Do you experience the deep frustration of bubbles ruining your carefully designed injection-molded products?
To effectively deal with bubbles in injection molded products, adjust injection speed and pressure, improve mold design, and thoroughly dry raw materials. These steps help reduce trapped air and enhance product quality.
These first small changes quickly solve some problems. Each part of the injection molding process offers more detailed answers. Exploring it has shown this to me. Minor changes to mold design and skillful handling of materials are important. Fixing bubbles in the process has been both difficult and satisfying for me. It’s like adjusting an instrument. Each note needs to be correct for a perfect song.
Adjusting injection speed reduces bubbles in molded products.True
Proper injection speed minimizes air entrapment, reducing bubble formation.
Ignoring raw material drying prevents bubble defects.False
Undried materials can release moisture, causing bubbles during molding.
How Can I Improve the Injection Molding Process?
Do you sometimes get confused by bubbles in injection-molded parts? I have felt that way as well. Changing the process often fixes the problem.
To improve the injection molding process, try lowering injection speed. Adjust pressure and optimize holding time. Carefully control temperatures and use a well-designed mold. These changes probably help reduce defects like bubbles. They really improve product quality.

Injection Speed Modifications
Reducing the injection speed1 can significantly decrease bubble formation. A turbulent flow during fast injection entrains air into the melt, leading to bubbles. Adjusting speed from 80mm³/s to 40-60mm³/s can help.
| Initial Speed | Adjusted Speed |
|---|---|
| 80mm³/s | 40-60mm³/s |
Pressure Adjustments
High injection pressure may cause air entrapment in the melt. By lowering pressure from 100MPa to around 80-90MPa, you reduce this risk while ensuring cavity fill.
Optimizing Holding Time
Prolonging holding time by 3-5 seconds ensures thorough melt compaction, expelling trapped air. Holding time adjustments from 5s to 8-10s are recommended.
Temperature Controls
A balance between melt and mold temperature is crucial. Lowering melt temperature (e.g., from 260℃ to 240-250℃) helps maintain melt viscosity, reducing bubbles.
| Material | Mold Temp (℃) |
|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Balance needed |
Exhaust System Improvements
Improving mold exhaust is important. It resembles opening windows in a stuffy room. Adding exhaust grooves or using breathable steel prevented air from getting trapped. Typical groove dimensions are depth: 0.02-0.05mm, width: 3-5mm.
Gate Design Considerations
Proper gate positioning prevents bubble issues. For thin-walled products, side or fan gates are preferable for uniform cavity fill. Ensure gate size avoids high-speed melt ejection.
Raw Material Processing
Fully dry materials with high hygroscopicity, like nylon (PA) and polycarbonate (PC), to prevent vapor bubbles. Set PA drying temperature at 80-100℃ for 4-6 hours; PC at 110-120℃ for 3-5 hours.
| Material | Drying Temp (℃) | Duration (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| PA | 80-100 | 4-6 |
| PC | 110-120 | 3-5 |
Material and Additive Adjustments
Switch materials with strong air permeability if other methods fail. Introducing anti-foaming agents can also aid in reducing surface tension, easing bubble release.
These adjustments have guided my journey to mastering injection molding, significantly improving product quality and operational efficiency through careful modification of parameters such as speed, pressure, and temperature.
Reducing injection speed decreases bubble formation.True
Lowering speed reduces turbulence, minimizing air entrainment.
Higher injection pressure prevents air entrapment.False
High pressure increases the risk of trapping air in the melt.
How Does Mold Design Influence Bubble Formation?
Have you ever seen a project ruined by annoying bubbles in injection molding? It’s very frustrating, isn’t it?
Mold design affects bubble formation. It influences air trapping, melt flow and cooling rates. A really good gate design reduces bubbles. Efficient exhaust systems and right mold temperature also help. These factors significantly decrease bubbles in molded items.

Understanding Bubble Formation in Injection Molding
I remember my first experience with bubble formation during an injection molding project – it was a nightmare! Air can get trapped in the plastic melt and cause bubbles. This usually occurs due to poorly designed molds or wrong process settings. Understanding how these bubbles form is crucial for anyone tackling this issue.
Key Design Elements Affecting Bubble Formation
Gate Design and Placement
The gate design is like the unsung hero of mold design. Placement of the gate can really impact the process. A wrong gate location may lead to uneven filling and more bubbles. For thin-walled products, a fan gate2 provides better melt distribution, reducing bubbles.
| Gate Type | Best Use Case |
|---|---|
| Side Gate | General-purpose |
| Fan Gate | Thin-walled applications |
| Edge Gate | Large-area parts |
Exhaust System Optimization
A solid exhaust system is very important. Inadequate venting traps air and causes bubbles. Effective venting channels3 help prevent this. Breathable materials like steel inserts also improve exhaust efficiency.
Mold Temperature Control
Mold temperature control is very important for good design. Adjustments in temperature can reduce bubble formation significantly. Stable cooling reduces shrinkage and vacuum bubbles. For some thermoplastics, maintaining 40-60℃ is effective.
Process Adjustments for Bubble Reduction
- Injection Speed and Pressure: Adjusting these is crucial! Reduce injection speed to 40-60mm³/sec to keep a laminar flow, helping avoid air entrapment. Finding the right pressure balance prevents air mixing.
- Holding Process Optimization: A few extra seconds in holding time compact the melt properly, pushing out trapped air.
Material Considerations
Material choice is significant. Materials like nylon need thorough drying to prevent moisture turning into vapor bubbles. Understanding material properties and possible additives reduces defects.
Mindful consideration of these factors helps mold designers significantly reduce bubble formation, improving both product quality and manufacturing efficiency. Mold design interaction with processing conditions is key to great injection molding results.
If you’re looking for more tips, check out mold improvement measures4 for great suggestions to improve product quality.
Improper gate placement increases bubble formation.True
Incorrect gate placement can lead to uneven filling and air entrapment.
High mold temperature always reduces bubble formation.False
High temperatures can cause excessive shrinkage, increasing vacuum bubbles.
Why Is Raw Material Preparation Crucial in Preventing Bubbles?
Recall when you discovered bubbles in your plastic items. Bubbles often occur because of the way raw materials were prepared.
Getting raw materials ready really helps stop bubbles. It is important to control moisture before starting the process. Proper drying and careful handling decrease trapped air. Product quality improves a lot.
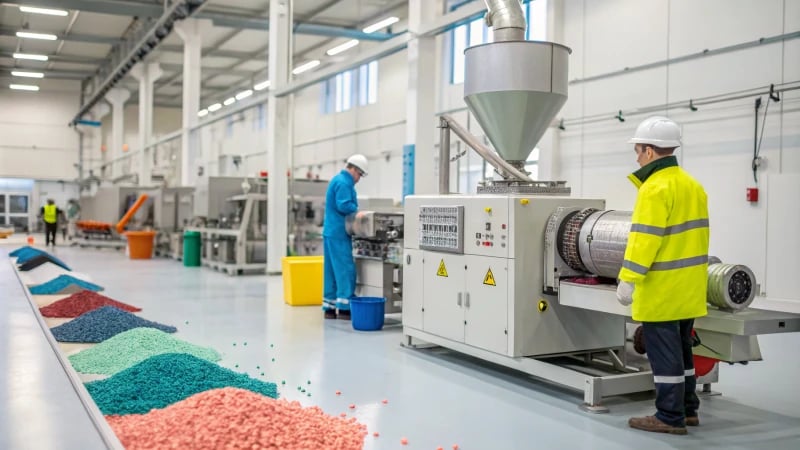

Importance of Drying Raw Materials
Consider moisture. A soggy cake happens when ingredients are damp. Raw materials can be similar. Moisture becomes vapor during molding, causing bubbles. It’s like using wet flour in baking. Hygroscopic plastics like nylon need proper drying. An effective drying method5 is very important. This helps a lot in reducing bubble problems.
| Material | Drying Temperature | Drying Time |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon (PA) | 80-100°C | 4-6 hours |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 110-120°C | 3-5 hours |
By adhering to these guidelines, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of bubble formation.
Material Selection and Additives
Once, changing materials solved my problem. Some plastics allow air to pass easily. Persistent bubbles made me switch materials or add anti-foaming agents. These additives lower the melt’s surface tension, letting bubbles escape.
Moreover, finding the right balance is key as additives’ impact on the product’s performance and quality must be evaluated. For example, while lubricants6 can enhance the melt flow, they might affect the final product’s strength.
Handling and Storage Practices
Handling and storage are very important. A mentor once taught me to treat my materials with care. Proper handling stops contamination. Controlled environments are essential.
Using airtight containers and maintaining low humidity levels are standard practices now. Regularly checking storage helps avoid moisture buildup that could compromise the material’s quality during molding.
Role in Injection Molding
Raw material preparation impacts the whole injection molding process:
- Melt Flow: Consistent melt flow begins with properly prepared materials, reducing turbulence and air entrainment.
- Filling Efficiency: Prepared materials fill molds evenly, minimizing voids and defects.
- Product Integrity: Ensures high-quality finishes without surface imperfections like bubbles.
I remember optimizing injection speed and pressure; lowering speed from 80mm³ to 40-60mm³ per second was crucial, along with adjusting pressure from 100MPa to 80-90MPa helped keep air out.
With these changes, I’ve really increased production efficiency7. Defect rates have dropped significantly because it all starts with getting raw materials right—this preparation sets the stage for success.
Drying nylon at 80-100°C for 4-6 hours reduces bubbles.True
Proper drying of nylon removes moisture, preventing bubble formation.
Lubricants in plastics always improve product strength.False
While lubricants enhance flow, they may compromise product strength.
How Do Additives Help in Reducing Bubble Formation?
Have you ever been amazed by the perfect surface of your favorite gadget? The smooth paint on a freshly coated wall can also leave you in awe.
Additives like anti-foaming agents and surfactants help lower bubble formation. These substances reduce surface tension. They create even dispersions. This action results in very few air pockets. Smoother final products emerge from this process.
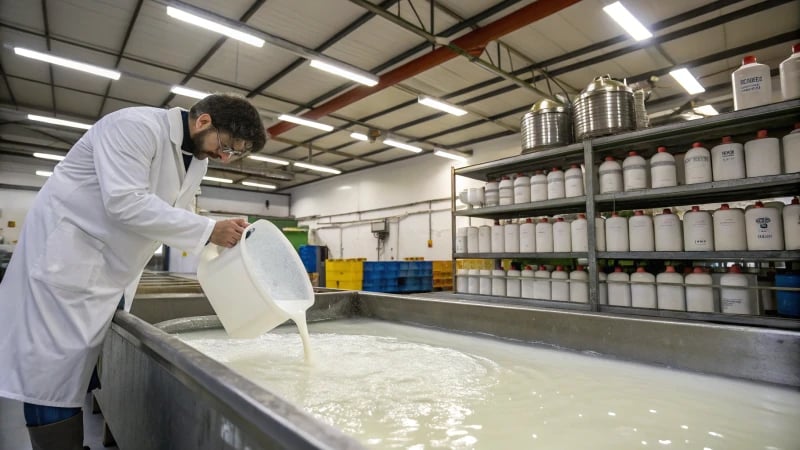

Understanding Additives in Material Processing
On my journey in the world of material processing8, I saw how additives really change things. These tiny helpers, like anti-foaming agents, adjust the surface tension. Gases then escape more easily, like giving a small push to help settle the material smoothly. Those annoying air bubbles do not stand a chance.
Types of Additives Used
1. Anti-Foaming Agents
Once, I worked on a project where the production line was very busy. Air got trapped everywhere. Anti-foaming agents came to the rescue, breaking the foam and preventing new bubbles from forming. They acted like real superheroes.
2. Surfactants
Surfactants have a calming effect. They reduce the surface tension of liquids. This leads to better mixing and stops bubbles very effectively.
Applications Across Industries
Plastics Manufacturing
While exploring injection molding9, I saw how important additives are in avoiding flaws. Adjusting melt viscosity with the right compounds helps prevent bubbles. Our devices then work well and also look really fantastic.
Paints and Coatings
In the paint industry, smooth finishes are crucial. Anti-foaming additives are the secret behind perfect paint surfaces. They keep air bubbles away from destroying our creative work.
Example Table: Common Additives and Their Functions
| Additive Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Anti-Foaming Agents | Reduce foam formation |
| Surfactants | Lower surface tension |
| Lubricants | Improve material flow |
| Stabilizers | Maintain consistency over time |
Considerations When Using Additives
Despite their benefits, I learned to be cautious with additives. Too much can disturb the balance and alter material properties or appearance. Each additive must match the product specifications10 very carefully. Overuse might disrupt the intended results.
Anti-foaming agents reduce bubble formation in paints.True
Anti-foaming agents prevent bubbles by breaking down foam, ensuring smooth paint application.
Surfactants increase bubble formation in plastics.False
Surfactants lower surface tension, aiding gas dispersion and reducing bubbles.
Conclusion
This article provides effective strategies to reduce bubble formation in injection molded products, focusing on adjustments in speed, pressure, mold design, and raw material processing.
-
Reducing injection speed is vital for minimizing defects like bubbles. Click to explore strategies for achieving optimal injection speed. ↩
-
This link explains how fan gates help in reducing bubble formation by ensuring even melt distribution. ↩
-
This link explores how effective venting channels prevent air entrapment, reducing bubble formation. ↩
-
Discover more strategies for improving mold design to enhance product quality by reducing defects. ↩
-
Discover best practices for drying hygroscopic plastics to prevent bubble formation in molded products. ↩
-
Learn how lubricants can affect the strength and quality of molded plastic products. ↩
-
Explore strategies to boost production efficiency and reduce defect rates in injection molding. ↩
-
Learn about how additives influence material properties and reduce bubble formation. ↩
-
Discover how certain additives improve the injection molding process by minimizing air pockets. ↩
-
Understand the balance needed when using additives to maintain desired product qualities. ↩






