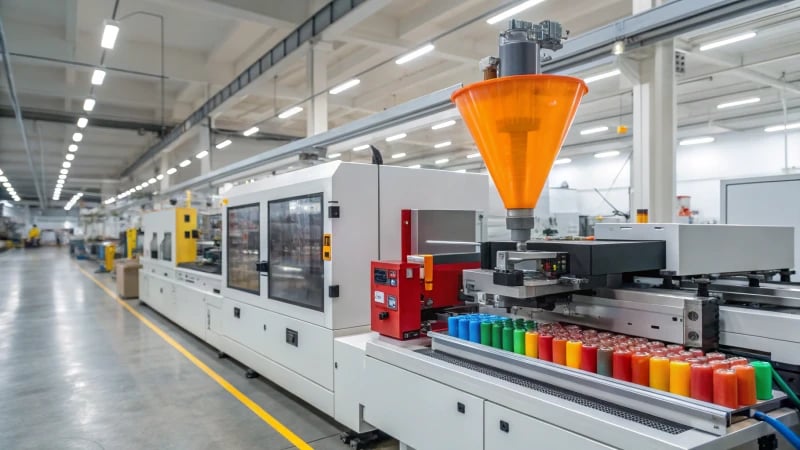
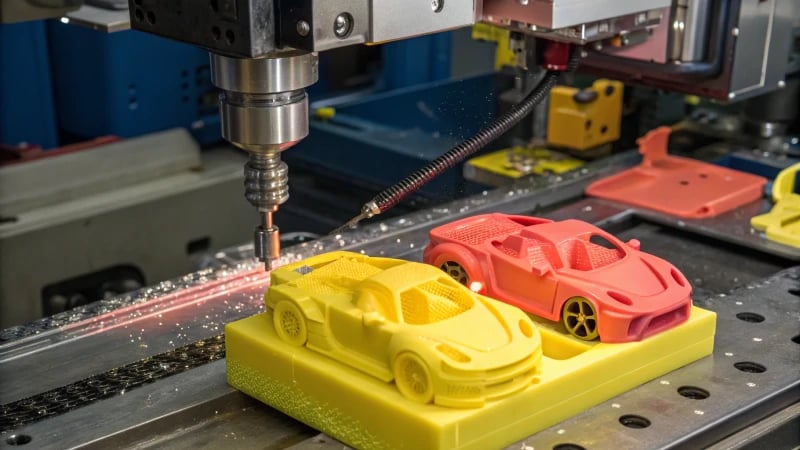
Remember the awe of holding a tiny, perfect toy car as a kid? There’s magic in how they’re made.
An injection molding machine makes toy cars by injecting molten plastic into molds for parts like body, wheels, and axles, using precise temperature and pressure control to ensure high-quality output.
When I first learned about injection molding, it was like uncovering the secret recipe to a cherished family dish. Each step is vital, from selecting the right plastic to designing detailed molds. It reminds me of those childhood days spent assembling model kits with my dad, where every piece had its perfect place.
Mold Design
The art of mold design is akin to sculpting. Imagine crafting a mold that captures every curve and detail of a toy car’s body, like the ones I admired on store shelves as a child. We can even design molds for features like windows or grilles. It’s fascinating how multi-cavity molds can churn out multiple car bodies in one go, boosting efficiency.
Material Selection
Choosing the right plastic is like picking the perfect ingredients for a cake. Plastics like ABS offer toughness and a smooth finish, while polypropylene adds flexibility. For transparent parts like windows, PMMA is ideal.
Injection Molding Process
The process begins with plastic pellets melting into a molten state. I recall watching similar processes in awe during factory tours. The molten plastic is injected into molds at precise temperatures and pressures, ensuring each cavity fills perfectly. After cooling and solidifying, components are ejected, ready to become part of a toy that brings joy to children everywhere.
Understanding these steps not only deepens my appreciation for toy cars but also sparks ideas on optimizing production. Whether you’re in product design or just curious like me, these insights can transform how we approach manufacturing challenges.
Injection molding machines use molds for toy car production.True
The machine injects molten plastic into molds to form toy cars.
Toy car molds are filled with molten metal, not plastic.False
Toy car molds are filled with molten plastic, not metal.

How Do You Design Molds for Toy Cars?
Designing molds for toy cars is like sculpting magic—each step is crucial to bringing these miniature vehicles to life with precision and charm.
Design toy car molds by crafting separate molds for the body, wheels, and axles using durable materials like ABS or PP. Use injection molding to melt, inject, cool, and eject parts efficiently.

Designing the Mold
I remember the first time I watched a toy car being molded—it was like witnessing art in motion. The process starts with designing a body mold1 that mirrors every curve and line of the toy car. It’s fascinating how each detail, from the sleek contours of the hood to tiny grilles, is captured within the mold’s cavity. For the wheels and axles, separate molds are crafted, each with its own unique dimensions and features. Using multi-cavity molds can be a game-changer, allowing several parts to be produced simultaneously, boosting efficiency.
| Mold Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Body Mold | Contours, windows, grilles |
| Wheel Mold | Circular shape, tread pattern |
| Axle Mold | Appropriate diameter and length |
Material Selection
Selecting the right materials is like choosing the best ingredients for a recipe. I’ve learned that using plastics like ABS ensures toughness and an appealing finish, while PP offers flexibility—perfect for withstanding rough play. For clear parts like windows, PMMA is my go-to choice. These materials ensure that every toy car not only looks good but can also handle some serious playtime.
The Injection Molding Process
Melting and Injection
The journey continues with melting plastic pellets in the injection-molding machine. Each type of plastic has its sweet spot temperature—like ABS, which melts beautifully at around 200-260°C. Watching the molten plastic being injected into the mold through a nozzle always feels like magic; precision is key here, ensuring every cavity is perfectly filled.
Cooling and Ejection
After injection, the cooling phase begins—it’s like waiting for a cake to set. The cooling time depends on material thickness and type but is crucial for solidifying the shape. Once cooled, the mold opens to reveal freshly minted car bodies, wheels, and axles. These components are then assembled into complete toy cars—a process that repeats effortlessly to produce more units efficiently.
Understanding these steps has been essential in refining my approach to mold design efficiency2, ensuring each tiny vehicle meets the highest quality standards while keeping production swift and cost-effective.
ABS plastic is used for toy car windows.False
PMMA, not ABS, is preferred for transparent components like windows.
Multi-cavity molds increase production efficiency.True
Multi-cavity molds produce multiple parts simultaneously, boosting efficiency.
Which Plastics Are Best Suited for Toy Car Manufacturing?
Choosing the right plastic for toy cars is like selecting the perfect ingredients for a favorite dish. Get it right, and you have something durable and delightful.
ABS and PP are ideal for toy cars due to their durability and flexibility, while PMMA is suitable for transparent parts like windows.

Understanding Plastic Types for Toy Cars
Let’s dive into the world of toy car manufacturing, where picking the right plastic is just as crucial as the design itself. Each plastic has its own personality, much like the characters in our favorite stories. Here are some of the most popular types.
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS)
I remember the first time I encountered ABS in toy car manufacturing. Its remarkable balance of toughness and rigidity struck me as similar to a beloved action figure—ready for any roughhousing. ABS‘s resilience makes it perfect for the main body of a toy car, capable of enduring countless play sessions.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Toughness | High |
| Rigidity | High |
| Surface Finish | Excellent |
The magic happens through injection molding, where ABS pellets3 transform under heat and pressure into solid, sturdy car bodies.
Polypropylene (PP)
Think of polypropylene as the flexible friend in your life—always bending, never breaking. It’s ideal for parts like bumpers or fenders that might take a few hits during playtime.
- Flexibility: Bends without breaking, like a gymnast.
- Impact Resistance: Stands firm against drops and collisions.
PP is cost-effective and often pairs with ABS for a dynamic duo in toy car designs.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
For those sleek, transparent parts like windows or lights, PMMA is the star. It offers clarity akin to glass but is much safer and lighter—a true winner in the safety department.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Transparency | High |
| Safety | Enhanced |
| Weight | Light |
Integrating Plastics with Design & Manufacturing
Designing molds that accommodate these plastics is like crafting a tailored suit—it must fit just right. Multi-cavity molds, for instance, can produce several components in one go, streamlining the production process. I once watched a multi-cavity mold work its magic, churning out multiple car bodies in one cycle—it was mesmerizing!
By aligning material selection with design needs, manufacturers can create toy cars that aren’t just functional but also visually appealing. Advanced techniques, like combining different plastics in one product (variety of plastics4), can enhance durability and flexibility while maintaining aesthetic charm. This comprehensive understanding empowers us to make informed decisions that elevate toy car production to new heights.
ABS plastic is ideal for toy car bodies.True
ABS offers high toughness and rigidity, perfect for durable car bodies.
PMMA is used for toy car bumpers.False
PMMA is used for transparent parts like windows, not bumpers.
How Does the Injection Molding Process Work in Detail?
Ever wondered how your favorite plastic toys or gadgets are made? Dive into the fascinating world of injection molding—a process that turns imagination into tangible creations with just a few precise steps.
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold. Key stages include mold design, material selection, injection, cooling, and ejection, ensuring precision and efficiency in creating parts.
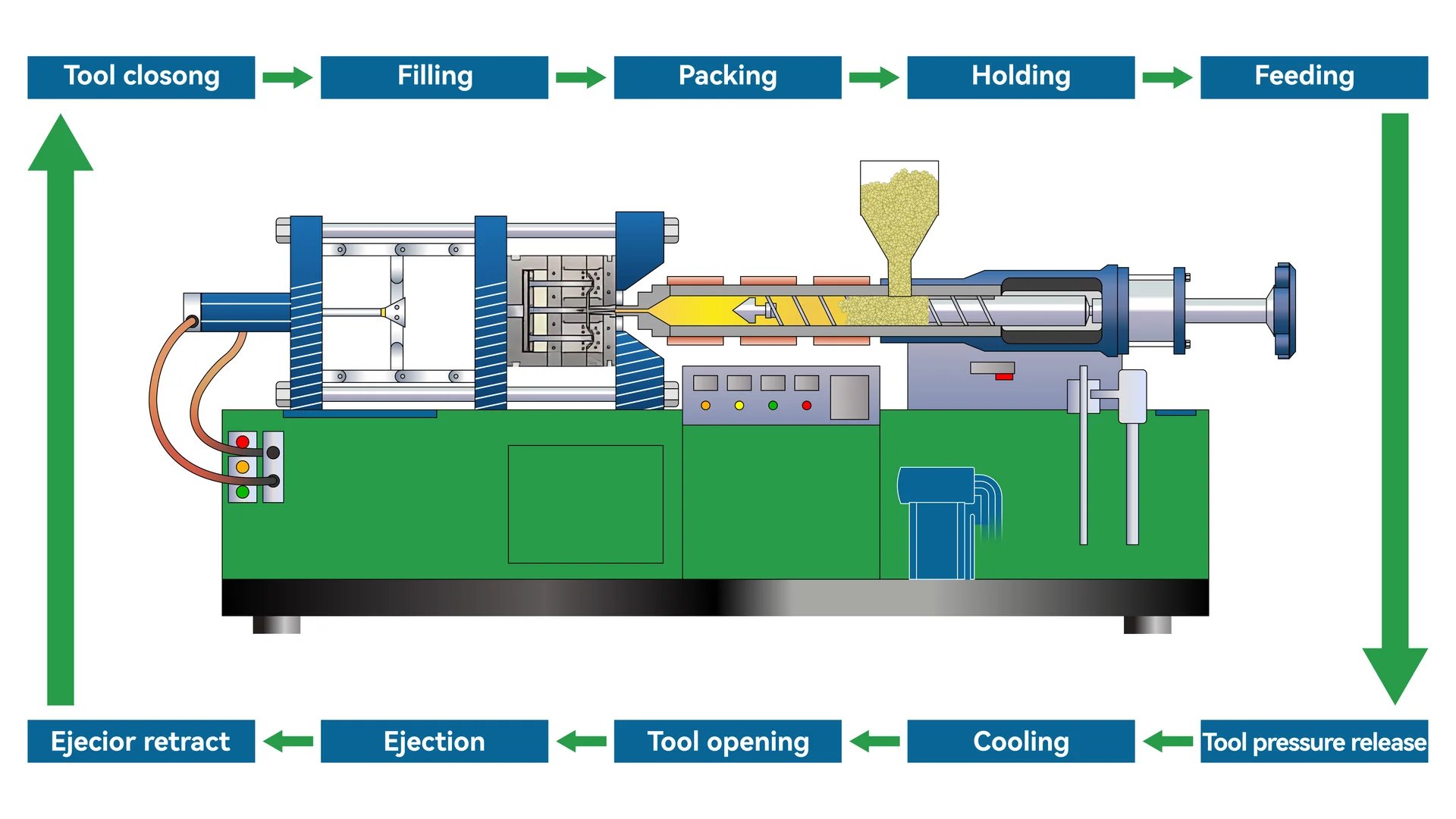
The Basics of Injection Molding
When I first learned about injection molding, it was like discovering the secret recipe behind all those intricate plastic parts we use daily. Imagine creating a tiny replica of a car, complete with all its parts, from scratch! This is what injection molding makes possible. It starts with mold design, which is crucial for defining every little feature of the product.
Mold Design
I remember working on my first toy car project, where every detail mattered. Designing a body mold wasn’t just about the shape—it was like sculpting a mini-masterpiece. We had to ensure the mold captured every contour of the car’s body and even included spaces for adding windows later. For the wheels and axles, separate molds were a must, each crafted to get the perfect circular shape and tread pattern.
| Mold Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Body Mold | Car contours, window provisions |
| Wheel & Axle | Circular shape, tread pattern |
| Multi-Cavity | Multiple parts per cycle |
Using multi-cavity molds felt like hitting the jackpot—it meant producing several pieces in one go, boosting efficiency and saving precious time.
Material Selection
Choosing the right material was always like picking the perfect ingredient for a recipe. The durability and feel of the toy car depended heavily on this choice. ABS was my go-to for its toughness and nice finish. Sometimes, though, for parts that needed to bend without breaking, I’d opt for PP. And when clarity was key, especially for windows, PMMA was unbeatable.
| Plastic Type | Properties |
|---|---|
| ABS | Toughness, rigidity, surface finish |
| PP | Flexibility, impact resistance |
| PMMA | Transparency |
The Injection Molding Cycle
Melting and Injection
Feeding plastic pellets into the machine always felt like starting a magic trick. You’d watch as they melted down into this gooey substance ready to become something new. Each type of plastic had its sweet spot—ABS needed temperatures around 200-260°C to hit that perfect molten state before being injected into the mold with just the right pressure.
Cooling and Ejection
Watching the mold cool and solidify was like seeing an artist’s creation come to life. The suspense as you waited to see if everything turned out just right was thrilling. And once cooled, opening that mold and ejecting the shiny new parts—there’s nothing quite like it.
- Cycle Efficiency: This process could produce parts at lightning speed, perfect for mass production.
- Precision: Maintaining consistent conditions ensured every part met high-quality standards.
Understanding these elements has deepened my appreciation for how crucial injection molding is in bringing countless products to life. If you’re curious about how this process evolves with technology, check out resources like modern manufacturing techniques5 and product design optimization6.
ABS is used for transparent components in molding.False
ABS is known for toughness and rigidity, not transparency.
Multi-cavity molds increase production efficiency.True
They produce several parts per cycle, enhancing efficiency.
Why Choose Multi-Cavity Molds for Manufacturing?
Imagine turning a single moment into multiple masterpieces. That’s the magic of multi-cavity molds in manufacturing.
Multi-cavity molds enhance manufacturing by producing multiple parts simultaneously, increasing efficiency, reducing per-unit costs, and ensuring consistent quality.

Enhanced Production Efficiency
I remember the first time I saw a multi-cavity mold in action—it was like witnessing a well-rehearsed symphony. Each cavity played its part perfectly, churning out identical parts in one go. Imagine if every minute you could produce four components instead of one. That’s precisely what happens with a four-cavity mold—it’s a remarkable boost in production efficiency7.
Cost-Effectiveness
Initially, I was skeptical about the higher upfront cost of these molds. But then it hit me—much like buying in bulk at the grocery store, the cost per unit drastically plummets over time. By spreading raw material and labor costs over more units, it just makes economical sense, especially for mass production.
Consistent Quality and Precision
Precision is everything in industries where a millimeter can make or break functionality. I recall working on a project where we needed to ensure each part was identical down to the finest detail. Multi-cavity molds delivered flawlessly, ensuring material properties remained uniform, minimizing defect rates significantly.
Flexible Design Capabilities
Flexibility is key in design, just like when I used to play with toy cars as a child, imagining endless configurations. With multi-cavity molds, manufacturers can simultaneously produce different components like car wheels and axles. It’s this flexibility that lets us push boundaries and optimize the production process8 creatively.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Produces multiple parts per cycle |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lowers cost per unit |
| Quality | Ensures consistent dimensions and material properties |
| Flexibility | Allows simultaneous production of different components |
Applicability Across Industries
The versatility of multi-cavity molds extends across various sectors—from consumer electronics to the automotive industry. I once visited an automotive plant and was amazed at how these molds efficiently created dashboard panels and door handles with such precision. It’s all about leveraging the right tools to meet those ever-increasing demands.
By embracing these advantages, manufacturers like us can harness the power of multi-cavity molds to streamline production and meet high-volume requirements. The trick is balancing the initial investment against long-term gains. And let’s not forget, choosing the right material selection9 is crucial for maximizing these benefits.
Multi-cavity molds reduce cycle time by producing multiple parts.True
Multi-cavity molds produce several parts per cycle, enhancing efficiency.
Multi-cavity molds increase defect rates in mass production.False
They ensure consistent quality, reducing defect rates through uniformity.
How do cooling and ejection impact the quality of toy cars?
Ever wondered how toy cars are made to be so durable and perfectly designed? It all boils down to the magic of cooling and ejection in their production.
Cooling and ejection are vital in toy car production, preventing warping and defects to ensure durable, visually appealing toys.

The Critical Role of Cooling in Toy Car Creation
I remember my first visit to a toy manufacturing plant. Watching those bright, shiny toy cars come to life was like witnessing a magic trick. But behind that magic is the meticulous cooling phase of injection molding. It’s not just about freezing molten plastic; it’s a dance of temperatures that determines if the toy car will stand up to rigorous play.
The cooling rate is like the heartbeat of the process—it influences how the material crystallizes, which in turn affects durability and that all-important surface finish10. If you rush it, you risk warping or shrinkage, and suddenly, your toy car’s sleek design looks more like a science experiment gone wrong.
Factors Influencing Cooling:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thicker parts require longer cooling times to ensure uniform solidification. |
| Plastic Type | Each plastic has unique thermal properties that dictate specific cooling needs. |
Perfecting Ejection for Top-notch Quality
Ejection might seem straightforward—just pop the part out, right? But I learned that there’s a fine art to it. The mold opens, and you have a few precious seconds to extract the newly minted toy without marring its surface. Done wrong, you end up with scratches or stress marks, imperfections that kids might not notice, but any self-respecting designer can’t ignore.
Ejection Techniques:
- Air Ejection: This method gently uses compressed air, perfect for avoiding surface damage.
- Mechanical Ejection: Pins or blades are the tools of choice here, essential for intricate designs.
Balancing Cooling and Ejection
The most enlightening moment came when I realized how cooling and ejection must work hand-in-hand. Pull the toy out too soon, and it could deform; wait too long, and it becomes brittle. The synchronization is key to crafting robust, beautiful toys.
Case Study: ABS Toy Cars
Ah, ABS plastic—the darling of toy car designers. It’s loved for its toughness and sleek look. But getting it right involves a delicate balancing act with cooling and ejection. Keep temperatures and timing precise to avoid nasty surprises like sink marks or flash—those pesky blemishes that scream "poor quality." Understanding these processes doesn’t just make for a great factory tour story; it equips designers to optimize their craft by mastering material behavior in the injection molding cycle. They can ensure every little car drives off the assembly line as a testament to durability and style.
Slow cooling leads to toy car warping.True
Slow cooling affects material crystallinity, causing warping or shrinkage.
Mechanical ejection reduces surface damage.False
Mechanical ejection can cause scratches; air ejection is gentler.
Conclusion
Injection molding machines create toy cars by injecting molten plastic into precisely designed molds, ensuring quality through careful material selection, temperature control, and efficient cooling and ejection processes.
-
Explore a comprehensive guide to designing intricate molds for toy cars, enhancing your understanding of key elements like body molds. ↩
-
Discover strategies to boost efficiency in mold design processes, ensuring quality while optimizing production time. ↩
-
Learn about ABS’s toughness and durability, crucial for making robust toy cars. ↩
-
Discover how combining plastics enhances toy functionality and appeal. ↩
-
Discover how injection molding integrates with contemporary manufacturing processes for optimized efficiency. ↩
-
Learn strategies to enhance design efficiency and functionality through optimized injection molding practices. ↩
-
Discover how reducing cycle time enhances production efficiency using multi-cavity molds. ↩
-
Explore how multi-cavity designs facilitate efficient manufacturing. ↩
-
Understand the role of materials in optimizing mold performance. ↩
-
Explore how different cooling rates impact the final appearance and texture of molded parts. ↩






