Injection molding is more than melting plastic. It’s both art and science.
Injection pressure is very important for plastic products’ shrinkage. High pressure lowers shrinkage because it compacts the melt. Low pressure increases shrinkage. This happens when the mold does not fill completely.
Imagine you are baking a cake and the batter does not fully fill the pan. The cake ends up uneven. When injection pressure is too low, the plastic melt does not completely fill the mold. This causes uneven shrinkage, like that unfinished cake. Conversely, too much pressure squeezes the molecular chains closely together. Shrinkage decreases and the result is a denser and more uniform product. In my experience, discovering the perfect injection pressure is similar to perfecting a cooking recipe. It demands careful attention and some experimentation. This balance probably improves product quality. It also boosts manufacturing efficiency.
High injection pressure reduces plastic shrinkage.True
High pressure compacts the melt, reducing shrinkage and local differences.
Low injection pressure ensures uniform mold filling.False
Low pressure can lead to insufficient filling, increasing shrinkage.
What Happens When Injection Pressure Is Too High?
Did you ever think about how changing injection pressure could change molding? Let’s look at the wonders and mistakes of finding the right balance.
High injection pressure compacts the plastic melt tightly. This reduces both overall and local shrinkage differences in molded items. Product quality becomes more consistent. Quality stays the same.

Effects on Shrinkage
High injection pressure in molding feels like getting everything right, only to find you’ve gone overboard. I recall when we pushed things too far at the factory. The plastic became so dense, similar to packing a suitcase for a long journey. This tight packing in the mold lowered the usual shrinkage1 we expect.
For example, polycarbonate often shrinks about 0.5%, but here it might only shrink 0.3%. It’s like squeezing into jeans after a hot wash – everything feels much snugger!
| Material | Normal Shrinkage | High Pressure Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 0.5% – 0.7% | 0.3% – 0.5% |
Local Shrinkage Differences
Complex molds with tricky shapes are like puzzle pieces in our business. High pressure spreads the melt evenly, smoothing out bumps between thick and thin walls, reducing local shrinkage differences2. It changes our outcomes, like how an iron flattens wrinkles on a shirt.
Impact on Equipment and Maintenance
But there’s another side to this story. Machinery wears down fast due to high injection pressure which can cause wear on mold components and may require more frequent maintenance to prevent damage, akin to fruit rotting in a time-lapse video. Frequent maintenance becomes essential to keep everything working well and maintain equipment longevity3.
Considerations in Automotive Applications
In automotive uses, it’s really different. Too much pressure in diesel engines can cause engine knock – a sound nobody wants to hear or damage fuel injectors. Perfect calibration for engine components4 is needed to keep things running smoothly.
Adjustments and Solutions
Balance is crucial – like spinning a plate on a stick. Monitoring systems really help maintain the right pressure level, helping keep production stable across various setups and ensuring consistent production5. Consistent production prevents those dreaded "uh-oh" moments.
High pressure reduces polycarbonate shrinkage to 0.3%.True
Excessive pressure compacts the melt, reducing shrinkage to 0.3%.
High injection pressure increases equipment longevity.False
High pressure causes wear, requiring more maintenance, reducing longevity.
Why Does Low Injection Pressure Increase Shrinkage?
Have you ever pondered why your well-crafted mold sometimes fails to create flawless components? Let’s explore how injection pressure contributes to shrinkage.
Low injection pressure causes more shrinkage. It stops the plastic melt from filling the mold completely. This results in more pores. Higher volume shrinkage appears during cooling.
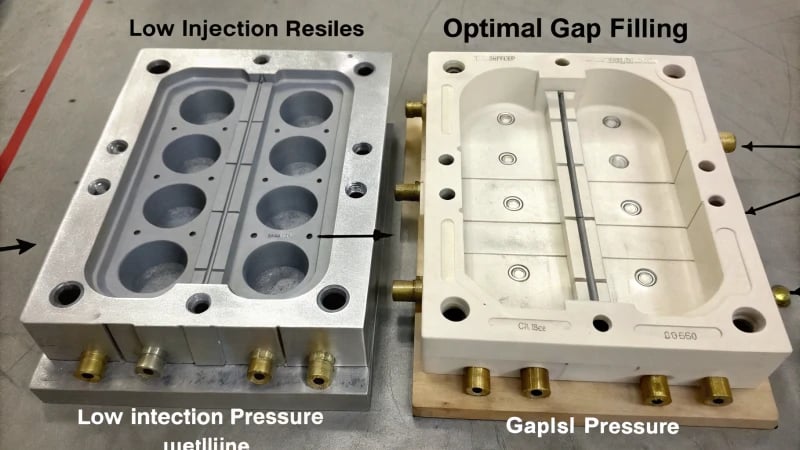
How Injection Pressure Affects Shrinkage
Have you ever seen a soufflé go flat after leaving the oven? That’s what low injection pressure does to plastic shrinkage. When pressure stays low, the melt cannot fill every tiny space in the mold. This leaves parts of the mold empty, similar to areas of a soufflé that don’t rise evenly. I once worked on a project where the stakes felt very high. The gap between a perfectly compacted piece and one filled with voids was just a few PSI.
| Pressure Level | Shrinkage Effect |
|---|---|
| High | Reduced overall shrinkage |
| Low | Increased overall shrinkage |
Mechanisms Behind Increased Shrinkage
Picture packing a suitcase without pressing everything down. At low pressure, the material’s chains sit loose, letting air pockets in. During cooling, these pockets grow, causing more shrinkage. Once, while testing polypropylene6, I noticed parts that should fit perfectly ended up mismatched due to unexpected shrinkage rates – up to 2.2% when I used less pressure.
Localized Shrinkage Variations
Low pressure can cause uneven filling, like pouring pancake batter into a pan that tilts – some spots get thicker. I have dealt with molds of different wall thickness where thin areas didn’t fill completely, leading to bent products.
Designers need to consider these effects when working with complex geometries. High-precision products require a balanced approach to injection pressure settings7 to ensure even filling and minimal shrinkage variance. Techniques like simulation can help predict outcomes and optimize settings before production begins.
I learned through trial and error (and quite a few nights fueled by coffee) that understanding and controlling injection pressure really matters for meeting product specs and achieving superior quality in plastic manufacturing. It’s about finding the perfect balance for smooth flow.
Low injection pressure increases shrinkage.True
Low pressure leads to under-filled cavities, causing higher shrinkage.
High injection pressure results in more shrinkage.False
High pressure reduces shrinkage by ensuring complete cavity filling.
How Can Designers Optimize Injection Pressure for Better Results?
Have you ever thought about why some plastic items look perfect, while others twist and shrink unexpectedly? The trick usually hides in controlling the injection pressure correctly.
I balance pressure settings carefully to control shrinkage. Even material spread is important. Adjustments depend on material type and product shape. These are crucial for outstanding outcomes.

Understanding Injection Pressure Effects
During my years working with injection molding, I have noticed that injection pressure plays a very important role in creating quality molded items. It really influences shrinkage, surface smoothness, and how closely the final size matches the design.
High Injection Pressure: More pressure packs the plastic melt8 tightly. This action really helps reduce shrinkage, similar to squeezing more toothpaste out of a tube. High pressure delivers consistent results, especially in areas with complex shapes.
| Material | Normal Shrinkage | High Pressure Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 0.5% – 0.7% | 0.3% – 0.5% |
Low Injection Pressure: Too little pressure often creates voids and uneven filling. Shrinkage increases and parts can warp, which I often see in thin sections.
Optimizing Injection Pressure
-
Material Considerations: Different plastics need different pressures. Polycarbonate9 likes high pressure to reduce shrinkage, but polypropylene10 needs less pressure to avoid issues.
-
Product Design: Mold geometry affects pressure needs. Each area has different thicknesses and requires specific pressure to ensure even filling and reduce local shrinkage.
-
Process Parameters: Monitoring temperature and injection speed is crucial. Adjustments here can really change the effect of pressure tweaks, leading to better results.
-
Simulation Tools: CAD simulations predict how changes in pressure will impact product quality before production starts. These tools are very helpful for making informed adjustments.
By concentrating on these factors, I achieve the right injection pressure for every project. This approach not only raises product quality but also improves efficiency, which is probably essential for remaining competitive in this fast-moving industry.
High injection pressure reduces shrinkage in polycarbonate.True
High pressure compacts the plastic melt, reducing molecular spacing.
Low injection pressure causes uniform shrinkage in all materials.False
Low pressure can cause voids and uneven filling, increasing shrinkage.
How Does Material Type Affect Shrinkage Dynamics?
Some plastic parts fit perfectly, while others do not fit at all. The secret often depends on understanding how these materials shrink.
The material used in injection molding greatly influences shrinkage through its molecular structure and thermal properties. Materials like polycarbonate and polypropylene show different behavior during cooling. Local and overall shrinkage rates change due to these properties. Different conditions impact these rates.

Understanding Material Influence on Shrinkage
I recall the first time I noticed how important choosing the right material was for my designs. It involved a project with detailed electronics for consumers. The precision needed felt very intimidating. That’s when I explored how different materials change as they cool. It’s really interesting to see how each material’s special structure and heat properties affect this process.
| Material | Normal Shrinkage (%) | High Pressure Shrinkage (%) | Low Pressure Shrinkage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | 0.5 – 0.7 | 0.3 – 0.5 | Not Applicable |
| Polypropylene | 1.0 – 1.5 | Not Applicable | 1.8 – 2.2 |
Molecular Structure and Density
One day, a friend in design talked about his trouble with polycarbonate11 under pressure. High pressure surprisingly decreased its shrinkage because it tightened the molecular chains. This discovery was huge for us! It showed me that knowing these structures leads to better design choices.
Thermal Properties Impact
Then there are thermal properties, which are like secret heroes in this process. Polymers that expand a lot with heat usually shrink more, changing the final size significantly during cooling.
Knowing this helped me choose mold sizes wisely, ensuring our products fit perfectly.
Practical Implications for Designers
As a designer, learning how materials affect shrinkage is key to getting the results we want. For instance, polycarbonate is often used for precise designs because it shrinks less when under high pressure.
I discovered that picking the right material saves many problems later on. So, if you want to enhance your designs, look at some detailed guides12. They were really helpful for me in improving how things are made and ensuring quality control.
Polycarbonate has lower shrinkage than polypropylene.True
Polycarbonate's normal shrinkage is 0.5-0.7%, while polypropylene's is 1.0-1.5%.
High thermal expansion polymers have less shrinkage.False
Polymers with high thermal expansion coefficients show increased shrinkage.
Conclusion
Injection pressure significantly affects plastic shrinkage; high pressure reduces overall and local shrinkage, while low pressure increases it, impacting product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
-
Discover how high injection pressure affects shrinkage, aiding in consistent product quality. ↩
-
Understand the role of injection pressure in reducing local shrinkage differences in complex molds. ↩
-
Learn how high pressure affects equipment longevity and maintenance needs. ↩
-
Explore how high fuel pressure impacts engine components and performance. ↩
-
Find out strategies for balancing injection pressure to maintain product quality and equipment health. ↩
-
Learn about the basic principles of injection molding to understand how pressure affects product quality. ↩
-
Discover methods to optimize injection pressure settings, crucial for minimizing shrinkage and improving product consistency. ↩
-
Explore why plastic melt plays a critical role in molding quality and how it affects shrinkage. ↩
-
Explore why plastic melt plays a critical role in molding quality and how it affects shrinkage. ↩
-
Learn about polypropylene’s specific shrinkage characteristics and how pressure adjustments can minimize defects. ↩
-
This link will offer detailed information on polycarbonate’s behavior under different injection pressures, useful for accurate mold design. ↩
-
Find comprehensive guides on selecting materials for injection molding, crucial for optimizing design and manufacturing processes. ↩






