Do you want to explore the interesting world of hard plastic molds? Let’s discover the art and science of creating these important tools!
To create a hard plastic mold, carefully design it, select suitable materials, manufacture and assemble it, solve issues, and conduct trial production. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance.
My journey as a mold designer shows that crafting a top-notch hard plastic mold takes many important steps. Each step builds on the previous one, bringing us closer to a flawless result. I start with sketching the design. Then, I work toward the final product. Creativity and precision both play essential roles. This blend makes me really excited about every project.
Designing the mold is the first step in mold making.True
The initial phase of creating a hard plastic mold involves designing it accurately to ensure proper functionality and quality.
Regular maintenance of molds is unnecessary for performance.False
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, regular maintenance of hard plastic molds is essential and should not be overlooked.
What Tools Do I Need for Mold Making?
Exploring mold creation feels both exciting and challenging. I remember standing in front of an empty canvas, not knowing where to begin. Important tools helped me build good molds. They gave me confidence.
Essential tools for mold making include CAD software for design, machining tools like milling and drilling machines, EDM, calipers, and torque wrenches for assembly, injection molding machines for trial production, and maintenance supplies, all ensuring high-quality mold production.
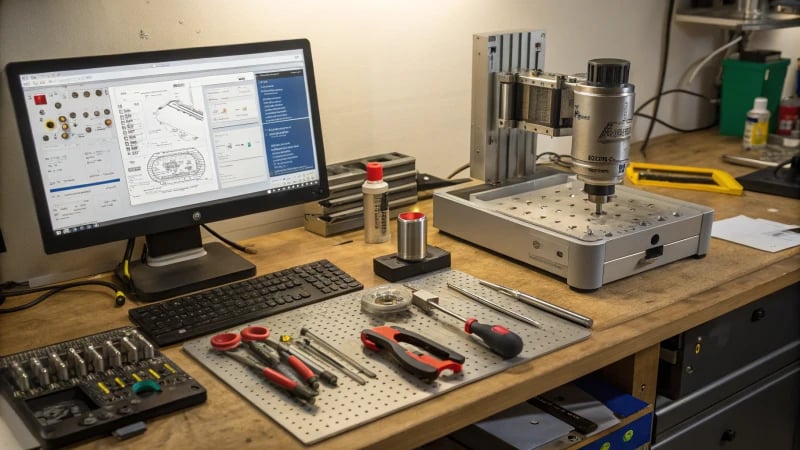
Essential Tools for Mold Making
Creating a mold requires a variety of tools that help in each phase of the process. Understanding these tools is crucial for achieving high-quality molds that meet product specifications.
-
Design Software: The journey begins with designing the mold. Using CAD software1 allows designers to visualize the mold structure, ensuring accuracy in dimensions and features like mold cavities and cooling systems.
-
Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is vital. Common options include:
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive |
| Aluminum Alloy | Lightweight and easy to work with | Less durable than steel |
| Copper Alloy | Excellent heat conductivity | Higher cost |
Selecting materials should align with the intended use and the characteristics of the final plastic product.
-
Machining Equipment: Processing and manufacturing require specific machinery:
- Milling Machines: For shaping mold parts precisely.
- Drilling Machines: To create holes for alignment and assembly.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Essential for intricate designs where high precision is necessary.
Investing in quality machines is critical to ensure accuracy and surface quality.
-
Assembly Tools: Assembling the mold components accurately is crucial. Tools such as:
- Calipers and Micrometers: For measuring dimensions during assembly.
- Torque Wrenches: To ensure parts are secured without damage.
Proper assembly leads to optimal functioning of the mold during production.
-
Trial Production Equipment: After assembly, trial runs are necessary to evaluate mold performance. This includes:
- Injection molding machines to test the mold with real materials.
- Quality control tools to inspect the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of produced items.
-
Maintenance Tools: Regular maintenance extends the mold’s life. Key tools include:
- Cleaning brushes and solvents for keeping the mold clean.
- Lubricants to reduce wear during operation.
Regular maintenance prevents costly repairs and ensures consistent performance.
CAD software is essential for mold design accuracy.True
CAD software helps visualize mold structures, ensuring precise dimensions and features, which is critical for effective mold making.
Copper alloy molds are the most durable option available.False
While copper alloys offer excellent heat conductivity, they are not as durable as steel, making this claim false.
How Do I Choose the Right Material for My Mold?
Picking the right material for your mold feels like choosing the perfect dance partner. You need one that matches your style. The material should perform well under pressure. It has to last for many years, which is very important. Let us explore this choice together!
To choose the right mold material, consider factors like strength, hardness, wear and corrosion resistance, and environmental conditions. Common options include steel, aluminum, and copper alloys, each suited for specific applications due to their unique properties.

Understanding Mold Material Properties
When I started designing molds, I saw that picking the right material was vital. Every project was like a puzzle and the material I chose became a key piece.
Key Material Properties to Consider:
- Strength: The material must handle pressure and forces during production. Think of lifting weights. If the bar is weak, it might break under pressure.
- Hardness: This relates to wear resistance and mold lifespan. Soft materials may wear out quickly, which can be frustrating.
- Wear Resistance: Maintaining mold integrity over time is crucial. Frequent repairs are troublesome.
- Corrosion Resistance: In wet or chemical environments, materials that resist rusting are necessary. Like my old bike, unprotected from rain, now needing repairs.
Explore more about material properties2 that affect mold selection.
Common Mold Materials
I’ve worked with many materials, each unique. Over time, I learned each serves different needs, similar to tools in my workshop.
| Material Type | Strength | Hardness | Wear Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High | High | Excellent | Moderate | High-volume production molds |
| Aluminum Alloy | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Good | Lightweight applications |
| Copper Alloy | Moderate | High | Excellent | Excellent | Heat transfer applications |
Explore deeper into material selection3 and consider these factors before deciding.
Environmental Considerations
The working environment of my mold is vital. It’s like choosing shoes for different weather. Using sandals in snow isn’t wise!
- For humid areas, I pick materials with high corrosion resistance.
- For high temperatures, I seek materials that withstand heat without weakening.
Explore more about environmental impacts4 to find suitable material choices.
Economic Factors
Budget constraints always influence decisions. Once, I wanted a top-grade steel mold but realized it wasn’t practical for small runs.
Considerations include:
- Production Volume: High volumes may justify durable materials like steel. Buying in bulk can be wise sometimes.
- Budget Constraints: I check if a cheaper material still meets my needs without losing quality.
Read more about cost-effective solutions5 for mold materials to enhance your project.
Professional Expertise
Mold design and material choice involve many details. Consulting with experts has been very valuable for me. Their knowledge helps face challenges and refine choices.
For expert advice, check out professional guidance6. Sometimes it’s best to rely on others’ experience.
Steel molds are best for high-volume production.True
Steel offers high strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-volume production molds where durability is essential.
Aluminum alloy is suitable for heavy-duty applications.False
Aluminum alloy has moderate strength and is generally not recommended for heavy-duty applications compared to steel.
What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid in Mold Production?
In mold production, avoiding common mistakes is very important. This helps deliver high-quality results. It also keeps costs reasonable. I have learned some key pitfalls over time. Let me share these mistakes. You can steer clear of them too.
To avoid common mistakes in mold production, emphasize precise design, careful material selection, accurate processing, thorough assembly, diligent trial runs, and regular maintenance and checks.

At the Beginning of My Journey in Mold Production
At the beginning of my journey in mold production, I felt overwhelmed. The process seemed full of complexities. Every step held its own challenges. Over time, I realized many mistakes were easily avoidable. We will explore these common pitfalls. You will probably avoid the headaches I once faced.
Overlooking Mold Design Specifications
One of the most prevalent mistakes in mold production is overlooking the design specifications. The design phase is crucial because it dictates the entire production process.
When designing the mold, several factors should be considered, including:
- Cavity and Core Design: Ensure the mold cavity and core are designed correctly to achieve the desired shape and size of the final product.
- Gate and Runner Systems: The configuration of these systems significantly impacts the flow of molten plastic into the mold, affecting cycle time and product quality.
- Cooling System Design: Proper cooling channels can prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage.
Utilizing advanced CAD tools7 can help streamline this process.
Ignoring Material Selection
Selecting the wrong materials for the mold can lead to a myriad of problems, including premature wear and tear or even complete mold failure.
Common materials include:
| Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High durability and wear resistance | Expensive and heavy |
| Aluminum Alloy | Lightweight and easy to machine | Lower durability compared to steel |
| Copper Alloy | Excellent thermal conductivity | Higher cost |
It’s essential to choose materials that match the specific requirements of your product and production environment. For more insights on material selection, visit material selection guidelines8.
Neglecting Precision in Processing
Another critical mistake is failing to maintain precision during the processing and manufacturing phase. Inaccuracies in machining can lead to:
- Poor fitting of mold components
- Reduced mold lifespan
- Increased defect rates in finished products
To mitigate these issues, ensure that appropriate machinery is used and that all operators are well-trained. Regular maintenance of equipment can also enhance accuracy. For techniques on maintaining machining accuracy, check out machining precision tips9.
Skipping Assembly and Debugging Steps
Some designers may rush through the assembly and debugging phases, leading to unforeseen issues later in production. Critical steps include:
- Accurate Matching: Ensuring parts fit together perfectly to avoid leaks and defects.
- System Functionality Testing: Testing mold opening, closing, and ejection mechanisms is vital before proceeding to production.
Developing a checklist for assembly can help ensure no steps are overlooked. You can find useful templates at assembly checklist resources10.
Underestimating Trial Production Importance
Trial mold production is often underestimated. This phase allows designers to:
- Identify defects or inefficiencies in the design.
- Assess the quality of the molded parts before full-scale production begins.
It’s a mistake to skip this step, as it can save time and resources by addressing issues early. For more information on optimizing trial runs, refer to trial production best practices11.
Neglecting Regular Maintenance
Lastly, many forget about the importance of regular maintenance during mold usage. Proper maintenance includes:
- Cleaning molds after use
- Lubricating moving parts
- Regular wear checks
Neglecting these practices can lead to decreased efficiency and increased production costs over time. For a maintenance schedule template, visit maintenance planning12.
Ignoring mold design specifications leads to production issues.True
Overlooking design specifications can result in defects and inefficiencies during mold production, impacting the final product's quality.
Skipping trial production is a common best practice.False
Trial production is essential to identify defects early, ensuring efficiency and quality before full-scale manufacturing begins.
How Can You Improve the Lifespan of Your Molds?
Do your molds wear out too quickly? I have discovered strategies to keep them lasting longer. Better molds help manufacturing run more smoothly and efficiently.
To extend mold lifespan, ensure regular maintenance with cleaning and lubrication, select durable materials, incorporate proper design features, conduct thorough trial productions, and seek professional expertise to reduce wear and enhance longevity.

Regular Maintenance
To ensure the longevity of your molds, regular maintenance is crucial. This includes:
- Cleaning: Clean the mold surface after finishing a production run. Leftover residue may cause corrosion or unwanted wear. A clean mold also ensures better product quality.
- Lubrication: Ignoring lubrication once caused me big problems. Now, I always apply suitable lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and extend mold life.
- Wear Checks: Inspections for wear or damage are part of my routine. Spotting problems early saves time and money.
Consider scheduling maintenance checks at regular intervals or after a set number of production cycles to catch issues early.
Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly affects the lifespan of your molds. When selecting materials, consider:
- Strength: Ensure that the material can withstand the pressures of the molding process without breaking.
- Corrosion Resistance: Opt for materials that resist corrosion, especially if working with harsh chemicals.
- Wear Resistance: High-wear resistance materials will last longer under frequent use.
Here’s a quick comparison table of common mold materials:
| Material Type | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Wear Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High | Medium | High |
| Aluminum Alloy | Medium | High | Medium |
| Copper Alloy | Medium | Low | Low |
Selecting the right material can help minimize replacements and extend mold life. For more insights on material selection, refer to this guide13.
Proper Design
A well-designed mold can significantly improve its lifespan. Focus on:
- Cooling Systems: Proper cooling helps avoid overheating during production, which can cause warping or cracking.
- Mold Cavity Design: Good shape and size ensure even pressure while injecting.
- Gate and Runner Design: Correct designs lower stress concentrations.
Utilizing CAD software can facilitate better design practices. You might find it beneficial to explore advanced CAD techniques14.
Trial Mold Production
Conducting trial runs is essential before full-scale production. This helps in:
- Identifying design flaws that could lead to premature wear or damage.
- Testing cooling efficiency and cycle times to optimize operations.
- Adjusting processes based on feedback from the trial phase, ensuring smoother production runs afterward.
Ensuring that trial production is thorough can save costs and extend the operational life of your molds. For detailed steps on trial production, check this resource15.
Professional Assistance
If you lack expertise in mold design or maintenance, consider consulting with professionals. They can offer:
- Expert Insights: Professionals give advice tailored to your specific mold applications and requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that molds meet strict testing and quality checks provides peace of mind and enhances longevity.
Engaging with professionals can provide peace of mind and enhance the longevity of your molds significantly. Learn more about finding qualified professionals here16.
Regular maintenance is essential for mold longevity.True
Consistent cleaning, lubrication, and inspections prevent wear and corrosion, ensuring molds function effectively over time.
Trial runs are unnecessary for mold production.False
Conducting trial runs helps identify design flaws and optimize processes, ultimately extending the lifespan of molds.
Conclusion
Learn key techniques for making hard plastic molds, including design, material selection, processing methods, assembly steps, trial production importance, and regular maintenance for optimal performance.
-
Explore our recommended resources to find detailed guides on tools needed for mold making, enhancing your skills significantly. ↩
-
This link offers detailed insights into various mold materials, helping you understand their properties and applications better. ↩
-
Explore this resource to learn how to select mold materials based on specific project needs and requirements. ↩
-
Discover important environmental considerations that affect mold material selection for various applications. ↩
-
Learn about cost-effective solutions for choosing mold materials without compromising quality or performance. ↩
-
Get expert advice and insights on mold design and material selection from industry professionals. ↩
-
This link provides essential tips to enhance your mold production process, helping you avoid costly mistakes. ↩
-
Learn about best practices in material selection for molds to ensure optimal performance and longevity. ↩
-
Explore ways to maintain machining precision to enhance quality and reduce waste in mold production. ↩
-
Access templates for effective assembly checks that will help you avoid errors during mold assembly. ↩
-
Find out how trial runs can help detect issues early in the production process, saving time and resources. ↩
-
Get a maintenance schedule template that helps keep your molds in top condition for longer service life. ↩
-
Discover practical strategies for extending your mold’s life by exploring this link. It will guide you through best practices tailored for manufacturing success. ↩
-
This resource provides expert tips on mold maintenance and care, ensuring you have all necessary insights to keep your equipment running smoothly. ↩
-
Learn about advanced CAD techniques that can help optimize mold design for better durability and efficiency. ↩
-
Find qualified professionals who can assist with your mold needs through this valuable resource. ↩





