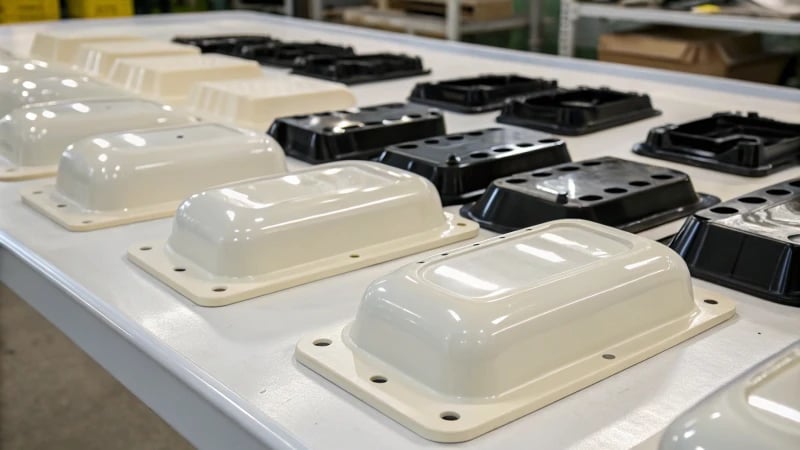
Have you ever seen annoying twists and bends in your plastic products?
Product warpage defects in injection molding stem from mold design, process parameters, and material properties. Key factors include uneven cooling, poor mold release, and material shrinkage. Addressing these issues can significantly reduce warpage.
This summary gives a brief idea about the causes of product warpage. Going into the details is very important. Each factor affects the outcome. For example, the design of the cooling system is important. The choice of material is also important. Exploring these elements helps a lot. People discover new insights and strategies. These insights help prevent warpage in manufacturing processes.
Uneven cooling causes product warpage in injection molding.True
Uneven cooling leads to differential shrinkage, causing warpage.
Mold release mechanisms have no effect on product warpage.False
Improper mold release can lead to stress and deformation.
How Does Mold Design Affect Product Warpage?
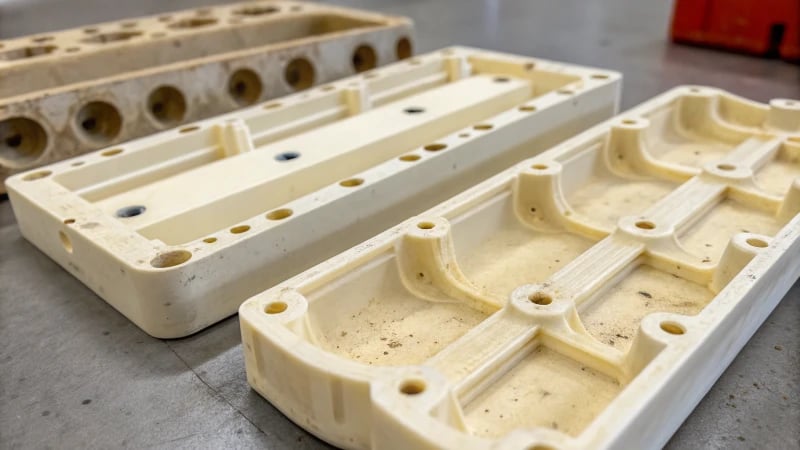
Have you ever thought your plastic product is joking around by bending and twisting unexpectedly?
Product warpage in injection molding usually comes from the mold design. Cooling system layout and demolding mechanisms play important roles. Many problems happen because of uneven cooling. Incorrect force distribution during demolding is another common cause.

The Role of Cooling Systems in Mold Design
Let me lead you through the complex world of mold design. This plays a crucial role in stopping product warping. In my early days, I noticed how tiny errors in design often led to annoying results.
Uneven cooling is a primary cause of product warpage. If the cooling pipes are irrationally designed, the plastic near these pipes cools and solidifies first, while other areas cool more slowly. For instance, when producing large flat products, cooling pipes concentrated in the mold center cause edge parts to cool slower, leading to shrinkage differences1.
Cooling System Parameters
I remember my first encounter with warping from uneven cooling. A large flat product had edges that wouldn’t stay in place. That taught me the importance of balancing cooling pipes. Pipes too centered slowed edge cooling, causing uneven shrinkage and warping.
The effectiveness of cooling is also determined by pipe diameter and spacing. Once, I ignored pipe spacing and diameter, thinking they were minor. But narrow or far-spaced pipes cooled plastic poorly. Warped products came as a result.
| Parameter | Effect on Cooling |
|---|---|
| Diameter | Smaller leads to less cooling |
| Spacing | Larger increases risk of uneven cooling |
It’s very important to set these parameters right for proper cooling.
Demolding Mechanisms and Warpage
Uneven ejector pins taught me another lesson. One project had pins not evenly placed. Demolding forces led to clear warping.
The mold release mechanism must be carefully considered. Uneven forces during demolding can lead to product warpage2. Products with inverted structures may experience warpage if mechanisms like sliders exert uneven forces.
Injection Molding Process Factors
Injection Pressure and Holding Pressure
Excessive injection pressure is stressful, like over-packing a suitcase. A product with varying wall thickness warped towards thicker walls due to pressure imbalance during demolding.
High holding pressure particularly affects products with uneven wall thickness, causing warping towards thicker walls.
Mold Temperature and Melt Temperature
I tried high mold temperatures for better fluidity but this increased shrinkage and warpage in crystalline plastics.
Higher mold temperatures prolong plastic melt cooling time, increasing shrinkage and deformation risks.
Finding the perfect temperature balance is essential.
Injection Speed
Fast injection may seem efficient but causes high shear stresses. I faced uneven melt distribution with rapid injection which led to unexpected warpage.
Fast injection speeds generate large shear stresses in the cavity forming residual stresses that cause post-demolding warpage.
Material Factors Influencing Warpage
Shrinkage Rate Variations
different plastics react differently to heat; Polyamide warped my long product due to its high shrinkage rate during cooling easily leading to warpage issues3. Considering directional shrinkage is necessary in mold design.
directional (anisotropic) shrinkage might affect long products differently along their length and width.
different plastics have varying shrinkage rates; Materials like polyamide exhibit large shrinkage during cooling easily leading to warpage issues4.
directional (anisotropic) shrinkage might affect long products differently along their length and width.
different plastics have varying shrinkage rates; Materials like polyamide exhibit large shrinkage during cooling easily leading to warpage issues5.
directional (anisotropic) shrinkage might affect long products differently along their length and width.different plastics have varying shrinkage rates; Materials like polyamide exhibit large shrinkage during cooling easily leading to warpage issues6.
directional (anisotropic) shrinkage might affect long products differently along their length and width.different plastics have varying shrinkage rates; Materials like polyamide exhibit large shrinkage during cooling easily leading to warpage issues7.
directional (anisotropic) shrinkag
Uneven cooling causes product warpage in mold design.True
Uneven cooling leads to differential shrinkage, causing warpage.
Smaller pipe diameter increases cooling efficiency.False
Smaller diameter pipes provide less cooling, increasing warpage risk.
How Does Injection Pressure Affect Warpage?
Have you ever wondered why some plastic parts just don’t stay straight?
Injection pressure impacts warpage by altering residual stress and cooling shrinkage. Very high pressure likely causes uneven cooling, which probably results in warpage. Precise adjustment of injection parameters reduces these effects.
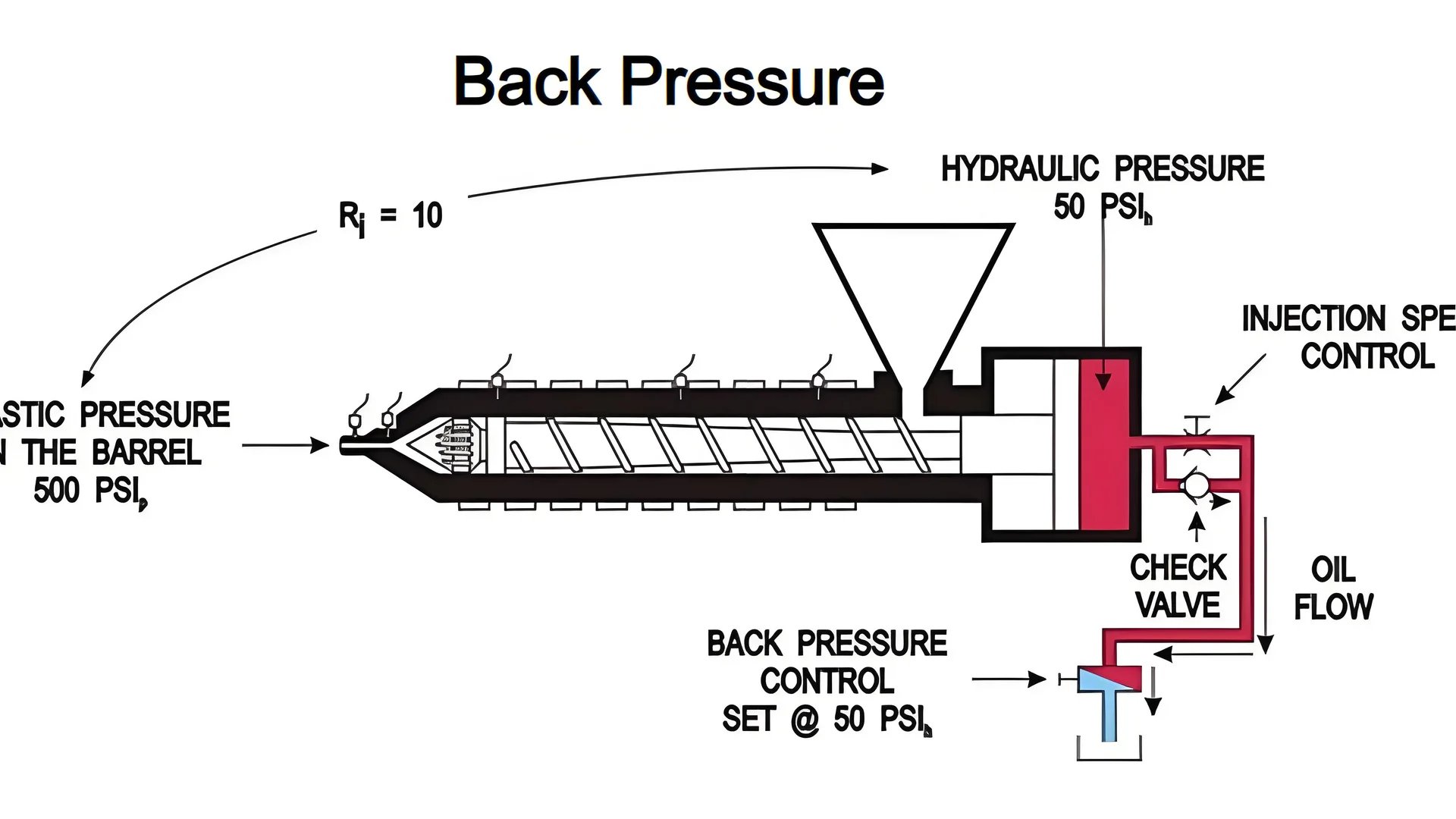
Understanding Injection Pressure’s Impact
When I started designing molds, injection pressure caught my interest. It seemed small but could decide a project’s success or failure. It’s like a secret ingredient that must be perfect. High pressure can push molten plastic too hard against mold walls. This creates uneven stress during cooling. I recall a project where a little extra pressure warped our product. We tried to hurry—lesson learned indeed!
Injection pressure directly affects how the molten plastic fills the mold cavity. During the injection molding process8, if the pressure is too high, it can lead to excessive force on the mold walls, causing internal stresses that are unevenly distributed, especially during cooling.
Factors Contributing to Warpage:
- Residual Stress: High injection pressure builds stress inside the part. Once out of the mold, it acts like a tense spring, often causing warping.
- Shrinkage Variation: Think of homemade cookies baking unevenly. Uneven shrinkage happens when areas near the mold walls cool faster than those inside due to incorrect pressure.
| Factor | Effect on Warpage |
|---|---|
| Residual Stress | Causes distortion post-cooling |
| Shrinkage Variation | Leads to uneven contraction |
Balancing Pressure and Cooling
Accurate injection and holding pressure can change everything. Properly adjusting these settings for days on a project ensured that plastic finally flowed into the mold without extra stress—perfecting this process is key.
Properly adjusting the injection and holding pressure9 can help minimize warpage. It’s crucial to find a balance where the plastic flows evenly into the mold without causing excessive stress.
Mold Design Considerations
Pressure isn’t the only factor; mold design matters a lot:
- Cooling System Design: An improper cooling system is like baking a cake in a cold oven. Pipes must be evenly spread to cool all mold parts consistently.
- Release Mechanism: Uneven demolding forces are like a stuck zipper—they frustrate and deform products. Balanced ejector pins prevent these problems.
In addition to managing injection pressure, consider factors like:
- Cooling System Design: An irrational design may exacerbate warpage; cooling pipes should be evenly distributed to ensure uniform cooling across all sections.
- Release Mechanism: Ensure demolding forces are balanced as uneven forces during demolding can lead to further product deformation.
Material Selection’s Role
Choosing the right plastic is also critical:
Some plastics, like crystalline ones, shrink more under high pressure and tend to warp more during cooling. Selecting materials with proper shrinkage rates prevents many headaches.
Different plastics react differently under high pressure; for instance, crystalline plastics may show more pronounced warpage due to their natural tendency to shrink more during cooling. Selecting materials with suitable shrinkage rates and crystallinity is essential.
Mastery of these elements dramatically reduces defects—designers like Jacky see this in action as products maintain their integrity and waste is minimized—this success is very rewarding.
High injection pressure increases residual stress.True
Excessive pressure during molding adds internal stresses, leading to warpage.
Proper cooling system design reduces warpage risk.True
Even cooling prevents uneven shrinkage and reduces distortion in molded parts.
How Do Material Properties Influence Warpage?
Do you ever wonder how small changes in materials twist whole products? It’s really interesting! Let’s look at the hidden forces that shape what we create.
Material properties like shrinkage rate, crystallinity and thermal expansion are very important in plastic manufacturing. These properties influence warpage significantly. Cooling and stress affect how materials behave. This can really lead to deformations.
Shrinkage Rate and Its Impact
My first experience with shrinkage rates10 was during a project with polyamide (PA). I watched a carefully crafted part twist out of shape, like a magic trick gone wrong. Materials with high shrinkage change significantly as they cool, causing different stresses across the product. In injection molding, ignoring these differences is like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole—things just do not fit.
| Material | Typical Shrinkage Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Polyamide (PA) | 0.8 – 2.0 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 1.0 – 2.5 |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 0.4 – 0.8 |
The Role of Crystallinity
Crystallinity plays a major role in shrinkage behavior. Imagine how crystalline plastics like polyethylene (PE) cool into neat ordered structures; it’s like puzzle pieces snapping into place. However, if pieces spread unevenly, warpage occurs. I have seen that uniform crystallization is really key to preventing these problems during the injection molding process11.
Thermal Expansion Coefficients
I discovered that the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is a vital factor dictating dimensional changes as temperatures shift. Materials with high CTE change considerably from molten states, so proper control during design and processing is important to reduce warping.
| Material | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (µm/m°C) |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 100 – 200 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 65 – 70 |
| Nylon | 80 – 120 |
Balancing Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties, such as modulus of elasticity, often surprise me with their impact on warping. Low-stiffness materials might bend under stress when cooling, but ensuring an even distribution of mechanical stress really helps lower this risk during cooling12.
Anisotropic Behavior of Materials
Anisotropic behavior was a revelation for me—in these materials, properties like shrinkage or strength vary by direction. In injection molding, such materials can shrink more in one direction than another, leading to warping if not considered in the design phase. Understanding this behavior actively helps in reducing defects in molded products.
In many projects, I learned that warpage is complex—like layers of an onion—with mold factors such as cooling systems and material details each playing an important role in determining a product’s final quality.
Polyamide has a lower shrinkage rate than ABS.False
Polyamide's shrinkage rate is higher (0.8-2.0%) than ABS (0.4-0.8%).
High CTE materials are prone to warpage.True
Materials with high thermal expansion coefficients change dimensions significantly, causing warpage.
What Are Effective Strategies to Minimize Warpage?
Ever struggled with warping in your production line? It’s really frustrating, isn’t it? Let’s explore practical ways to solve this problem. Keep your products in excellent condition.
To reduce warpage, pay attention to cooling systems. Adjust injection pressures carefully. Select the right materials for the job. These methods are important. These methods target mold design. They also focus on process parameters. Material selection also plays a big role. It leads to less distortion. It really improves quality.

Mold Factors
-
Cooling System Design: When I started with mold design, I noticed how important the cooling system is. Uneven cooling is a major cause of warpage. If cooling pipes are not distributed evenly, different parts of the plastic will cool at different rates. Imagine large flat items with cooling only in the center; edges stay warm, making the cooling uneven.
Parameter Effect on Warpage Cooling Pipe Size Small diameters may cause insufficient cooling Pipe Spacing Large spacing results in uneven cooling -
Mold Release Mechanism: I also found out how vital a good mold release system is. Uneven forces during demolding can lead to warpage. Picture opening a delicate shell with unequal pressure; you might get cracks or even break it completely.
Injection Molding Process Factors
-
Injection Pressure: Injection pressure is tricky. Excessive pressure during injection can lead to high residual stresses. Once, too much pressure left hidden stresses in the product, leading to bending in thicker areas.
-
Mold Temperature: Then there’s mold temperature. Higher temperatures make cooling slower and increase shrinkage.
Temperature Factor Result Mold Temperature Longer cooling, more shrinkage Melt Temperature Increased fluidity, higher shrinkage -
Injection Speed: Injection speed needs careful handling. Fast speeds generate shear stresses that result in internal residual stresses, leading to post-demolding warpage.
Plastic Material Factors
-
Shrinkage Rate: Now, about plastic – each type shrinks differently. Plastics like polyamide have high shrinkage rates, causing warpage.
-
Crystallinity: Crystallinity matters too. Uneven crystallization leads to different shrinkage rates.
By considering these factors and implementing smart solutions13, manufacturers can significantly reduce warping in their products, leading to better quality and efficiency. Check out special molding methods14 for better results and investigate various plastics15 to pick the best ones with less warpage.
Uneven cooling causes warpage in plastic products.True
Uneven cooling leads to differential shrinkage, causing warpage.
Higher mold temperatures reduce warpage in injection molding.False
Higher mold temperatures increase cooling time and shrinkage, causing warpage.
Conclusion
Product warpage in injection molding arises from uneven cooling, mold design flaws, improper pressure settings, and material properties. Addressing these factors is crucial for quality manufacturing.
-
Explore how the layout of cooling systems impacts the uniformity of product cooling, affecting shrinkage and warpage. ↩
-
Discover how different injection pressures influence residual stress levels within molded plastics. ↩
-
Learn about the best practices in injection molding that help mitigate warpage risks effectively. ↩
-
Learn about the best practices in injection molding that help mitigate warpage risks effectively. ↩
-
Learn about the best practices in injection molding that help mitigate warpage risks effectively. ↩
-
Learn about the best practices in injection molding that help mitigate warpage risks effectively. ↩
-
Learn about the best practices in injection molding that help mitigate warpage risks effectively. ↩
-
Gain insights on how injection pressure influences the molding process, helping you optimize settings for quality parts. ↩
-
Discover best practices for setting injection and holding pressures to minimize warpage and improve product quality. ↩
-
This link provides detailed data on shrinkage rates across various plastics, essential for designers managing warpage. ↩
-
Learn about the relationship between crystallinity and injection molding processes to better control product quality. ↩
-
Explore effective cooling strategies to minimize warpage and ensure uniform material properties. ↩
-
This link provides deeper insights into proven techniques for reducing warpage during the molding process. ↩
-
Explore advanced methods in injection molding that help in minimizing product distortion and improving quality. ↩
-
Understand how different plastic properties influence warpage and how to choose the right materials for your needs. ↩






