. These insights keep my designs not just up to par but future-proof, aligning with evolving standards and innovations.
By understanding how material selection affects mold performance, I can fine-tune my designs for greater efficiency and durability, ensuring top-notch quality in production.
High thermal conductivity reduces cycle times.True
Materials with high thermal conductivity transfer heat efficiently, speeding up cooling.
Titanium is the cheapest material for molds.False
Titanium has very high costs compared to other materials like aluminum.
What Are the Best Cooling Techniques for Thin-Wall Molds?
Ever wondered how to keep your thin-wall molds cool and your production line running smoothly? Dive in to discover techniques that might just change the way you work!
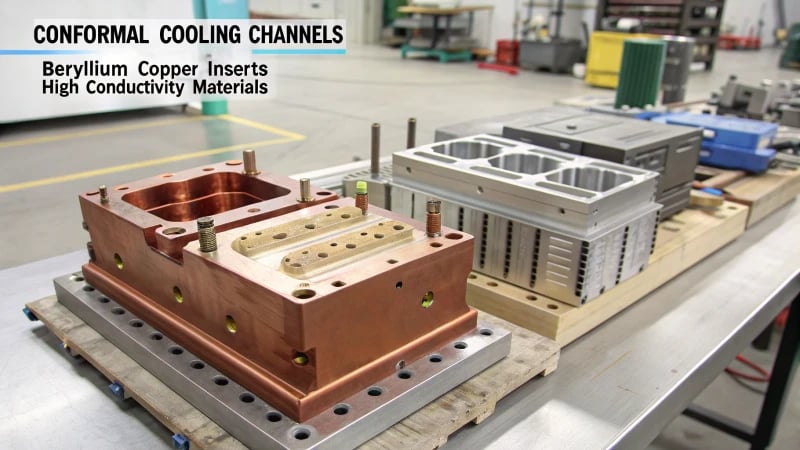
The best cooling techniques for thin-wall molds are conformal cooling, beryllium copper inserts, and using high-conductivity materials, which improve heat dissipation, reduce cycle times, and enhance part quality.
Understanding Thin-Wall Molding Challenges
I remember the first time I had to design a thin-wall mold. It was like trying to solve a Rubik’s cube in the dark. Thin-wall molds demand efficient cooling to avoid defects like warping or incomplete filling. That’s where conformal cooling6 channels came into play for me. These are tailored to the mold’s geometry, offering superior heat transfer, minimizing cycle times, and improving part consistency.
Conformal Cooling Channels
I found conformal cooling fascinating because it involves creating custom-shaped channels close to the mold’s surface. They follow the contours of the part, ensuring a uniform temperature distribution. This technique was a game-changer for me, especially with complex shapes where traditional straight-line cooling failed.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Improved heat transfer | Higher initial cost |
| Reduced cycle time | Requires advanced tooling |
Beryllium Copper Inserts
One of my colleagues once joked that using beryllium copper7 inserts is like having a turbo button on your mold. These inserts enhance thermal conductivity, conducting heat away quickly and reducing hot spots that could lead to defects. They’re ideal for areas requiring rapid cooling or intricate features.
High-Conductivity Materials
Using materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum, has been another strategy I’ve leaned on. These materials disperse heat efficiently, complementing other cooling strategies to maintain uniformity across the mold surface.
Active Cooling Systems
Implementing active cooling systems such as water or air jets can be like having an ace up your sleeve. They further expedite the cooling process, which is essential for maintaining tight tolerances and ensuring high-quality finishes in thin-walled components.
Summary Table
| Technique | Primary Benefit | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Conformal Cooling | Uniform temperature distribution | Complex geometries |
| Beryllium Copper Inserts | Quick heat dissipation | Areas with rapid cooling needs |
| High-Conductivity Materials | Efficient heat dispersion | General mold surfaces |
Over the years, I’ve learned that employing a combination of these techniques can significantly enhance thin-wall molding8 efficiency and quality. The advancements in mold technology continue to impress me and promise further improvements in these areas.
By understanding and implementing the right cooling techniques, we designers and manufacturers can achieve optimal results in thin-wall molding processes, ensuring high-quality products with reduced production times. And let me tell you, there’s nothing quite like seeing a perfectly cooled mold come out just right.
Conformal cooling reduces cycle times in thin-wall molding.True
Conformal cooling channels improve heat transfer, minimizing cycle times.
Beryllium copper inserts are cost-effective for all mold types.False
While effective, beryllium copper inserts have higher initial costs.
What Are Common Defects in Thin-Wall Molding and How to Prevent Them?
Every time I tackle thin-wall molding, I’m reminded of how even the smallest defects can feel like massive hurdles. Yet, with a bit of know-how, they become entirely manageable.
Common defects in thin-wall molding, such as warpage, burns, and internal cracks, can be prevented through optimized mold design, precise control of process parameters, and selecting appropriate materials.
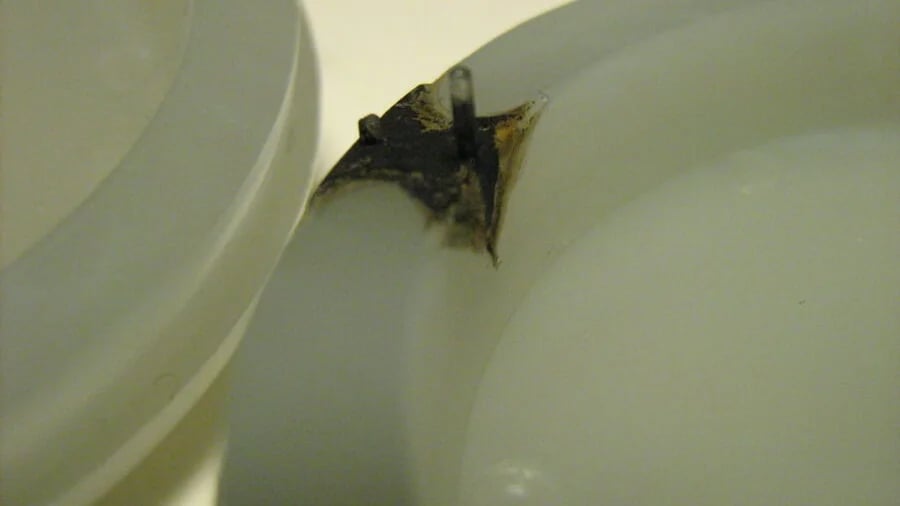

Understanding Thin-Wall Molding
When I first ventured into the world of thin-wall molding, it felt like trying to master a delicate dance. This process is all about creating parts that are thinner than what traditional methods typically allow. It’s especially popular in industries like electronics and automotive, where every ounce counts.
Common Defects in Thin-Wall Molding
-
Warpage: I remember the frustration of dealing with warpage when a part wouldn’t sit right. It often happens due to uneven cooling or leftover stresses in the material. To keep warpage at bay, I focus on ensuring uniform cooling by tweaking the mold temperature and opting for top-notch materials.
-
Burn Marks: These pesky dark streaks can sneak up on you, often caused by trapped air or cranking up the temperature too high. I’ve learned that adjusting the injection speed and improving venting can significantly reduce these unsightly marks.
-
Internal Cracks: These are a nightmare and often stem from high injection pressures or inadequate material drying. My approach? Properly dry the materials and carefully adjust pressures to keep cracks at bay.
| Defect Type | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Warpage | Uneven cooling | Optimize mold temperature |
| Burn Marks | Trapped air/High temperature | Adjust injection speed, improve venting |
| Internal Cracks | High pressure/Inadequate drying | Proper drying, adjust injection pressures |
Material Selection9
Choosing the right material feels like picking the perfect tool for a job—it’s crucial for preventing defects. Materials with consistent properties and excellent flow characteristics make all the difference in thin-wall molding. Delving into appropriate materials10 can drastically impact your project’s success.
Process Optimization11
Fine-tuning process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed is where things get interesting. I often use simulation tools to test various scenarios before jumping into actual production. It’s a game-changer; you should explore more on process optimization12.
Mold Design Considerations13
A well-designed mold is like a trusted ally in preventing defects. It should promote uniform cooling and have adequate venting to fend off burns and warpage. Check out mold design14 best practices to elevate your thin-wall molding game.
In this ever-evolving journey of creating high-quality outputs, understanding each defect’s root cause is key. Whether it’s through design refinement, meticulous material selection, or precise process control, every step we take strengthens product integrity and cuts down waste—ultimately driving efficiency in our manufacturing processes.
Warpage is caused by uneven cooling in thin-wall molding.True
Uneven cooling leads to residual stresses, causing warpage.
Burn marks are eliminated by increasing injection speed.False
Reducing injection speed and improving venting prevent burn marks.
Why Is Uniform Wall Thickness Crucial in Thin-Wall Molding?
I remember the first time I realized how crucial uniform wall thickness was in molding. It was like an "aha" moment that changed everything.
Uniform wall thickness in thin-wall molding prevents defects, ensures smooth flow, and maintains structural integrity, enhancing production efficiency and quality with reduced waste and faster cycle times.
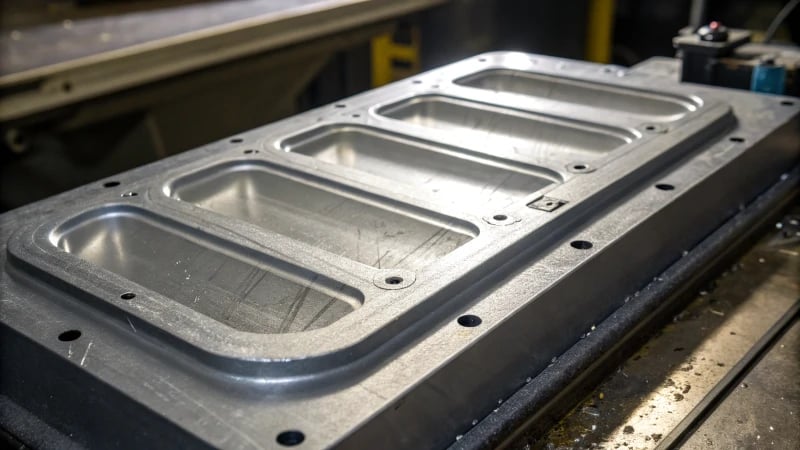

The Role of Uniform Wall Thickness in Quality Control
I recall working on a project where the slightest deviation in wall thickness led to unexpected warping. It was a tough lesson learned, but it highlighted how crucial uniformity is. Defects like warping and sink marks15 occur when thicker areas cool slower than thinner ones, causing internal stresses.
Material Flow and Structural Integrity
On another project, I noticed how inconsistent wall thickness disrupted material flow during injection. The product ended up with weak spots because certain areas cooled prematurely. Ensuring uniform thickness helps maintain the structural integrity16 by promoting even cooling and solidifying the final product.
Efficiency in Production Processes
Uniform wall thickness doesn’t just enhance quality—it boosts efficiency. I once managed to cut down cycle times significantly just by maintaining consistent thickness. Less wastage and faster production became the new norm. Here’s how it breaks down:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced Cycle Time | Uniform cooling speeds up the process |
| Material Efficiency | Less wastage due to consistent flow |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower defect rates mean fewer rejections |
Design Considerations
In my design process, keeping wall thickness uniform is always top of mind. I leverage CAD tools to simulate and analyze potential issues17 early on, saving time and resources. It’s all about preventing problems before they arise, ensuring smooth production every step of the way.
Uniform wall thickness prevents warping in thin-wall molding.True
Consistent thickness ensures even cooling, reducing internal stresses.
Inconsistent wall thickness speeds up production cycle time.False
Inconsistency causes uneven cooling, increasing cycle time and defects.
Conclusion
Effective mold design for thin-wall injection molding requires optimizing material flow, maintaining uniform wall thickness, and utilizing advanced cooling techniques to enhance quality and reduce defects.
-
Explore how adjusting wall thickness impacts cost and production efficiency in thin-wall molding processes. ↩
-
Learn about simulation tools that help identify potential weaknesses in wall thickness distribution during the design phase. ↩
-
Discover innovative cooling channel designs that improve cycle times and maintain product quality in injection molding. ↩
-
Learn how thermal conductivity affects mold efficiency and cooling times. ↩
-
Discover techniques to evaluate the economic feasibility of different materials. ↩
-
Learn how conformal cooling channels optimize cooling efficiency in complex mold geometries. ↩
-
Explore why beryllium copper inserts are favored for their excellent thermal conductivity. ↩
-
Gain insights into advanced techniques that improve thin-wall molding efficiency. ↩
-
Discovering the best materials enhances understanding of their properties, aiding in defect prevention. ↩
-
Discovering the best materials enhances understanding of their properties, aiding in defect prevention. ↩
-
Exploring optimization techniques can lead to improved efficiency and quality in molding. ↩
-
Exploring optimization techniques can lead to improved efficiency and quality in molding. ↩
-
Learning about design tips helps in creating molds that minimize defects effectively. ↩
-
Learning about design tips helps in creating molds that minimize defects effectively. ↩
-
Learn about common defects like sink marks in injection molding and how they affect product quality. ↩
-
Explore why maintaining structural integrity is crucial for the durability and reliability of molded products. ↩
-
Discover how CAD tools help designers like Jacky foresee and address design challenges effectively. ↩






