I remember the first time I chose mold steel. It felt like selecting the right partner for a long trip. The stakes were very high!
Pros of varying mold steel hardness and toughness include tailored durability and cost efficiency. Cons may involve potential wear, reduced precision, and increased maintenance needs.
I discovered that selecting the right mold steel involves understanding trade-offs, not just metrics. Steels with high hardness resist wear and keep precise sizes. In one project with watch parts, S136 steel was vital for tight tolerances. However, another time, a dashboard mold cracked because it was brittle. This caused problems.
High toughness steels became favorites for complex shapes like phone shells. These shapes must handle stress without breaking. But these steels wore out quickly when working with fiber-reinforced plastics. Every choice taught me significant lessons. Balancing these properties is key for effective manufacturing. Understanding these details is very important. It probably makes decisions better for efficiency and product quality.
High hardness steel offers excellent dimensional accuracy.True
High hardness mold steel maintains dimensional accuracy during long cycles.
High toughness steel is highly resistant to wear.False
High toughness mold steel has poor wear resistance compared to high hardness.
What Impact Does High Hardness Have on Mold Steel Performance?
Mold steel plays a vital role in manufacturing. People care about it because it balances hardness with performance.
High hardness in mold steel increases wear resistance and keeps size accuracy. This is important for good molds. Hardness may also bring problems like brittleness and tough processing. Finding a balance is essential for the best outcomes.
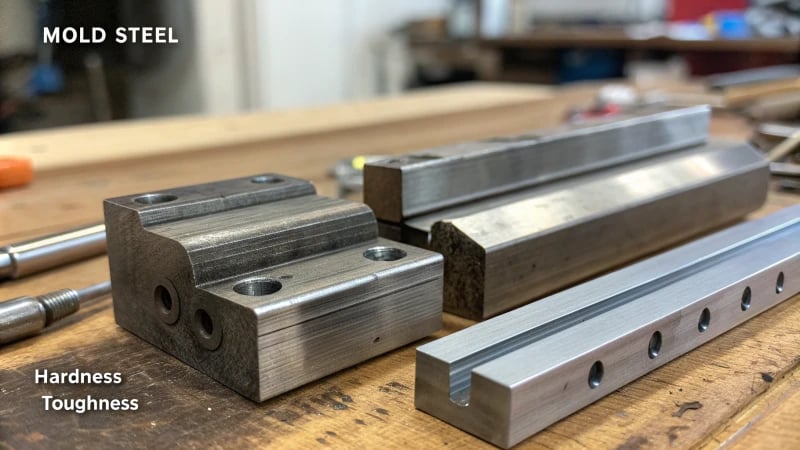

Advantages of High Hardness Mold Steel
High hardness mold steels offer several benefits that make them suitable for specific applications.
-
Dimensional Accuracy: The ability to retain dimensional accuracy during injection molding is crucial. High hardness steels, such as S136, are ideal for precision mechanical parts1, ensuring minimal changes after long cycles.
-
Surface Quality: A higher hardness level allows for superior surface finishing. For instance, carbide mold steel used in optical lenses can achieve remarkable smoothness, enhancing the final product’s optical performance.
-
Wear Resistance: Mold steels with high hardness resist abrasive wear, making them perfect for use with abrasive materials like glass fiber. This extends the mold’s life and maintains product quality.
| Feature | Example | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Watch parts molds | Consistent tolerance levels |
| Surface Quality | Optical lens molds | Superior smoothness |
| Wear Resistance | Glass fiber reinforced nylon molds | Extended mold life |
Disadvantages of High Hardness Mold Steel
While high hardness offers many benefits, it comes with drawbacks that can affect mold performance.
-
Poor Toughness: These steels are prone to cracking under stress. For large, complex parts, the brittleness2 can lead to breakage during molding.
-
Processing Challenges: Special tools and techniques are required, increasing time and cost. Processing carbide steel demands precise control over cutting parameters to avoid micro-cracks.
Comparing High Hardness and High Toughness Mold Steels
A balance between hardness and toughness is often needed.
-
Toughness Benefits: High toughness steels like P20 offer fracture resistance during high-impact molding, accommodating complex shapes without breaking.
-
Dimensional Stability Trade-offs: While toughness provides durability, it may compromise on maintaining dimensional accuracy over time.
| Characteristic | High Hardness Steel | High Toughness Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Fracture Resistance | Low | High |
| Processing Ease | Challenging | Easier |
Understanding these trade-offs allows for informed decisions when selecting mold steel. Designers must weigh these factors based on specific production needs and desired outcomes. By leveraging insights into material properties, manufacturers can optimize mold designs for enhanced performance across various applications. For more on balancing material characteristics3, explore industry resources that delve deeper into these considerations.
High hardness mold steel retains dimensional accuracy.True
It resists pressure during injection molding, maintaining precision.
High toughness mold steel has excellent wear resistance.False
It lacks wear resistance, leading to faster surface wear.
Why is toughness important in mold steel selection?
The toughness of mold steel is really important. It must handle not only pressure but also last a long time. Products need to be reliable. Mold steel needs to stay strong for a very long period.
Choosing steel with strong toughness is important. It prevents breaks in the metal. Tough steel handles high stress very well. Molds made from this steel survive complex procedures. Over time, they stay efficient. This is very crucial.
Understanding Toughness in Mold Steel
At first, toughness in mold steel seemed confusing. Think of it like hiking boots. You need boots strong enough for rocky paths. Toughness in mold steel means absorbing energy and resisting hits without breaking. This is really important in making complex products.
Toughness refers to a material’s ability to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. In mold steel selection4, toughness ensures that molds can withstand high-impact forces without cracking, a common issue with high hardness steels.
Advantages of High Toughness Mold Steel
-
Fracture Resistance: One time, we used P20 steel for phone shell molds. The problem involved controlling stress without hurting the mold. P20’s ability to resist cracking really helped, even under massive pressure.
-
Adaptability: Tough steels adjust well, like smart travelers. For example, H13 steel works well with soft PVC materials. It stays precise even when facing hard demolding problems.
| Mold Steel | Toughness (J/cm²) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| P20 | 5-7 | Electronic housings |
| H13 | 7-9 | Soft PVC products |
Challenges with Low Toughness Mold Steel
No material is perfect. Tough steels might bend slightly over time because they are not as hard. This impacts precision in things like precise gears.
- Dimensional Stability: While tough steels are less likely to break, they may slightly deform over time due to lower hardness. This can affect the precision of products like high-precision gears.
When working with harsh materials, wear happens faster, harming surface quality and accuracy.
- Wear Resistance: Tough steels can wear faster when used with abrasive materials like glass fiber reinforced plastics. This wear affects both surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
Comparing Toughness with Hardness
Balancing toughness and hardness is tricky. High hardness gives great wear resistance but might crack easily under pressure. On the other hand, tough steels avoid breaking but may wear out faster.
Both toughness and hardness are essential, but they often trade off against each other:
-
Advantages of High Hardness:
- Keeps size and shape.
- Preserves surface quality.
-
Disadvantages of High Hardness:
- Breaks easily.
- Needs careful processing.
Strategic Selection for Specific Applications
Picking the right balance fits the project needs:
For example, molds for lenses need high hardness for quality yet electronic casings must have high toughness to handle impacts well.
Selecting the appropriate balance of toughness and hardness depends on specific application requirements.
Further insights on strategic mold selection can be explored here5.
High hardness mold steel ensures minimal dimensional changes.True
High hardness mold steel resists pressure, maintaining dimensional accuracy.
High toughness mold steel has excellent wear resistance.False
High toughness mold steel lacks wear resistance, wearing faster with fillers.
What Are the Processing Challenges with Different Mold Steels?
Moving through the world of mold steels feels like assembling a challenging puzzle. Each kind offers its own difficulties and benefits. A sharp eye for details is necessary. Problem-solving skills are crucial too.
Dealing with mold steels involves solving issues like hardness, toughness and machining problems. Each kind needs special care to achieve high performance and quality. Understanding these details is very important for the best production results.

Challenges of High Hardness Mold Steel
High hardness mold steels are intriguing. These steels shine with their dimensional accuracy6 and resistance to wear. I remember puzzling over the tiny precision needed for watch part molds. Each millimeter counted. However, these steels have their own issues:
-
Machining Problems: Working with these steels was hard. Special tools and exact settings were needed, much like following a tricky recipe where a single error could spoil everything. I faced strong cutting forces, always alert to avoid tiny cracks that might ruin the project.
-
Brittleness: There’s a downside. These steels resist wear but tend to crack under pressure, especially in detailed or big molds. I’ve painstakingly controlled stress during injection to stop them from breaking.
| Aspect | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Maintains precision but hard to machine |
| Wear Resistance | High but prone to cracking |
Challenges of High Toughness Mold Steel
High toughness mold steels are strong, like good friends who handle anything. But they struggle with long-term steadiness:
-
Dimensional Stability: These steels change size over time, which was problematic when precision was vital – like in gear molding.
-
Wear Resistance: Their lower hardness led them to wear quickly with rough materials. It was like seeing your favorite tool wear too fast, damaging the mold’s life and my calmness.
| Aspect | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Fracture Resistance | Excellent but suffers in wear resistance |
| Adaptability | Good but compromises dimensional accuracy |
Factors Influencing Material Choice
Picking the right mold steel is like choosing the perfect tool. You must balance problems against needed features:
-
Application Needs: Sometimes, precise work is most important, directing me to high hardness steels despite the challenge in processing them.
-
Material Makeup: The plastic type and filler content greatly impact wear rates. I’ve realized this can determine a project’s success.
For more detailed insights into how these materials perform under specific conditions, consider exploring additional resources on mold design principles7. Understanding these factors aids in making informed decisions that enhance production efficiency and product quality across various manufacturing scenarios.
Explore more about high-toughness steel applications8 for insights into specific industry use cases and the adaptation techniques employed by professionals in the field.
High hardness mold steel improves dimensional accuracy.True
It resists plastic melt pressure, ensuring minimal changes during cycles.
High toughness mold steel has excellent wear resistance.False
Its low hardness leads to faster wear, especially with filled plastics.
Which Mold Steel Type is Best for Your Application?
Have you ever looked at a metal mold and asked yourself, "What makes it so perfect?" It begins with picking the correct steel.
The best type of mold steel relies on specific needs like how hard, tough and resistant to wear it is. Steels with high hardness offer precision and quality. On the other hand, steels with high toughness excel at resisting fractures in tough conditions.
Understanding High Hardness Mold Steel
When I began learning about creating molds, high hardness mold steels became my favorite tools for jobs that need precise work. Crafting tiny watch pieces, for example, demands intense accuracy. These special steels provide unmatched precision. They keep their shape even after long use, which is very important for tiny details. However, working with them is tricky. These steels seem like a smart but stubborn friend; they endure wear but may crack if handled roughly.
Advantages of High Hardness Mold Steel:
- Dimensional Accuracy: Holds precision even after long use. Learn more9
- Surface Quality: Gives a very smooth finish.
- Wear Resistance: Survives the friction from materials.
Disadvantages:
- Toughness: Could break if pushed too hard.
- Processing Difficulty: Needs special tools and methods.
High Toughness Mold Steel Explained
High toughness steels like P20 or H13 are like reliable off-road vehicles; they perform really well in tough situations. If you make complex items or things that get hit often, like electronic casings, these steels are your best choice. They handle hits and stress like experts. Yet, their shape might change over time, which is sometimes surprising.
Advantages of High Toughness Mold Steel:
- Fracture Resistance: Avoids damage in detailed work.
- Adaptability: Handles hard demolding tasks with ease.
Disadvantages:
- Dimensional Stability: Accuracy might get worse after long use.
- Wear Resistance: Not very strong against harsh materials.
Comparison Table: High Hardness vs. High Toughness Mold Steel
| Feature | High Hardness Steel | High Toughness Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Excellent | Moderate |
| Surface Quality | High | Moderate |
| Wear Resistance | Strong | Low |
| Toughness | Low | High |
| Processing Ease | Difficult | Moderate |
Finding the right balance between these qualities feels like juggling. However, it guarantees effective production and high-quality goods. Looking back at past projects, choosing the correct steel meant the difference between easy progress and lots of problems. Think about what your project needs—this choice could really be your secret weapon.
High hardness mold steel ensures minimal dimensional changes.True
High hardness steel resists pressure during molding, maintaining dimensions.
High toughness mold steel has superior wear resistance.False
High toughness steel has lower wear resistance compared to high hardness steel.
Conclusion
This article explores the pros and cons of high hardness and toughness mold steels in injection molding, emphasizing the importance of balancing these properties for optimal manufacturing outcomes.
-
Discover how high hardness steel benefits precision parts production by retaining dimensional accuracy over extended use. ↩
-
Explore the challenges of using high hardness steel, including brittleness and processing difficulties, to make informed material choices. ↩
-
Learn how balancing material characteristics in mold steel can enhance performance and meet specific production requirements. ↩
-
Exploring this link will offer a deeper understanding of the role toughness plays in choosing the right mold steel. ↩
-
This link provides comprehensive strategies for selecting mold steel based on specific industrial applications. ↩
-
This link provides insights into achieving precision with high hardness steels, essential for maintaining quality in intricate molds. ↩
-
Understanding mold design principles helps optimize material selection and processing strategies for diverse applications. ↩
-
Explore practical examples of high-toughness steel use in various industries, offering valuable adaptation strategies. ↩
-
Explore how high hardness mold steels enhance dimensional accuracy and surface quality in precision applications. ↩






