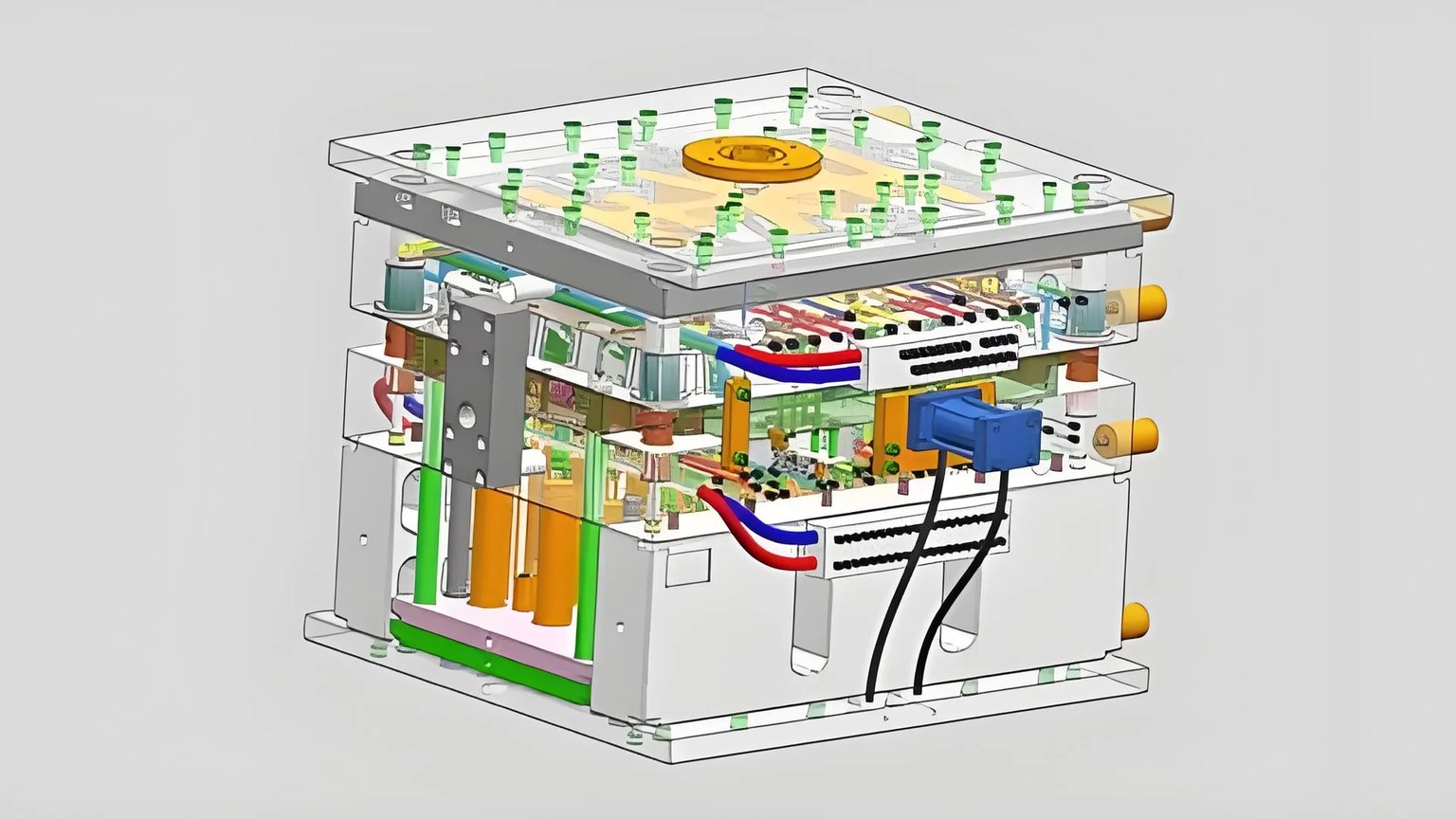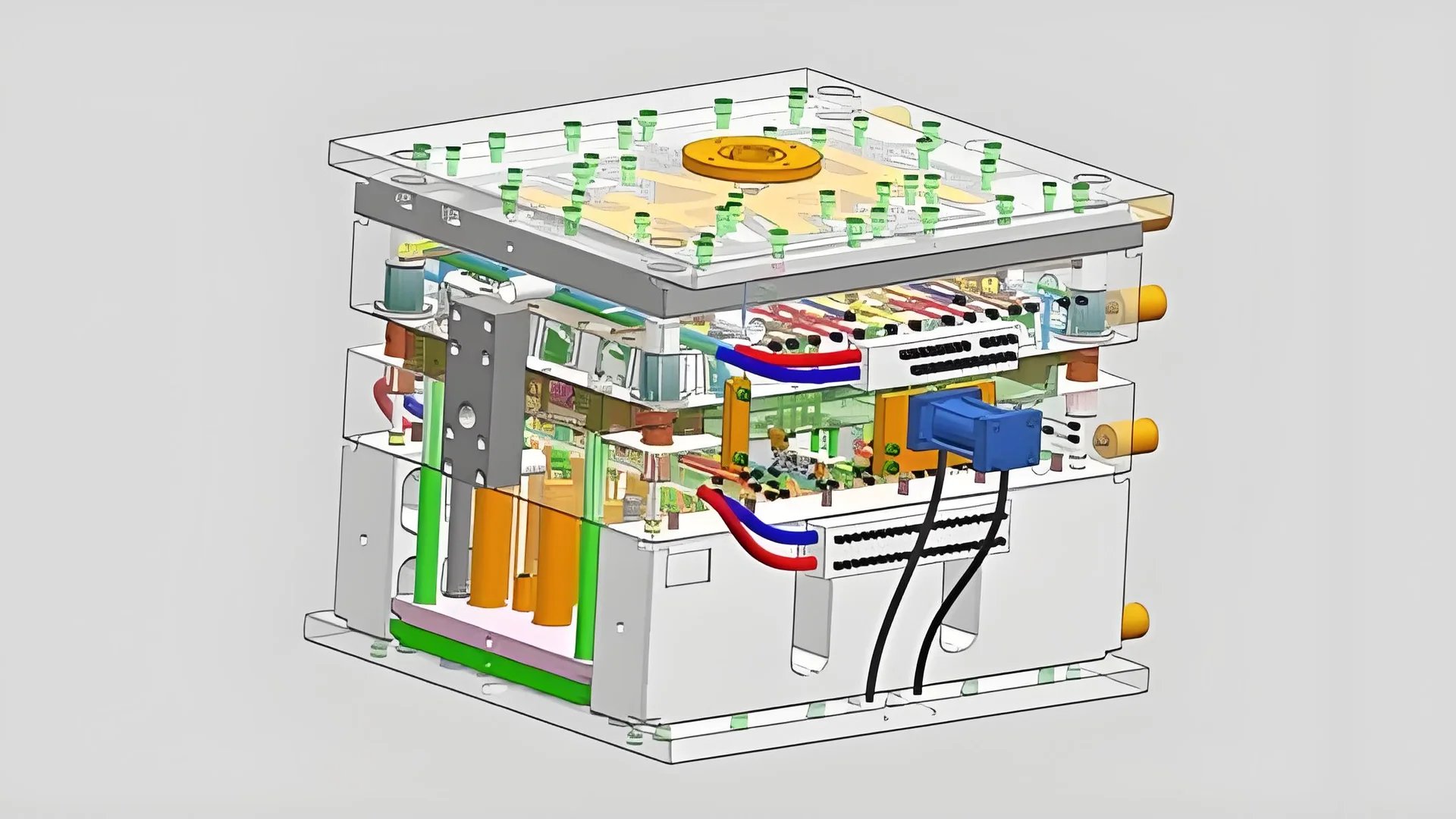
I never understood how important mold cooling systems truly were until witnessing them at work. They play a critical role in the process. Mold cooling is essential.
The mold’s cooling system moves coolant through channels. This removes heat from the mold. It speeds up plastic solidification. Production becomes faster. Quality really improves by stopping warping. The mold lasts longer without overheating damage.
I remember watching a factory tour. The guide explained why good cooling systems matter in injection molding. It was fascinating. These systems really reduce the molding cycle time, especially for thin-walled products. Heat must be managed well. This improves production speed. Quality stays high too. Good cooling stops overheating. Overheating might harm molds. Such cooling changes manufacturing and product quality.
Cooling systems shorten the molding cycle.True
Effective cooling systems reduce the time needed for plastic to solidify.
Oil is the most common cooling medium in molds.False
Water is the most common due to its high specific heat capacity and low cost.
How Does the Cooling System Impact Mold Efficiency?
Have you ever thought about why your injection molding process is not really efficient? Your cooling system could be the key. An efficient cooling system really matters. It often affects the whole process.
A cooling system in injection molding is vital. It reduces cycle times and helps improve product quality. It also extends mold life. This system manages temperatures well. Proper temperature control is very important.
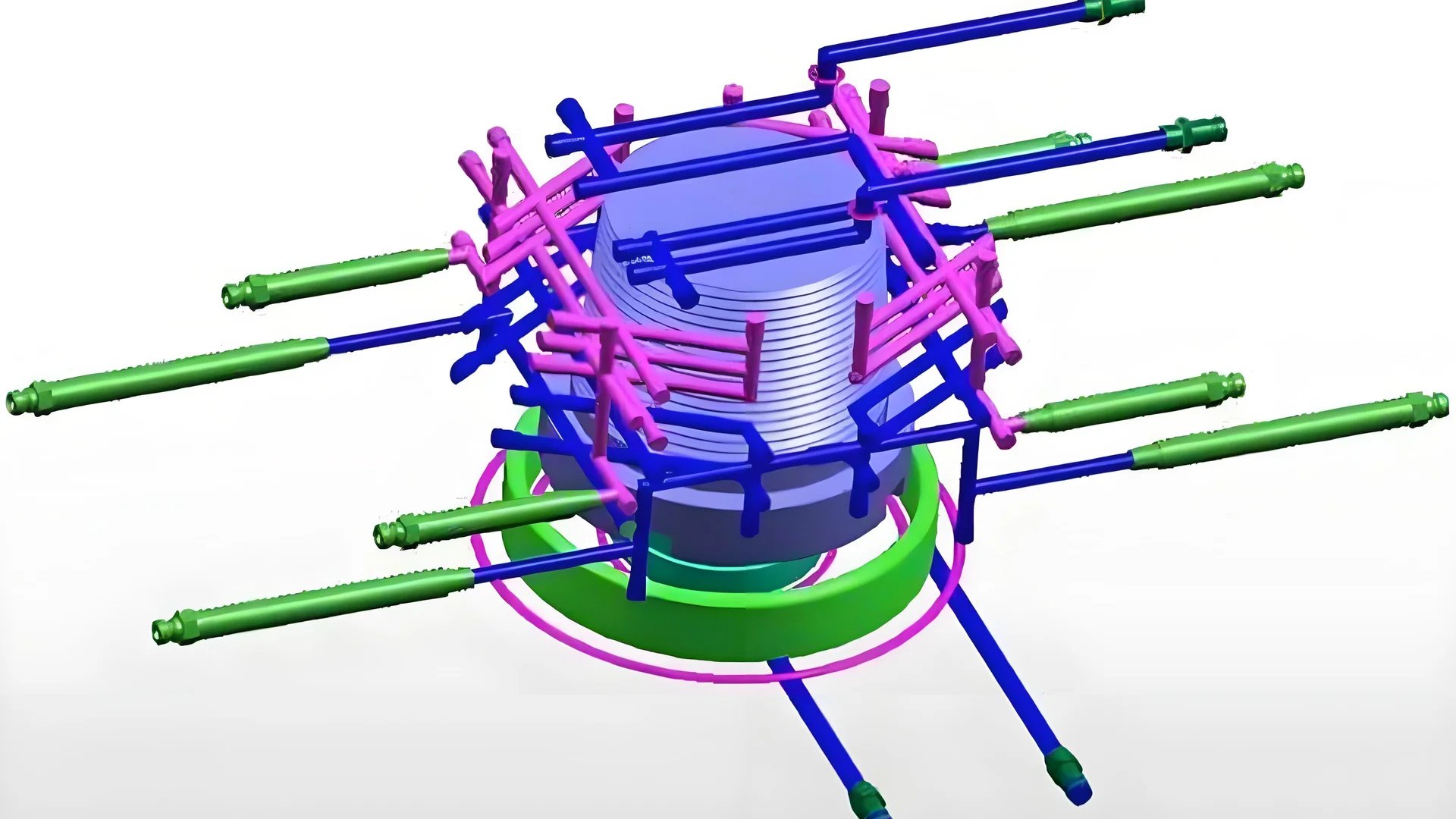
Shortening the Molding Cycle
When I started with injection molding, I was really surprised by how much the cooling system affected the process. Imagine hot, melted plastic entering a mold, ready to take shape. But it needs to cool down fast. It must become solid quickly to be removed from the mold so the next batch can start. That’s when the cooling system steps in, like a hero calming down a heated scene.
Once, we worked on speeding up production for thin containers. Our cycle time was too long, wasting valuable minutes. We adjusted our cooling setup. This change reduced our cycle time drastically – from thirty seconds to just over ten. It felt like watching slow motion turn to real-time. It was easier to meet our goals.
Improving Product Quality
Uniform cooling is essential for maintaining high-quality standards in molded products. Once, we faced a problem with warped large parts. Everything else was fine except the cooling. Uneven cooling caused parts to shrink at different speeds. By changing the cooling channels for even cooling, we got flat panels consistently. Cooling has a massive impact on quality—really impressive impact.
Understanding the importance of cooling uniformity1 is key to producing consistent, high-quality parts.
Extending Mold Life
Cooling is crucial for speed and quality and also for mold life. A mold we used started cracking from too much heat. Then I realized – keeping the mold cool prevents damage and extends its life. With optimal cooling, we stopped early wear and saved on repairs.
Proper efficient mold management2 includes optimizing the cooling system to avoid premature wear and costly repairs.
Key Components of a Cooling System
With more mold work, I valued the cooling systems’ details:
- Cooling Channels: Linear, circular or spiral channels depend on the mold’s shape. Spiral channels often provide better cooling for odd shapes.
- Cooling Medium: Water is usually my choice for its low cost and efficiency; however, treated water or oil works best for precise work.
- Cooling Connectors: Good connectors are important to stop leaks and keep things running smoothly.
The role of effective connectors3 in ensuring reliable operation cannot be overstated.
Design Considerations for Cooling Systems
Designing a cooling system feels like solving a puzzle:
- Distance from Cooling Channel to Cavity Surface: The optimal distance balances efficiency and surface quality.
- Channel Layout: Must fit perfectly with symmetrical designs preferred for regular shapes while complex designs require detailed analysis.
- Flow and Flow Rate: Proper control prevents vibration and ensures adequate cooling without compromising precision.
Ultimately, an optimized cooling design4 contributes significantly to both productivity and quality in injection molding processes.
Looking back, I see how vital the cooling system is in this field—whether improving an existing process or starting new—knowing its role is essential for productivity and quality.
Cooling systems shorten injection molding cycles.True
Effective cooling systems reduce heat quickly, allowing faster demolding.
Oil is the most common cooling medium in molding.False
Water is more commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and cooling efficiency.
How Do Cooling Channels Affect Product Quality?
Have you ever thought about how cooling channels might greatly affect the quality of a product?
Cooling channels play a vital role in keeping product quality steady. They help distribute heat evenly during manufacturing. Good channels stop problems such as warping and size changes. This action improves the product’s strength. It’s really important.

The Role of Cooling Channels in Manufacturing
I remember my first walk through the manufacturing floor. The noisy machines and complex processes surrounded me. The injection molding area really stood out. Cooling channels there performed a quiet yet vital job. They kept everything at the perfect temperature.
Cooling channels are vital in manufacturing, especially for injection molding. They remove extra heat from molds, which helps to shorten the molding cycle5 time significantly. Think about changing cycle times from many seconds to just a few; that is very efficient. This efficiency is crucial for thin-walled products.
Impact on Product Quality
Different cooling methods produce different results. I recall a project with uneven cooling that ruined a batch of products due to noticeable warping—very disappointing indeed. Uniform cooling is key to product quality as it lowers internal stress and warping, ensuring products meet high-quality standards, especially for large or complex parts.
Components and Design Considerations
Every design detail is important when considering cooling channels. Shapes like linear, spiral, or circular affect temperature distribution significantly. I noticed spiral channels helped with uniform cooling, particularly in round molds.
The space between channels and molds is crucial too; the precision needed amazed me. Ideally, this should be between 1.5 to 2.5 times the channel diameter to avoid excessive temperature gradients that could affect surface quality—it’s like threading a needle with heat.
Prolonging Mold Longevity
Proper cooling designs do more than improve quality; they extend mold life by preventing prolonged exposure to high temperatures that might crack molds—similar to not overheating a favorite skillet.
Cooling Channel Layout and Efficiency
Arranging cooling channels for a mold’s shape is quite artistic. Simple shapes use symmetrical layouts while complex designs need advanced mold flow analysis6 to perfect every detail and ensure comprehensive coverage without losing precision.
Adjusting coolant flow rates using valves and pumps further refines this process, matching it to specific mold sizes and product requirements.
Reflecting on these insights, cooling channels are crucial in manufacturing as they play a major role in creating high-quality products. Each decision—from channel layout to coolant flow—contributes to exceptional results.
Cooling systems reduce injection molding cycle time.True
Effective cooling systems quickly remove heat, shortening the molding cycle.
Oil is the most common cooling medium in injection molding.False
Water is the most common cooling medium due to its high specific heat.
What Are the Key Components of a Mold Cooling System?
Have you ever thought about how plastic parts get their perfect shape? The answer lies in something many people overlook꞉ the mold cooling system in injection molding.
A mold cooling system has cooling channels, cooling media and connectors. These parts work together to take away heat from the mold. They remove heat efficiently. This leads to even cooling. This process helps produce items of high quality.
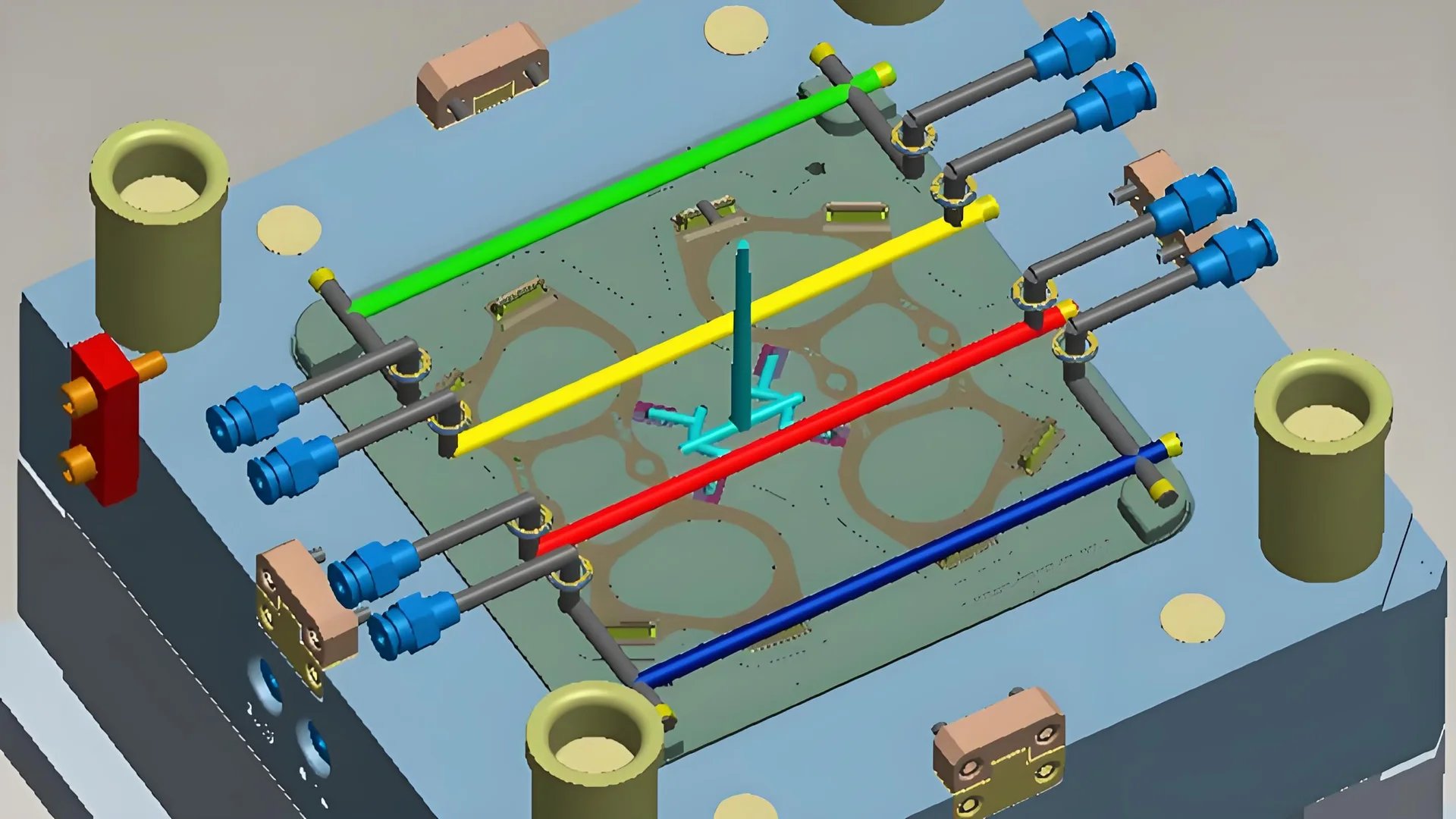
Role of Cooling Systems
Cooling systems play a crucial role in injection molding by efficiently removing heat from the mold. This allows molded products to solidify quickly, reducing cycle time significantly. It’s like a magic trick where time goes from many seconds to just a few, especially for thin designs. Speed is not the only thing that matters; high-quality products come from even cooling. Uniform cooling is essential for reducing internal stress and preventing warping in finished products, which is crucial for big, flat pieces.
Maintaining optimal mold temperatures prevents damage due to heat fatigue, thereby extending mold lifespan. I saw how keeping the right temperature makes the mold last longer and protects it from breaking down.
Components of a Mold Cooling System
Cooling Channels
Cooling channels are integral to a mold’s structure and can be straight, circular, or spiral. Their design directly affects cooling efficiency. For instance, using spiral channels helped evenly cool a round product once. The diameter of these channels significantly impacts their effectiveness:
- Smaller diameters limit coolant flow and cooling efficiency.
- Larger diameters may weaken the mold.
Cooling Media
Water is the hero due to its low cost and high heat capacity. However, specific applications may require treated water or antifreeze mixtures to prevent scaling or freezing. In scenarios where water isn’t suitable due to material reasons, switching to oil was necessary despite its higher cost and fire risk.
Cooling Connectors
Connectors might seem boring but are essential for linking cooling channels with external systems. High-quality connectors ensure a leak-proof seal and reliable coolant flow. The hoses must resist rusting and provide flexibility for installation adjustments.
Design Considerations
Channel Distance from Cavity
The spacing between the cooling channel and the mold’s surface was tricky for me at first. It is best to keep it 1.5 to 2.5 times the channel diameter to avoid large temperature gradients that affect product quality.
Channel Layout
Channel layout acts like a map for traveling efficiently through the mold’s shape:
- Symmetrical layouts result in even cooling for regular shapes.
- Complex shapes often require customized designs derived from mold flow analysis7.
Coolant Flow Control
Controlling coolant flow is like tuning a musical instrument:
- Too much flow causes shaking.
- Too little hurts efficiency.
Adjustments are made via valves or pumps using temperature differential measurements to optimize flow rates for larger molds.
Cooling channels improve product quality by reducing warping.True
Uniform cooling reduces internal stress, preventing warping and distortion.
Oil is the most common cooling medium in injection molding.False
Water is commonly used due to its large specific heat capacity and low cost.
How Does Cooling Media Choice Impact Mold Performance?
Ever thought about how the cooling media in injection molding could be a game-changer? Let’s dive into how this choice affects every aspect of mold performance.
Selecting the correct cooling material is key for mold performance. It impacts cooling speed. This directly affects how long each cycle takes. It also influences product quality. It really matters for mold durability. Water is often used. It is both efficient and affordable. Oil is another choice. It cools more slowly, suitable for certain materials. The correct cooling medium increases production speed. It also keeps quality consistent.
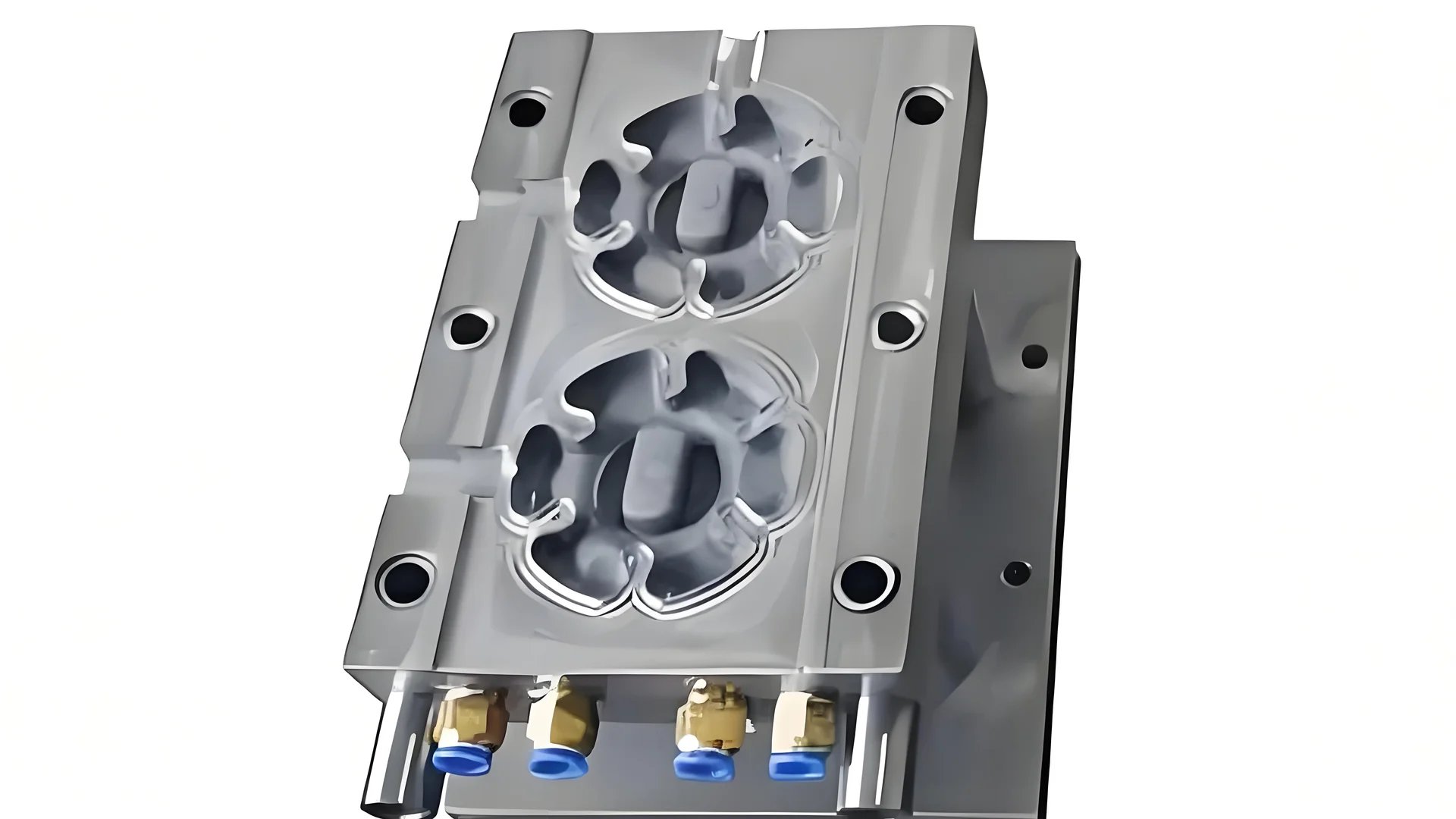

The Role of Cooling Media in Injection Molding
When I started with injection molding, I was really surprised by how cooling media affected the process. It’s like picking between coffee or tea; each serves different needs. In molding, whether you use water, oil, or another liquid, your choice controls how the mold deals with heat. Water is popular because it handles heat well and costs less, but it might cause scaling if untreated. I remember facing scaling issues – it was a big problem! Oil costs more but works well for slow cooling where control matters.
Understanding these dynamics helps optimize injection molding processes8 and ensure consistent product quality.
Effects on Cycle Time and Production Efficiency
I still remember realizing increased speed with water. Thin plastic items went from taking a long time to just seconds. Imagine your daily travel time cut in half – that’s how water impacts cycle times. Sometimes, though, a slower method is better, like when steady temperature changes matter, making oil the right option.
The choice between these media should be aligned with the production goals and material characteristics to maximize efficiency.
Impact on Product Quality and Mold Longevity
Even cooling is vital. It stops bending, like when wood warps with moisture. Picking the right media enhances product quality and prolongs mold life by avoiding heat damage.
Using an optimal cooling medium ensures that temperature variations within the mold are minimized, thereby preventing warping and enhancing dimensional accuracy.
Additionally, the right cooling media can prolong mold life by preventing thermal fatigue.
Considerations for Cooling System Design
Designing a cooling system is like solving a puzzle; each part must fit perfectly. You need to get channel layouts and flow rates just right. Spiral or circular channels might sound fancy, but they keep temperature even. Watch flow rates; they’re like stereo volume – off balance can ruin things.
By measuring the temperature difference across the cooling system, operators can fine-tune flow rates to meet specific production requirements9.
Cooling channels improve mold life.True
Proper cooling prevents high temperatures, reducing mold fatigue and damage.
Oil is the most common cooling medium.False
Water is the most commonly used cooling medium due to its efficiency.
What are the key principles for effective mold cooling?
Have you ever thought about staying calm in mold design? Good cooling improves product quality and efficiency. Yes, it really does. It probably transforms everything.
Effective mold cooling requires carefully designing the cooling channel layout. The distance from the mold cavity should be appropriate. The coolant flow rate must be controlled. This approach helps spread heat evenly. Uniform heat distribution decreases cycle times. High product quality is maintained. No defects like warping happen. Mold life becomes longer.

The Role of Cooling Systems
Imagine those days when you’re rushing to finish tasks and time seems to fly by. That’s how I feel with injection molding10. Cooling systems help speed up the process and keep quality high. By rapidly dissipating heat, they enable quicker solidification of the plastic melt, allowing molds to open sooner. This is crucial for thin-walled products where every second is crucial.
Optimizing Product Quality
I remember dealing with warping in big, flat products. It was frustrating to see them bend! Uniform cooling minimizes internal stress and prevents warping. When parts cool unevenly, they shrink differently, leading to defects. An effectively designed system reduces dimensional deviations, ensuring flatness in large plate-like products. A balanced approach to cooling can thus maintain high-quality standards.
Extending Mold Life
Taking care of molds is like caring for an old car. Good maintenance stops damage. Proper cooling prevents the mold from enduring prolonged high temperatures, which can lead to heat fatigue and mechanical deterioration. By controlling the mold’s temperature within an optimal range, the risk of cracks is minimized, significantly extending the mold’s service life.
Components of an Effective Cooling System
- Cooling Channels: Choosing the right type matters. Circular channels are great for round molds, spreading temperature evenly.
- Cooling Mediums: Water is cheap and useful; however, oil may be used for sensitive materials despite its slower rate and higher cost.
- Connectors: Leaks cause problems. I use high-quality connectors to prevent this.
Cooling Channel Design Points
- Distance to Cavity: This needs balance—typically 1.5-2.5 times the channel diameter ensures a balanced temperature gradient without compromising product surface quality.
- Channel Layout: Must suit the cavity’s shape and product structure; symmetrical layouts are ideal for uniformity while complex structures need tailored arrangements based on mold flow analysis.
Coolant Flow Management
Managing coolant flow is like tuning musical instruments—precision is key to remove heat without causing issues. Effective coolant flow ensures efficient heat removal without causing vibrations that affect precision. I adjust flow rates with valves and pumps; watching temperature changes helps in checking effectiveness. In large molds, higher flow rates are necessary for optimal cooling efficiency.
These ideas are not just theories—they are real steps I use to raise production quality and cut costs.
A cooling system shortens the molding cycle.True
Efficient cooling removes heat quickly, reducing cycle time.
Oil is the most common cooling medium in mold systems.False
Water is commonly used due to its high specific heat capacity.
Conclusion
Mold cooling systems are vital in injection molding, enhancing production efficiency by shortening cycle times, improving product quality through uniform cooling, and extending mold life by preventing overheating.
-
Explores how uniform cooling prevents product defects. ↩
-
Learn strategies to enhance mold durability. ↩
-
Understand how connectors impact system reliability. ↩
-
Find comprehensive guidelines for designing efficient systems. ↩
-
Learn about how cooling channels expedite manufacturing cycles. ↩
-
Explore techniques for optimizing cooling channel placement. ↩
-
Discover strategies for effective cooling channel layouts in intricate molds. ↩
-
Explore why water is preferred for efficient cooling in molding. ↩
-
Discover techniques for fine-tuning coolant flow for better efficiency. ↩
-
Explore how cooling systems improve injection molding efficiency and product quality. ↩