I remember feeling very overwhelmed when I first learned about plastic molding in product design. Yet, this knowledge is probably crucial for everyone working in manufacturing. Truly essential.
Plastic molding processes include injection, extrusion, blow, compression, transfer, vacuum, and rotational molding, each with unique methods to cater to various product needs and characteristics.
Let’s explore different plastic molding methods together. Every technique has its own charm and challenges. You can make a toy that delights a child. You can also design complex parts for electronics. Learning about these techniques helps creativity. It also aids decisions in design tasks.
Injection molding is one of the most common plastic processes.True
This claim highlights the prevalence of injection molding in manufacturing due to its efficiency and versatility.
Blow molding is used exclusively for producing solid plastic items.False
This claim is false as blow molding primarily creates hollow objects like bottles, not solid items.
- 1. What is Injection Molding and How Does It Work?
- 2. How Does Extrusion Molding Compare to Other Processes?
- 3. What Are the Advantages of Blow Molding?
- 4. How Do Compression and Transfer Molding Differ?
- 5. What Applications Benefit from Vacuum Molding Techniques?
- 6. Why Should You Consider Rotational Molding for Large Plastic Products?
- 7. Conclusion
What is Injection Molding and How Does It Work?
Did you ever think about how your favorite plastic toys or gadgets are created? Injection molding plays a big role in that process. Let’s explore this interesting world together.
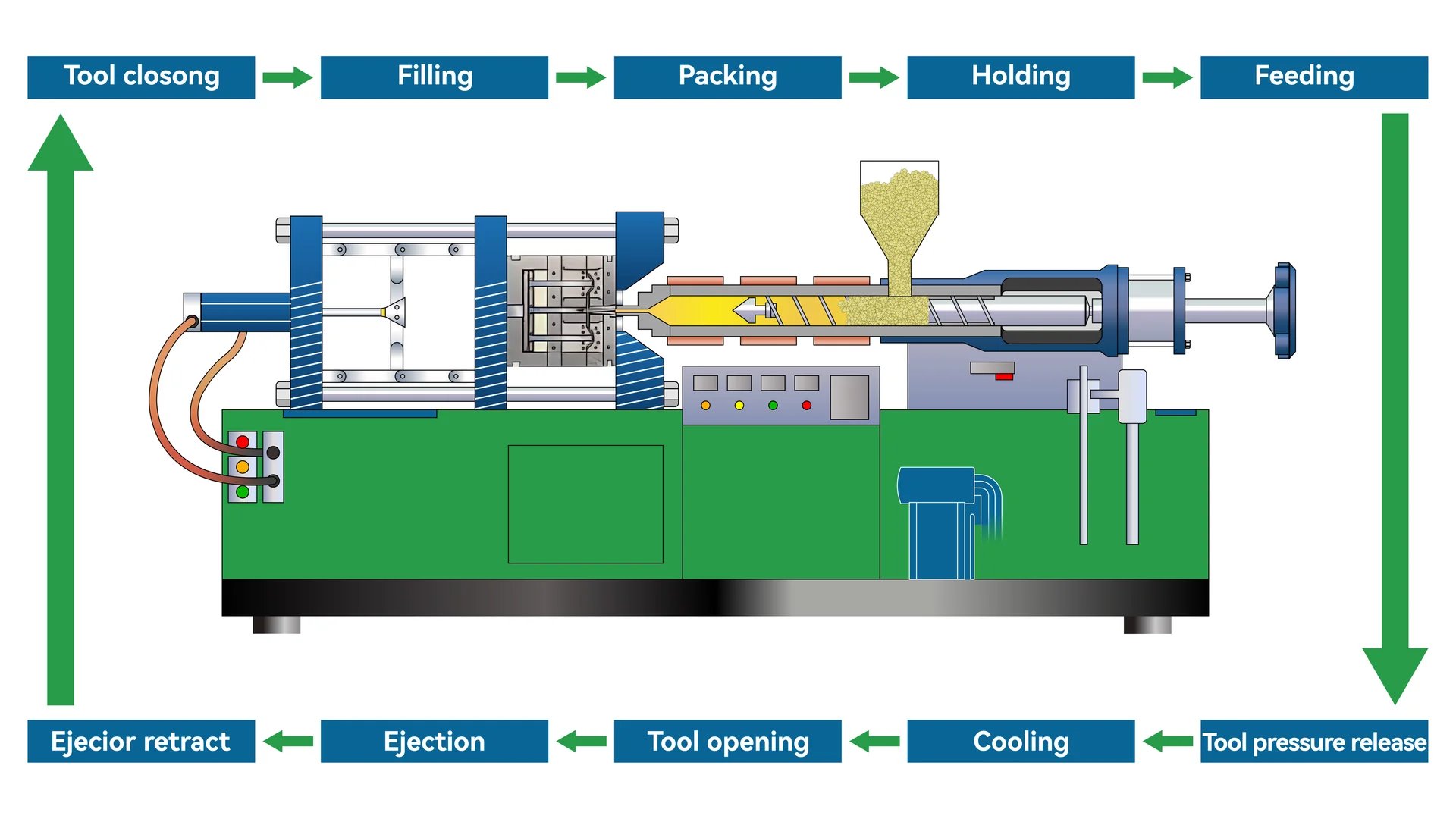
Injection molding melts plastic granules to inject into molds at high pressure, cooling to form solid shapes. It’s efficient for mass-producing complex items.

Understanding Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting material into a mold. This method is particularly prevalent in the plastic industry and offers several advantages for large-scale production.
The process begins with plastic granules being fed into the barrel of an injection molding machine. Here, they are heated until they melt and then injected under high pressure into a closed mold cavity through a nozzle. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens to release the finished product.
This method is effective for creating products like plastic toys1 and electronic housings due to its ability to produce complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy.
Key Features of Injection Molding
The following table summarizes the key features of injection molding:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | High efficiency, making it suitable for mass production. |
| Complex Shapes | Capable of producing intricate designs that are difficult with other methods. |
| Automated Production | Can be automated to enhance productivity. |
| Mold Cost | Initial costs for molds are high, impacting overall project budgets. |
| Design Modification | Modifying designs post-production can be challenging and costly. |
Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is used in a variety of industries. Here are some common applications:
- Consumer Electronics: For producing casings and components that require precision.
- Automotive Parts: Used to create durable and lightweight parts, such as dashboards and panels.
- Medical Devices: Ideal for making components that require high levels of cleanliness and precision.
Comparison with Other Molding Techniques
To understand where injection molding stands in the spectrum of manufacturing processes, it’s beneficial to compare it with other methods:
| Molding Technique | Principle | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Molding | Plastic is melted and formed into continuous shapes (e.g., pipes). | High efficiency but limited to fixed cross-sectional shapes. |
| Blow Molding | Air is blown into a parison to create hollow products (e.g., bottles). | Best for hollow items; challenges in wall thickness uniformity. |
| Compression Molding | Material is heated and pressed into a mold; suited for thermosetting plastics. | High dimensional accuracy but longer production cycles. |
| Rotational Molding | Plastic is heated in a rotating mold to form large hollow products. | Uniform wall thickness, but lower efficiency and longer cycles compared to injection molding. |
Injection molding stands out due to its versatility and efficiency, especially when mass-producing plastic components. For a deeper dive into its advantages and potential drawbacks, consider exploring resources related to advantages of injection molding2.
Injection molding is primarily used for plastic parts.True
This claim is true as injection molding is a dominant method in the plastic manufacturing industry.
Injection molding can only produce simple shapes.False
This claim is false; injection molding excels at creating complex shapes with high accuracy.
How Does Extrusion Molding Compare to Other Processes?
Have you ever been lost in complicated manufacturing methods, unsure which direction to choose for your product? I have experienced this too. Learning about extrusion molding compared to other techniques can really open new opportunities for your project. It really can.
Extrusion molding creates continuous profiles by pushing molten plastic through a die, making it cost-effective for certain projects. In contrast, injection molding uses high pressure for complex shapes and is efficient for mass production, catering to different production needs.

Comparing Extrusion Molding to Injection Molding
Extrusion molding and injection molding are two prevalent methods in plastic manufacturing, each with unique advantages.
Injection Molding involves melting plastic granules and injecting them into a closed mold under high pressure.
- Speed and Efficiency: This process produces products very quickly, making it ideal for mass production.
- Product Complexity: I remember the first finely detailed toy I held made through injection molding. It fascinated me that intricate shapes emerged from just a few steps.
- Cost Considerations: The mold is expensive, but with automation benefits, it is probably worth it.
Learn more about Injection Molding3.
On the other hand, Extrusion Molding continuously produces plastic profiles by forcing molten plastic through a die.
- Continuous Production: It reminds me of watching a river flow – constant and steady! This method supports high production rates for simple shapes.
- Product Shape Limitations: Extrusion is best for products with fixed cross-sections like pipes or sheets. This discovery showed me new possibilities and limits.
- Cost Efficiency: The simplicity of the equipment seemed more affordable compared to injection molding, which was helpful, especially for budgeting.
Blow Molding vs. Extrusion Molding
Blow molding is another contrasting method primarily used for creating hollow plastic products.
- Process Variations: Techniques like extrusion blow molding extrude a tubular parison and then blow it into a mold. It is like blowing up a balloon – fun yet precise!
- Applications: Working on a project with plastic bottles showed me the importance of uniform wall thickness for quality.
- Efficiency: Costs here vary with complexity; balancing these with extrusion options is essential.
Explore the nuances of Blow Molding4.
Compression and Transfer Molding Insights
Compression molding and transfer molding are suitable for thermosetting plastics but differ significantly from extrusion molding.
- Compression Molding: At a workshop, we placed raw materials in heated molds. Seeing the transformation was incredible! Heat and pressure form products.
- Advantages: Parts had impressive dimensional accuracy, but I noticed longer cycle times as well.
- Limitations: It is less efficient for larger production runs than extrusion.
- Transfer Molding: Similar yet distinct, this method injects melted plastic under pressure into the mold.
- Complexity: It offers more creative freedom but is costlier.
Delve into Compression Molding5.
- Complexity: It offers more creative freedom but is costlier.
Summary Table of Comparison
| Process Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High efficiency, complex shapes | High mold cost, design changes difficult | Toys, electronic housings |
| Extrusion Molding | Continuous production, lower costs | Limited shapes | Pipes, sheets |
| Blow Molding | Good for hollow shapes | Wall thickness control issues | Bottles, containers |
| Compression Molding | High accuracy | Long cycles, lower efficiency | Electrical parts, tableware |
| Transfer Molding | Complex shapes with inserts | Higher costs, potential waste | Precise components |
Final Thoughts on Extrusion’s Place in Manufacturing
In choosing between extrusion molding and other methods, consider your specific product requirements and production goals. Each method offers distinct benefits that can align with different manufacturing needs.
Extrusion molding is ideal for continuous production of simple shapes.True
Extrusion molding excels at producing items with a constant cross-section continuously, making it efficient for simple designs like pipes and sheets.
Injection molding is more cost-effective than extrusion molding.False
While injection molding has high mold costs, its automation can balance expenses, but extrusion often has lower equipment costs overall.
What Are the Advantages of Blow Molding?
Have you ever wondered how those shiny plastic bottles come to be? Let me take you on a journey through the fascinating world of blow molding. This manufacturing method truly stands out. Blow molding is very special.
Blow molding is cost-effective with low tooling expenses, offers design flexibility, efficient production, works with various thermoplastics, and generates less waste, ideal for large-scale hollow plastic products.
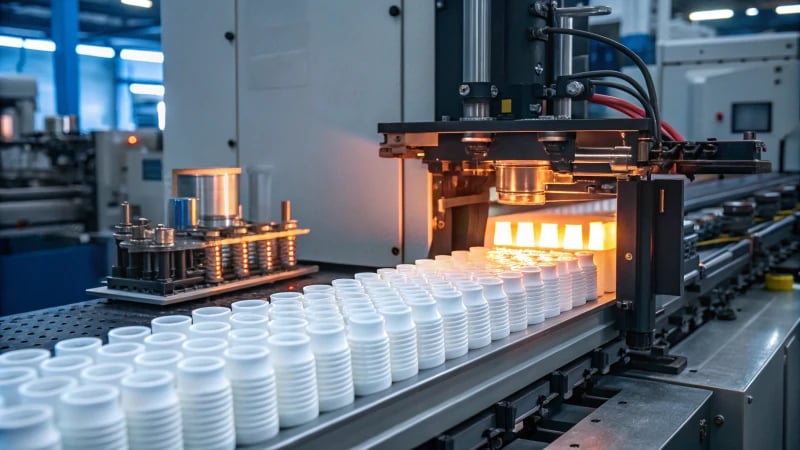

Understanding Blow Molding Advantages
Blow molding is a widely adopted manufacturing process, particularly for producing hollow plastic products like bottles and containers. Its primary advantages stem from both economic and production efficiency perspectives.
1. Cost-Effectiveness
Blow molding generally requires lower tooling costs compared to methods like injection molding. This makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize initial investment while achieving high volume production. The process is particularly beneficial for products with simple designs. To learn more about cost comparison, check out this cost analysis6.
2. Design Flexibility
The blow molding process allows for greater design flexibility, enabling manufacturers to produce complex shapes without incurring substantial additional costs. For instance, manufacturers can create multi-layer bottles for different applications, providing opportunities for innovation in product design. Explore the various design possibilities through this design flexibility guide7.
3. High Production Efficiency
One of the key advantages of blow molding is its ability to produce large quantities of products quickly. This is especially true in extrusion blow molding, which allows continuous production with minimal downtime. The speed of the process ensures that manufacturers can meet high demand without compromising quality.
| Advantage | Details |
|---|---|
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower tooling costs compared to injection molding |
| Design Flexibility | Ability to create complex shapes easily |
| High Production Efficiency | Rapid production with minimal downtime |
| Material Versatility | Compatibility with various thermoplastics |
| Reduced Waste | More efficient material usage minimizes waste |
4. Material Versatility
Blow molding accommodates a wide range of thermoplastic materials, allowing manufacturers to choose the most suitable materials for their products. This versatility enables the production of items that require specific physical properties, such as flexibility or resistance to impact. If you want to see how different materials affect blow molding, check out this material compatibility list8.
5. Reduced Waste
The blow molding process typically generates less waste than other methods like injection molding. The efficiency in material usage not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainability goals, making it an appealing choice for environmentally-conscious manufacturers.
In conclusion, blow molding presents several advantages that make it a preferred choice in the manufacturing industry, particularly for producing hollow plastic products. Each of these advantages contributes significantly to its popularity and effectiveness in various applications.
Blow molding is more cost-effective than injection molding.True
Blow molding typically has lower tooling costs, making it a cheaper option for high volume production compared to injection molding.
Blow molding produces more waste than other manufacturing methods.False
The blow molding process is designed to minimize waste, making it more efficient compared to methods like injection molding.
How Do Compression and Transfer Molding Differ?
Have you ever thought about how your favorite products are produced? Let’s explore the interesting world of molding. There are two main molding methods꞉ compression molding and transfer molding. We will discover the important differences between these two techniques.
Compression molding shapes materials using heat and pressure in molds, while transfer molding injects heated materials into molds for complex shapes, also using pressure.

Understanding the Basics of Compression and Transfer Molding
Compression molding and transfer molding are two distinct processes in the plastic manufacturing industry, each with its unique principles and applications.
Compression Molding Overview
Compression molding involves placing a specific amount of plastic material into an open heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed and pressure is applied. This process is particularly suitable for thermosetting plastics.
- Production Process:
- Place raw material in the mold.
- Close the mold and apply heat and pressure.
- Allow the material to cure and cool.
- Open the mold and eject the final product.
Compression molding is used widely for products like electrical components and melamine dinnerware due to its high dimensional accuracy and minimal flash generation.
Transfer Molding Overview
Transfer molding, on the other hand, involves melting plastic in a separate chamber and then injecting it into a closed mold cavity via a plunger or screw mechanism.
- Production Process:
- Heat the plastic material in a feeding chamber.
- Inject the molten plastic into the mold under pressure.
- Allow it to solidify before demolding.
This method is favored for producing intricate shapes and fine inserts, typically used in electrical parts and components.
Key Differences Between Compression and Transfer Molding
To highlight the differences more clearly, let’s summarize them in the following table:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Transfer Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Molding Principle | Plastic placed in heated mold cavity | Molten plastic injected from separate chamber |
| Material Type | Primarily thermosetting plastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| Production Efficiency | Lower efficiency, longer cycles | Higher efficiency, faster cycles |
| Complexity of Shapes | Limited to simpler shapes | Capable of complex shapes |
| Cost of Equipment | Lower initial cost, simple molds | Higher cost due to complex structures |
| Flash Generation | Less flash | Can have more flash |
| Applications | Electrical parts, durable goods | Fine inserts, electrical components |
Applications and Suitability
Both molding methods have distinct applications that make them suitable for different products:
- Compression Molding is ideal for larger, simpler shapes with high volume needs, such as automotive parts9.
- Transfer Molding excels in applications requiring fine details, such as electronic components10.
Understanding these differences helps manufacturers choose the right process based on product specifications, desired efficiency, and cost considerations.
Compression molding is suitable for thermosetting plastics only.True
Compression molding primarily works with thermosetting plastics, making it ideal for durable goods and electrical components.
Transfer molding has lower production efficiency than compression molding.False
Transfer molding is generally more efficient with faster cycles compared to compression molding, which has longer production times.
What Applications Benefit from Vacuum Molding Techniques?
Have you ever wondered how products we use every day are created so smoothly? Vacuum molding really changes the situation in many industries. This method is very important. Vacuum molding helps improve both quality and efficiency. It makes our lives maybe just a bit easier.
Vacuum molding is used in medical device casings, food packaging, electronics, automotive parts, and toys, enabling the creation of large, lightweight, complex shapes that enhance both aesthetics and functionality.
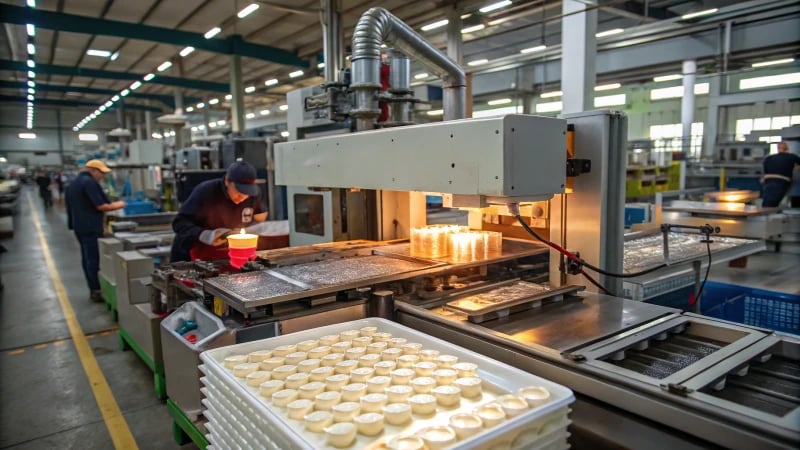

Understanding Vacuum Molding Applications
Vacuum molding is a versatile manufacturing process that has found applications across various industries. This technique is particularly effective for producing large, thin-walled plastic products, making it beneficial in sectors where weight and precision are crucial.
1. Medical Industry
In the medical field, vacuum molding is employed to create components such as medical device casings, trays, and packaging. These products often require high-quality finishes and precise dimensions.
Example: Surgical trays are often made using vacuum molding, ensuring that instruments are stored safely and hygienically. The lightweight nature of these trays aids in handling and transportation.
For further insights on how this technique benefits healthcare, check out medical applications11.
2. Food Packaging
The food industry also benefits from vacuum molding techniques, particularly for creating packaging that maintains freshness and integrity. The ability to mold complex shapes allows manufacturers to design unique containers that attract consumers while ensuring safety.
Example: Vacuum-formed trays for fruits and vegetables provide a protective barrier while allowing visibility for consumers. This not only enhances the product’s appeal but also reduces spoilage.
Explore more about this application in food safety at food packaging trends12.
3. Consumer Electronics
Vacuum molding plays a crucial role in the production of casings for consumer electronics. Devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops benefit from the lightweight yet durable properties of vacuum-formed plastics.
Example: The outer shell of a laptop is often produced using vacuum molding due to its ability to produce intricate designs while maintaining strength.
Learn more about this process in electronics at electronics packaging13.
4. Automotive Components
In the automotive sector, vacuum molding is utilized for producing interior trim pieces, dashboards, and various covers. The technique’s ability to create large parts with consistent wall thickness is vital in this industry.
Example: Car door panels and consoles are often made using vacuum molding to achieve a balance between aesthetic appeal and functionality.
For more details on automotive applications, visit automotive innovations14.
5. Toys and Recreational Products
The toy industry also leverages vacuum molding to create colorful, lightweight products that capture children’s attention. The method allows for the rapid production of complex shapes, which is ideal for toys.
Example: Action figures and playsets are frequently produced through this process, enabling intricate designs that are both appealing and safe.
Check out toy manufacturing insights at toy production15.
Summary Table of Applications
| Industry | Key Products | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | Surgical trays, device casings | High-quality finishes, hygiene |
| Food | Packaging trays | Freshness retention, consumer appeal |
| Consumer Electronics | Device casings | Lightweight, durable |
| Automotive | Interior trim pieces | Aesthetic and functional balance |
| Toys | Action figures | Intricate designs, rapid production |
Vacuum molding is used in medical device manufacturing.True
This claim is true as vacuum molding creates precise components for medical devices, ensuring high-quality finishes and hygiene.
Toys are rarely made using vacuum molding techniques.False
This claim is false; vacuum molding is commonly used to produce colorful and intricate toy designs efficiently.
Why Should You Consider Rotational Molding for Large Plastic Products?
Let me guide you through the world of rotational molding. It is probably becoming popular for creating large plastic items. Stick around if you’re curious. You might discover the solution you’ve been looking for.
Rotational molding is ideal for large plastic products due to its cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and uniform wall thickness, making it superior to techniques like injection molding.
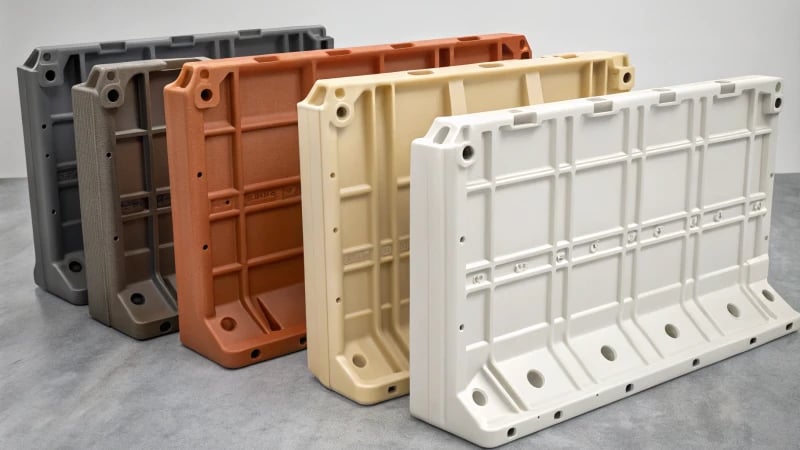

Understanding Rotational Molding
Rotational molding, often referred to as rotomolding, is a unique manufacturing process ideal for creating large, hollow plastic products. It involves placing plastic powder or granules into a mold, which is then heated and rotated on multiple axes. This technique enables the plastic to melt evenly and adhere to the mold’s interior surface, leading to a uniform product wall thickness.
When I first studied rotational molding, it felt like finding a hidden treasure in manufacturing. This special process creates large, hollow plastic items. It works in a fascinating way. Plastic powder or granules go into a mold. The mold spins on many axes while it heats up. As it spins, the plastic melts and coats the inside surface evenly. This results in nice, uniform wall thicknesses.
One of the most significant advantages of this method is its ability to produce large and complex shapes without the constraints typically found in other molding processes. For example, products such as large tanks for water storage can be efficiently manufactured using rotational molding due to the method’s flexibility.
Benefits of Rotational Molding
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to processes like injection molding16, the initial investment for molds in rotational molding is lower. This is particularly beneficial for larger products where mold costs can escalate.
- Material Efficiency: The method minimizes waste since excess material can be reused in subsequent batches, making it a sustainable choice for manufacturers.
- Design Flexibility: Rotomolding allows for the incorporation of various design elements effortlessly; adding inserts or creating intricate details is simple without losing functionality.
Comparing Molding Techniques
Below is a comparison table outlining key differences between rotational molding and other common molding processes:
| Feature | Rotational Molding | Injection Molding | Blow Molding | Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Mold Cost | Low | High | Medium | Medium |
| Production Cycle | Long | Short | Short | Medium |
| Wall Thickness Uniformity | High | Varies | Varies | High |
| Product Size Limitations | Large | Small to Medium | Medium | Small |
| Material Waste | Low | Medium | Medium | High |
Applications of Rotational Molding
This method thrives in many industries with common applications including:
- Large Containers: Such as tanks for chemicals or water storage; they are used everywhere!
- Automotive Parts: Including fuel tanks and body panels crafted with precision.
- Consumer Products: Toys and outdoor furniture – imagine the joy these bring!
For more in-depth information on applications of rotational molding, you may explore specific case studies17.
Limitations to Consider
While there are many benefits to rotational molding, there are also limitations. The production cycle tends to be longer compared to other methods such as injection molding18, which may not be suitable for urgent or high-volume production needs. Additionally, while the design flexibility is advantageous, complex geometries can sometimes lead to challenges in mold fabrication.
Understanding these nuances helps designers decide if rotational molding aligns with their project requirements and production timelines.
Rotational molding is cost-effective for large products.True
The initial investment for molds in rotational molding is lower, making it ideal for larger products.
Rotational molding produces smaller plastic items effectively.False
This method is designed specifically for large, hollow products, not small items.
Conclusion
Explore the diverse plastic molding processes—each with unique methods and applications—essential for product design and manufacturing efficiency.
-
Click here for an in-depth look at the benefits of injection molding in manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Explore various applications of injection molding across different industries. ↩
-
This link will provide deeper insights into injection molding benefits and limitations, essential for decision-making in manufacturing. ↩
-
Discover the key differences between blow molding and extrusion molding to see which suits your product needs better. ↩
-
Learn about compression molding techniques and how they compare to extrusion molding for thermosetting plastics. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of blow molding in manufacturing processes and how it compares to other techniques. ↩
-
Find out how blow molding stacks up against injection molding in terms of cost and efficiency. ↩
-
Learn about different materials used in blow molding and their impact on production. ↩
-
Explore detailed insights into the nuances between compression and transfer molding processes to enhance your understanding. ↩
-
Find out which molding technique is better suited for your specific project needs and production goals. ↩
-
Discover how vacuum molding techniques can improve product design across multiple industries. ↩
-
Learn about innovative food packaging solutions using vacuum molding. ↩
-
Explore the impact of vacuum molding in consumer electronics manufacturing. ↩
-
Find out how the automotive industry utilizes vacuum molding for efficient production. ↩
-
Understand the role of vacuum molding in toy manufacturing and design. ↩
-
Discover how rotational molding can enhance your product designs and manufacturing efficiency. ↩
-
Learn about the applications of rotational molding in various industries and its practical advantages. ↩
-
Understand the limitations of rotational molding compared to other techniques to make an informed decision. ↩





