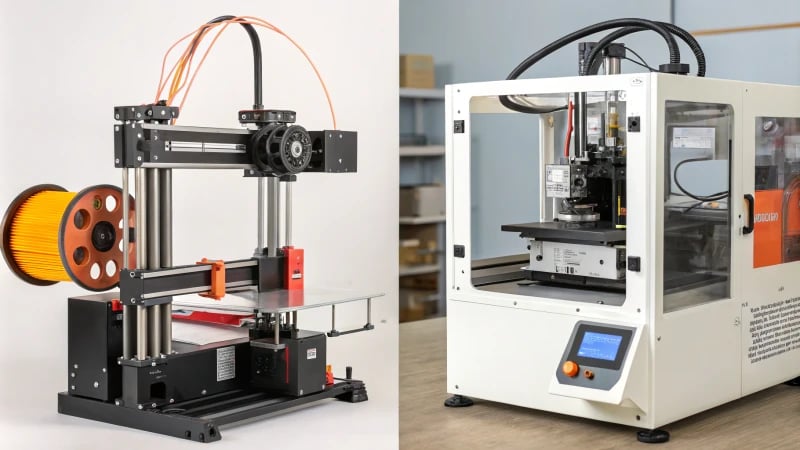
Deciding between 3D printing and injection molding probably seems confusing. I faced this choice before. Knowing the strengths of each method is very important. You need this understanding to bring your designs to life.
3D printing forms objects layer by layer from digital designs. This process is excellent for custom and complex designs. Injection molding shapes products by pouring molten plastic into molds. It excels in mass production. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right process for your project. It is really important to know these differences.
In my journey through manufacturing, I discovered that understanding the differences between 3D printing and injection molding is very important. Each method has its own charm and challenges. 3D printing allows for creating complex designs. Injection molding offers fast mass production. I recall my first experience with a 3D printer. I was amazed as it built layers from a digital model. It felt like watching a sculpture form from clay. However, I also value the precision and efficiency of injection molding. It is really useful for making large batches quickly. Let’s explore these differences together!
3D printing builds objects layer by layer.True
This method adds material incrementally, contrasting with injection molding, which uses molds.
Injection molding is more cost-effective for low-volume production.False
Typically, injection molding is more economical for high-volume runs due to setup costs.
- 1. What Are the Advantages of 3D Printing Over Injection Molding?
- 2. How Does Injection Molding Ensure High Production Efficiency?
- 3. What Factors Influence Material Selection in Both Processes?
- 4. How Do Cost Structures Compare Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding?
- 5. How Do Design Complexities Shape My Manufacturing Choices?
- 6. When Should I Choose 3D Printing Over Injection Molding?
- 7. Conclusion
What Are the Advantages of 3D Printing Over Injection Molding?
Have you ever felt stuck choosing between 3D printing and injection molding? I certainly have! Let’s explore the special benefits of 3D printing. It probably could transform how we think about production.
3D printing stands out when compared to injection molding. It offers design flexibility. Initial costs are lower for small batches. Complex shapes are easy to create. This characteristic is really excellent for rapid prototyping. Customized parts benefit from this method too.

Principles of Manufacturing
3D printing has changed how we create things and excitement fills me when I explore its uses. This technology operates on the principle of additive manufacturing, building objects layer by layer from digital models. If I have an idea, I bring it to life without many of the limitations of older methods. For example, with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)1, I was amazed by the precision in heating, extruding and depositing thermoplastic materials. It felt magical!
In contrast, injection molding focuses on reducing material. It heats thermoplastics until they melt and then injects them into molds under high pressure. This method is very efficient for producing many items but creating molds has high initial costs, which poses a challenge, especially for beginners or small-scale projects.
Productivity Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Ideal for small batches | Best for large-scale production |
| Lead Time | Shorter for initial pieces | Longer due to mold preparation |
| Speed | Slower for complex designs | Fast once molds are created |
For me, 3D printing excels in productivity. It suits small batches or one-time pieces because it skips the extensive setup of injection molding. Once, I needed a quick prototype. 3D printing let me create it fast without mold-making stress.
Nevertheless, for large production, I recognize that injection molding is superior. When molds are set, they produce parts very quickly.
Product Quality and Precision
Regarding quality, I once printed a complex piece with delicate internal structures. While 3D printing has made strides in quality, it still faces challenges in surface finish and precision; printed items often require post-processing for a smooth finish. However, its ability to create designs impossible with traditional methods—like lightweight lattice designs—can be beneficial for specific applications.
On the other hand, injection molding consistently offers high-precision products with excellent surface quality. Seeing designs come to life with detail is amazing! But if you want very complex internal designs, injection molding may struggle due to mold limitations.
Material Selection
| Method | Material Variety | Performance Adjustability |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Limited; primarily thermoplastics | Restricted based on technology |
| Injection Molding | Extensive; includes thermoplastics | Highly customizable through additives |
With materials, 3D printing often limits me mainly to thermoplastics like PLA and ABS. These work well for many projects but feel restrictive when I need something special. In contrast, injection molding provides a wider choice and allows customization with various additives and fillers offering unique performance enhancements.
Cost Structure Analysis
In terms of costs, I’ve found 3D printing more budget-friendly for small runs since no molds are needed—a huge relief! As project size grows, the cost benefits balance out; injection molding involves higher startup costs due to mold creation but offers lower per-item costs in large volumes. This is key to remember when planning to increase production.
In summary, both 3D printing and injection molding have clear benefits depending on project needs. Understanding their differences is crucial for making smart choices as a designer. Whether it’s the flexibility of 3D printing or the efficiency of injection molding, these insights guide my project decisions.
3D printing is more cost-effective for small production runs.True
3D printing eliminates mold costs, making it cheaper for small batches compared to injection molding, which incurs high initial mold creation costs.
Injection molding allows for greater material variety than 3D printing.True
Injection molding supports a wider range of materials and customization options through additives, unlike 3D printing's limited thermoplastic options.
How Does Injection Molding Ensure High Production Efficiency?
Have you ever thought about how factories produce plastic parts so fast and cheaply? Injection molding is the secret that makes this possible and I’m eager to explain how it happens!
Injection molding achieves high production efficiency. Optimized mold designs play an important role. Advanced machinery contributes much. Automation technologies significantly help. These elements allow for rapid manufacturing. They support cost-effective mass production. The parts produced are high-quality plastic.

Understanding Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a material reduction manufacturing technique that operates on the principle of high-volume production. By heating thermoplastic or thermosetting plastic until it reaches a molten state, it is injected into a pre-designed mold cavity under high pressure. This process allows for rapid cooling and solidification of the material, producing high-quality parts quickly.
The efficiency of this method is largely attributed to the mold design, which dictates the shape and details of the product. Once a mold is established, it can be used repeatedly, significantly reducing production times for each unit. For example, a high-speed injection molding machine can produce parts in just seconds, making it ideal for mass production scenarios.
Factors Contributing to High Production Efficiency
Several factors contribute to the overall efficiency of injection molding, including:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Mold Design | Optimized molds allow for quicker cycles and better cooling, leading to reduced production times. |
| Material Properties | The choice of thermoplastic or thermosetting plastic can impact cycle times and finished product quality. |
| Machine Technology | Advanced injection molding machines improve speed and consistency in production. |
| Batch Size | Larger batch sizes lower the per-unit cost due to economies of scale, enhancing overall efficiency. |
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Efficiency
Advancements in technology have played a pivotal role in improving the efficiency of injection molding processes. For instance, automated systems and robotics are increasingly integrated into production lines, enabling:
- Precision: Consistent part quality through accurate injection control.
- Speed: Reduced cycle times with faster material handling.
- Flexibility: Adaptation to different designs without substantial downtime for mold changes.
These improvements not only boost productivity but also enhance the quality of products, ensuring that manufacturers can meet stringent industry standards.
Cost Efficiency with Injection Molding
While the upfront cost of creating molds can be significant, injection molding proves cost-effective for large production runs. As the number of produced units increases, the cost per unit decreases sharply due to:
- Lower material waste: Efficient use of materials minimizes waste.
- Faster production times: High-speed machines can produce thousands of units per day.
- Reduced labor costs: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention in production.
In summary, injection molding ensures high production efficiency through optimized processes, technological advancements, and cost-effective practices. Manufacturers can leverage these advantages to enhance their operations and improve product offerings.
Injection molding reduces production time significantly.True
The injection molding process allows for rapid cooling and solidification, leading to faster production cycles compared to traditional methods.
Mold design does not affect production efficiency.False
Optimized mold designs are crucial for reducing cycle times and improving overall efficiency in injection molding processes.
What Factors Influence Material Selection in Both Processes?
Picking the right material is like choosing the best ingredients for a recipe. It probably decides whether the final result is successful or not. One very important choice in engineering involves this decision. This is true, especially in methods like 3D printing and injection molding.
Material choice in engineering depends on cost, material features, ability to make, product quality and environmental effects. Understanding these helps in choosing designs that work well and look good in 3D printing and injection molding.
Knowing Material Choice Factors
Material choice in processes such as 3D printing and injection molding depends on key points. Each point affects how well the final product works, its ease of manufacturing and the cost.
- Cost Structure
Material cost is important in choosing materials. I remember struggling with budget limits when creating a prototype. In 3D printing, costs mainly involve equipment, material and labor. Yet, savings in cost per unit become less important as batch sizes grow, compared to older methods.
In contrast, injection molding has high upfront costs for mold creation. But, once made, large batches reduce the unit cost a lot. This makes it great for large-scale production.
- Material Properties
Different processes allow for various materials with unique features. 3D printing has fewer options like thermoplastics and resins, limiting some uses. I was eager to use a special material once, only to find it didn’t work with my printing tech.
Yet, injection molding comes with more thermoplastics and thermosets, offering more options with additives. This helps in getting specific traits like strength and heat resistance.
-
3D Printing Materials:
-
Thermoplastics (PLA, ABS)
-
Metal powders
-
Ceramics
-
Photosensitive resins
-
Injection Molding Materials:
-
Various thermoplastics (e.g., polycarbonate)
-
Thermosets
-
Additives for more traits
-
Manufacturability and Design Complexity
Design complexity also decides material choice. 3D printing is good for complex shapes hard to make with injection molding due to mold limits. I made a light structure with lattice designs that only 3D printing could create easily. Yet, for precision and smooth surfaces, injection molding might be best due to its precise mold abilities. -
Product Quality and Precision
Quality needs affect material choice. Injection molding gives high-quality products with great surfaces and precise sizes. But, hard-to-mold inner structures can be tough to do well. Meanwhile, 3D printing has improved in precision, yet layer lines and surface roughness may need extra work to improve quality. I often spend more time refining printed models to satisfy clients.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental impact grows as a factor in material choice. Recyclable or biodegradable materials are preferred. For instance, some 3D printing materials are eco-friendly, swaying their use in green projects.
Also, the making processes impact the environment differently:
- 3D printing produces less waste as it adds material.
- Injection molding is efficient for mass making but creates more waste during mold making and uses much energy for heat.
Final Thoughts on Material Choice Factors
Choosing materials involves various factors, from cost and making ease to environmental concerns. By thinking about all these aspects together, designers and engineers can decide better for good performance and eco-friendly goals.

Understanding Material Selection Criteria
When I first entered engineering, I quickly realized that choosing the right materials is more than a simple task. It’s the foundation of every successful design. Material selection involves knowing how each material reacts and fits the production steps. It also strongly affects the environment. Let’s look at these factors together.
Material selection in engineering processes like 3D printing and injection molding is influenced by several critical factors. Each factor impacts not just the performance of the final product but also its manufacturability and cost-effectiveness.
-
Cost Structure
The cost of materials plays a significant role in the selection process. In 3D printing, the costs are primarily associated with equipment depreciation, material expenses, and labor costs.
However, as batch sizes increase, the unit cost savings become less significant compared to traditional methods.Conversely, injection molding incurs high upfront costs for mold making. But once the mold is created, producing large batches can drastically lower the unit cost due to efficiency. This makes it a preferred choice for mass production.
| Process | Initial Cost | Cost per Unit with Small Batch | Cost per Unit with Large Batch |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Injection Molding | High | Very High | Low |
-
Material Properties
Different processes allow for various materials with unique properties. 3D printing offers limited options like thermoplastics and resins, which may restrict some applications.
On the other hand, injection molding provides a wider selection of thermoplastics and thermosets, enabling more customization through additives. This flexibility is beneficial in achieving specific mechanical properties such as toughness and heat resistance.-
3D Printing Materials:
- Thermoplastics (PLA, ABS)
- Metal powders
- Ceramics
- Photosensitive resins
-
Injection Molding Materials:
- Various thermoplastics (e.g., polycarbonate)
- Thermosets
- Additives for enhanced properties
-
-
Manufacturability and Design Complexity
The complexity of design can also dictate material choice. 3D printing excels at producing intricate geometries that may be difficult or impossible to achieve through injection molding due to mold design limitations.
For instance, lightweight structures with internal lattice designs can be efficiently produced using 3D printing methods. However, if a product requires high precision and a smooth finish, injection molding might be preferred due to its capabilities in producing detailed molds. -
Product Quality and Precision
Quality expectations also guide material selection. Injection molding typically results in high-quality products with excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy. However, complex internal structures can be challenging to mold effectively.
In contrast, while 3D printing has made strides in improving precision, issues such as layer lines and surface roughness can necessitate post-processing steps to enhance product quality.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental impact is becoming an increasingly important factor in material selection.some keywords
Materials that are recyclable or biodegradable are favored in both processes. For example, some 3D printing materials are designed to be eco-friendly,some keywords which can influence their selection in sustainable design initiatives.
Additionally, the production processes themselves have different environmental footprints:
- 3D printing often results in less waste since it’s an additive process.some keywords .
- Injection molding, while efficient for mass production, some keywords can generate more waste during mold creation and requires energy-intensive heating processes.
Final Thoughts on Material Selection Factors
The decision on material selection encompasses a spectrum of factors ranging from cost and manufacturability to environmental impact.some keywords By considering these elements holistically,some keywords designers and engineers can make informed decisions that align with both performance requirements and sustainability goals.
3D printing materials are limited compared to injection molding.True
3D printing primarily uses thermoplastics and resins, while injection molding offers a broader range of materials, enhancing customization and properties.
Injection molding is more cost-effective for large production runs.True
Once the mold is made, injection molding significantly reduces the cost per unit for large batches, making it ideal for mass production.
How Do Cost Structures Compare Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding?
Choosing between 3D printing and injection molding might feel confusing. Cost structures for these methods could seem like a puzzle. So, how do these two methods compare?
3D printing and injection molding have very different cost structures. Factors such as how much is produced, material prices, work costs and machinery expenses really matter. 3D printing is great for small quantities or tailored pieces. Injection molding, however, excels in mass production. Injection molding is perfect for large quantities. It saves money over time.
Overview of Cost Structures
When comparing the cost structures of 3D printing and injection molding, it is essential to understand how each method operates and what factors influence their costs.
Cost Factors in 3D Printing
-
Equipment Costs: The initial investment for 3D printing equipment can vary significantly. Entry-level printers are relatively inexpensive, while industrial machines can be quite costly. The depreciation of this equipment is a primary factor in the overall cost.
-
Material Costs: Materials used in 3D printing, such as thermoplastics or metal powders, can be expensive. However, the ability to print complex shapes without molds can offset some material costs when producing custom items.
-
Labor Costs: Labor costs can be lower for small batch productions since there’s no need for skilled workers to create molds. This aspect can make 3D printing a more affordable option for prototyping or short runs.
-
Production Scale: For larger production runs, the unit cost of 3D printing does not decrease as significantly as it does with injection molding, which can affect the overall cost effectiveness.
Cost Factors in Injection Molding
-
Upfront Mold Costs: Injection molding requires a significant initial investment to create molds, which can be cost-prohibitive for low-volume production. The cost of molds can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars depending on complexity.
-
Material Efficiency: Once molds are made, injection molding is highly efficient in terms of material usage, resulting in lower per-unit costs as production scales up. This efficiency makes injection molding an attractive option for mass production.
-
Production Speed: The speed of production in injection molding can lead to reduced labor costs over time. High-speed machines can produce parts in seconds, drastically lowering the labor cost per unit when producing large volumes.
-
Quality Control: The high precision and quality of injection-molded parts mean less post-processing, which can save costs associated with finishing and quality assurance.
| Cost Factor | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Equipment Cost | Moderate to High | High (due to mold costs) |
| Material Costs | Higher for specialty materials | Lower (bulk purchasing advantages) |
| Labor Costs | Lower for small batches | Lower for large-scale production |
| Production Scale | Less efficient at scale | Highly efficient |
Summary of Economic Implications
In essence, while 3D printing offers flexibility and lower costs for smaller runs, injection molding shines in large-scale manufacturing due to its efficiency and reduced unit costs with higher volumes. Companies must consider their specific needs—such as production volume and part complexity—when deciding which method to use for cost-effective manufacturing.
For further exploration of these manufacturing techniques, check out this in-depth analysis2 on the economic implications of production methods.
3D printing is cheaper for small batch productions.True
3D printing offers lower labor costs and no mold expenses, making it economical for producing small quantities.
Injection molding is more efficient for large-scale production.True
Injection molding reduces per-unit costs significantly as production volume increases, making it ideal for mass manufacturing.
How Do Design Complexities Shape My Manufacturing Choices?
Do you ever think about how the details of a design influence what choices we take in manufacturing? I have thought about it too. These insights are really important for improving production steps.
Design complexities are very important in shaping manufacturing choices. They influence production methods, material selection and cost efficiency. Understanding how these elements interact is crucial. Product development relies heavily on this understanding. Professionals like Jacky must balance design aesthetics with practical production needs. Jacky must do this, really.

Understanding Design Complexities
Understanding design complexities involves more than just technical skills. It’s about balancing looks with how things work. I am a product designer and often face this challenge. Jacky, a fellow designer, also faces this with over ten years of experience in consumer electronics. Every choice affects how we produce, pick materials and manage costs.
Manufacturing Methods: 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding
3D Printing
- Additive Manufacturing: I remember the thrill of using 3D printing the first time. I watched my digital model turn into reality, piece by piece. This method offers great flexibility for designs, especially for complex shapes. Traditional methods struggle with these shapes.
- Production Flexibility: 3D printing shines when creating small batches. It avoids high initial costs for molds. For example, when I quickly needed a prototype for a new electronic part, I chose 3D printing3. It helped me modify and perfect my design faster than injection molding ever could.
Injection Molding
- Efficiency in Mass Production: For mass production, injection molding changes the game. I designed a product that suddenly had high demand. Once we switched to injection molding, parts were produced in seconds after mold creation.
- Cost-Efficiency: Initially, creating molds can be very expensive. As production increases, the cost per unit drops fast. It’s like the start of a tough race; but once you get going smoothly, everything becomes easier. For instance, if Jacky designs a popular consumer product that requires thousands of units, he might opt for injection molding4 to maximize efficiency and reduce costs over time.
Productivity Considerations
Productivity is crucial when choosing between these methods. Understanding these factors helps align designs with project goals:
| Aspect | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Slower for complex parts | Fast once mold is ready |
| Ideal Batch Size | Small batches or prototypes | Large-scale production |
| Setup Time | Minimal | Significant for mold creation |
| Cost per Unit | Higher for large batches | Lower at scale |
Choosing can be overwhelming; but understanding these factors orients designs to fit project needs.
Quality and Precision
Quality is essential for any product. The manufacturing process you pick affects quality greatly:
- 3D Printing: This offers design flexibility but requires time to post-process to reach consumer product quality. It’s like cooking; sometimes you need to let it sit and perfect it before serving.
- Injection Molding: Produces parts with high precision and smooth finishes consistently. Complex internal structures often challenge mold creation, requiring careful planning.
Understanding these trade-offs allows Jacky to align design choices with quality requirements.
For detailed comparisons on achieving high precision in manufacturing, consider exploring this link5.
Material Selection and Cost Structure
Material choice impacts design complexity and expenses:
- 3D Printing: Offers limited materials which can curb creativity; this method handles complex internal structures well but I often want more material variety.
- Injection Molding: Offers a wide range of materials that help meet specific needs because adjusting material properties with additives is crucial.
In terms of costs, while 3D printing may offer lower costs for prototypes, injection molding becomes more economical as production scales. Making smart decisions based on these factors is critical for timelines and budgets.
3D printing is ideal for small batch production.True
3D printing allows for quick production of small batches without molds, making it efficient for prototypes and limited runs.
Injection molding is more cost-effective for large quantities.True
Once molds are created, injection molding reduces per-unit costs significantly, making it suitable for high-volume production.
When Should I Choose 3D Printing Over Injection Molding?
Have you ever been unsure whether to choose 3D printing or injection molding? Let’s explore the details of these two interesting manufacturing methods. Maybe find out which one suits your project best.
When choosing between 3D printing and injection molding, think about how many items you need. Also, consider the complexity of the design, material choices and cost. 3D printing works well for making small batches or very detailed designs. For large-scale production, injection molding is often better.

Deciding Between 3D Printing and Injection Molding
Deciding between 3D printing and injection molding is not only about technology; it’s an emotional adventure that reflects our imagination and goals. When I began in product design, I felt torn between the freedom of 3D printing and the quickness of injection molding. Each method has its unique appeal. Knowing when to choose either method can truly improve your project.
Understanding the Basics
First, I needed to understand the basics of these methods to decide wisely. 3D Printing is like painting a picture, creating it layer by layer from a digital design. Once, I worked on a custom model using Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Watching the plastic melt and take shape felt magical. On the other hand, Injection Molding is like building a structure where every detail relies on the mold’s design. This method offers amazing precision but brings its own challenges.
Evaluating Productivity Needs
Productivity often changed the game for my projects.
- 3D Printing excels in producing single pieces or small batches without the need for complex molds, significantly reducing lead times. However, larger or more complex parts can take considerable time to print.
- Injection Molding, on the other hand, is highly efficient for mass production. After the initial mold creation, a high-speed machine can produce countless identical parts in mere seconds. This makes it ideal for large-scale industrial applications.
| Method | Lead Time for Small Batches | Lead Time for Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Short | Long |
| Injection Molding | Long | Very Short |
Assessing Product Quality and Precision
Product quality has always been crucial.
- 3D printed items have their charm but sometimes show rough edges and lines. I made a nice lamp that needed hours of polishing to reach its best state. Despite this, I liked that 3D printing let me explore complex internal designs impossible with traditional methods.
- Conversely, Injection Molding gave me a sense of artistry and perfection. The precision and surface of the products were fantastic – everything smooth and exact. However, complex molds sometimes caused challenges.
Material Selection Considerations
Material choice adds complexity to choosing manufacturing methods:
- With 3D Printing, I often felt limited. Options like PLA and ABS were decent, but I wished for more variety. Each technology had strict material rules, which felt restricting.
- On the other hand, Injection Molding opened many possibilities. The wide range of available plastics allowed me to modify materials with additives to improve strength or heat resistance. My designs became more solid.
| Manufacturing Method | Material Variety | Customization Options |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | Limited | Low |
| Injection Molding | Extensive | High |
Analyzing Cost Structure
Cost is often a big factor in manufacturing choices:
- At first, 3D Printing was affordable for small quantities since there were no big mold expenses. But as production increased, unit costs stayed high, which was disappointing.
- Conversely, while Injection Molding had high initial costs for mold creation, it became cost-effective for large batches due to decreased unit costs.
| Production Size | 3D Printing Cost | Injection Molding Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Small Batch | Lower | Higher |
| Large Batch | Higher | Lower |
By reflecting on these factors – molding principles, productivity needs, product quality, material choices and cost structure – I’ve managed to navigate the world of manufacturing with more assurance. Whether you prefer 3D printing or injection molding, trust your intuition and remember that every project offers unique challenges and rewards. For more insights on optimizing your manufacturing process, check out this guide6.
3D printing is ideal for small production runs.True
Due to its additive nature, 3D printing excels in producing small batches quickly without the need for molds.
Injection molding offers more material options than 3D printing.True
Injection molding supports a wider variety of materials, allowing for customization and enhanced properties compared to 3D printing's limited selection.
Conclusion
Explore the differences between 3D printing and injection molding regarding production methods, material choices, costs, and product quality to make informed manufacturing decisions.
-
This link provides deeper insights into the advantages of additive manufacturing technologies compared to traditional methods. Discover how to leverage 3D printing in your projects. ↩
-
This link provides a detailed analysis that will help you better understand the economic implications of choosing between these two manufacturing methods. ↩
-
Discover how design complexities can streamline your manufacturing processes and enhance product quality. This insight will help you make informed decisions. ↩
-
Learn about different manufacturing methods influenced by design complexities and how they can affect production efficiency and costs. ↩
-
Gain insights into cost structures associated with different manufacturing techniques when dealing with complex designs. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of 3D printing vs. injection molding to understand which method aligns best with your project needs. ↩






