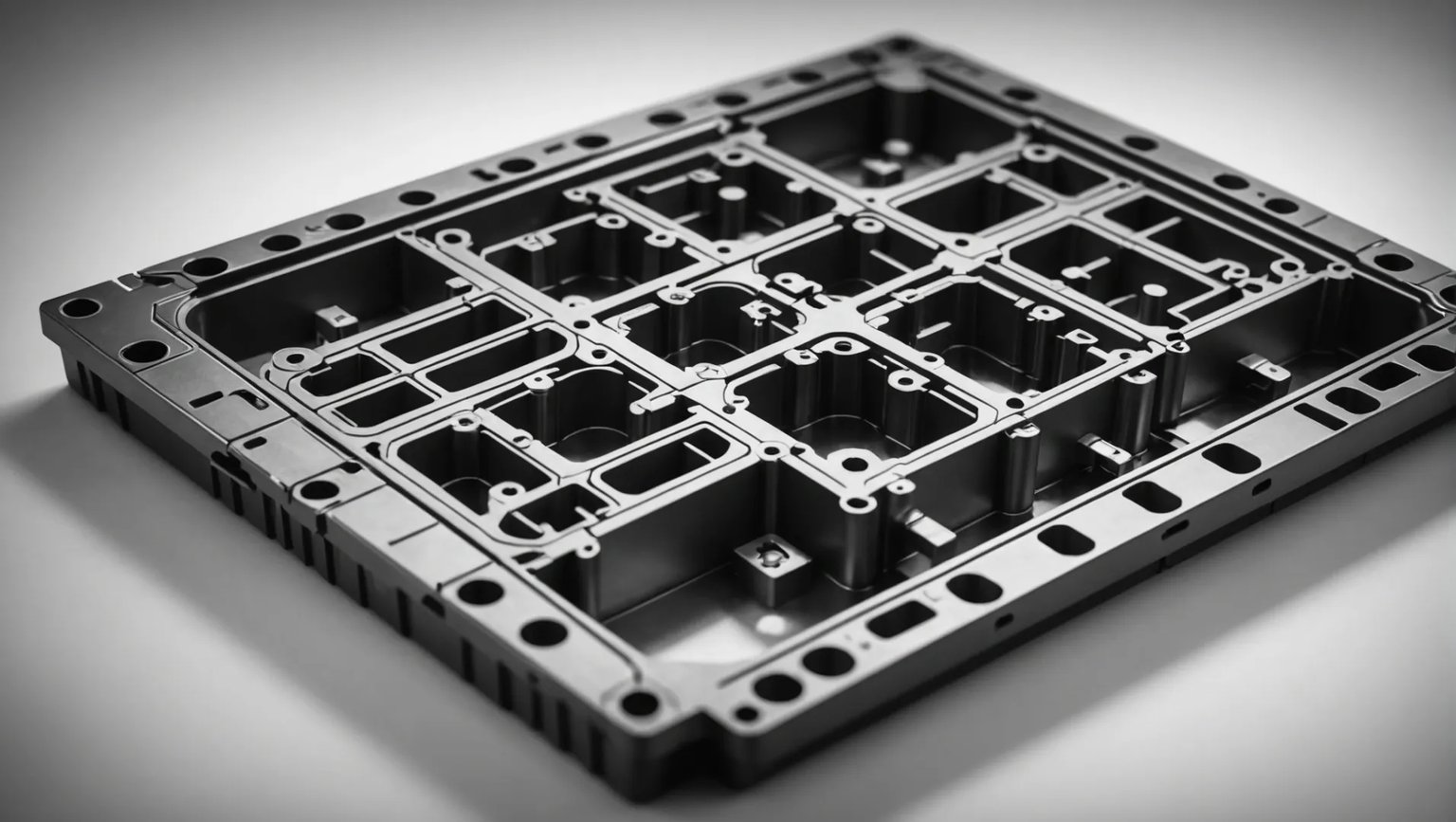
Ever wondered how those perfectly molded plastic parts come to life? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of 3-plate plastic injection molds!
A 3-plate plastic injection mold works by using a runner system to guide molten plastic into a cavity where it solidifies into the desired shape. This mold type consists of three main plates, facilitating efficient part separation and automated gate removal.
But this is just the tip of the iceberg! Stick around as we unravel the intricacies and benefits of 3-plate molds that make them a game-changer in various industries.
3-plate molds automate gate removal during mold opening.True
3-plate molds separate parts from gates automatically, reducing manual steps.
What Are the Key Components of a 3-Plate Mold?
Understanding the key components of a 3-plate mold is essential for optimizing the plastic injection molding process, offering efficiency and precision in manufacturing.
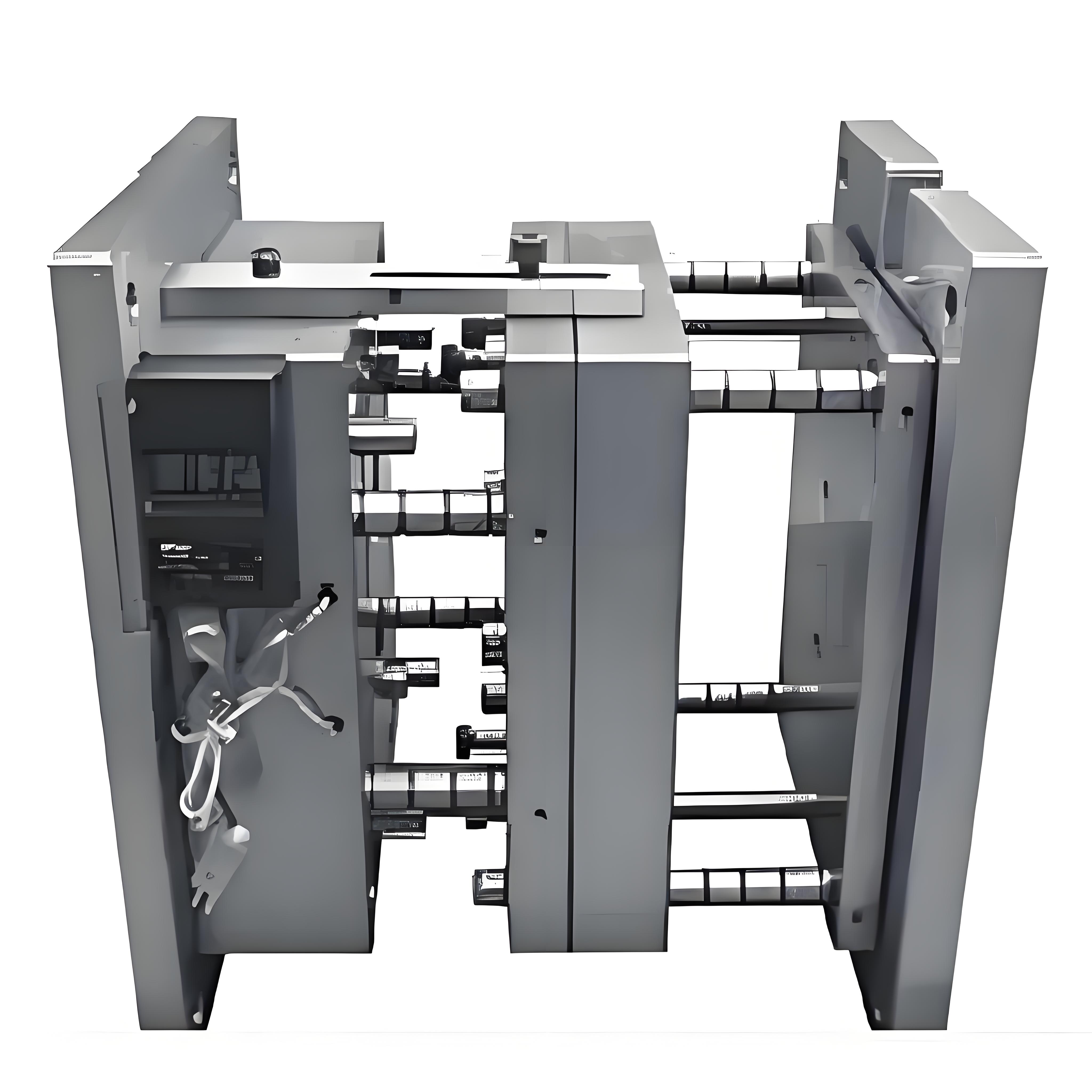
A 3-plate mold consists of fixed and moving mold plates, a runner plate, and various components like guide pins and ejection mechanisms, which collectively facilitate the molding process by controlling the flow and solidification of plastic.
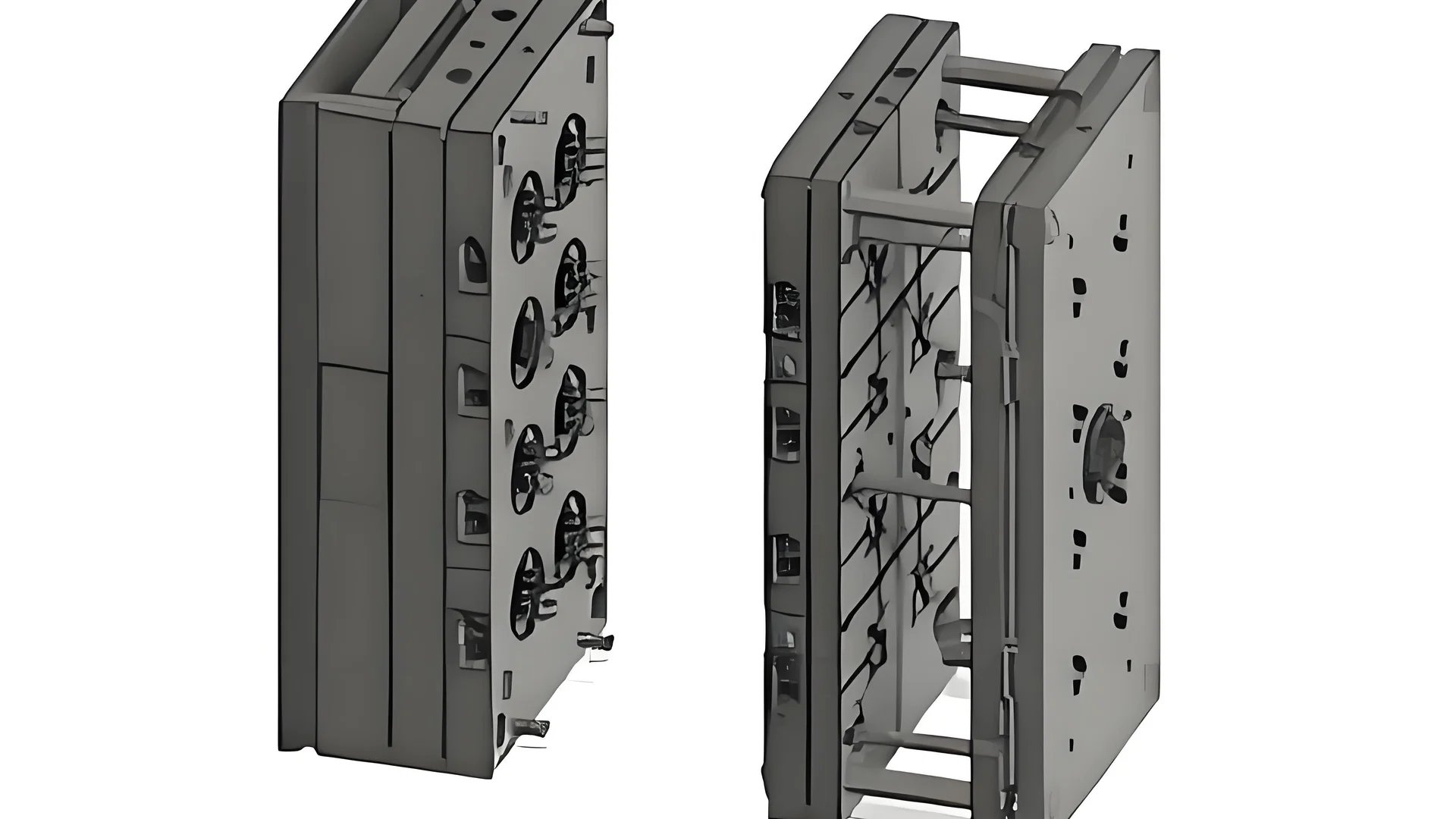
Structural Composition of a 3-Plate Mold
The three-plate plastic injection mold1 is designed to improve the efficiency and quality of molded plastic parts. Its structure can be broken down into several key components:
Fixed Mold Base Plate
The fixed mold base plate is secured to the fixed mold plate of the injection molding machine. It serves as the foundational element that holds and aligns other components of the fixed mold.
Fixed Mold Plate
Tasked with shaping the outer surface of the plastic part, the fixed mold plate often features guide pins and gate sleeves. These components ensure precise alignment and help manage the flow of molten plastic.
Moving Mold Plate
This plate is attached to the moving mold plate of the machine and shapes the inner surface of the plastic part. It typically includes cores and guide sleeves, contributing to the accurate formation of complex interior geometries.
Pad
Located between the moving mold base plate and the moving mold plate, the pad adjusts the closing height of the mold. It also provides space for the installation of the ejection mechanism.
Moving Mold Base Plate
Similar to its fixed counterpart, this base plate supports and aligns components within the moving mold section, ensuring stability during operation.
Runner Plate (Middle Plate)
The runner plate is a critical component that sits between the fixed and moving mold plates. Its primary function is to channel molten plastic from the machine’s nozzle into the mold cavity via a network of runners and gates.
Ejection Mechanism
A hallmark of 3-plate molds is their automated ejection mechanism, which includes push rods, push plates, and reset rods. This system efficiently removes finished parts from the mold, enhancing production speed and consistency.
Table: Key Components at a Glance
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fixed Mold Base Plate | Aligns and holds fixed mold components |
| Fixed Mold Plate | Molds outer surface, includes guide pins |
| Moving Mold Plate | Molds inner surface, includes cores |
| Pad | Adjusts closing height, houses ejection mechanism |
| Moving Mold Base Plate | Aligns and holds moving mold components |
| Runner Plate | Directs molten plastic into cavity |
| Ejection Mechanism | Removes parts from mold post-cooling |
Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining mold integrity2 and ensuring efficient operation. Together, they contribute to producing high-quality plastic parts with minimal waste.
The runner plate directs molten plastic into the mold cavity.True
The runner plate channels plastic from the nozzle to the cavity.
The moving mold plate shapes the outer surface of the part.False
The moving mold plate shapes the inner surface, not the outer.
How Does the Injection Molding Process Work with 3-Plate Molds?
The 3-plate mold in injection molding enables efficient production with automated gate removal, making it crucial for high-precision plastic parts.
In a 3-plate mold, molten plastic is injected into a runner system, travels through gates, and enters a mold cavity. After solidification, the mold opens in stages to separate the part from the runner system and eject it. This process allows for precise shaping and minimizes post-processing.

The Structural Composition of 3-Plate Molds
Understanding the structural composition3 of 3-plate molds is essential for grasping their operational efficiency. This type of mold consists of several key components:
- Fixed Mold Base Plate: Anchored to the fixed plate of the machine, it holds other fixed mold components in place.
- Fixed Mold Plate: It forms the outer surface of the part and usually includes guide pins and gate sleeves.
- Moving Mold Plate: Connected to the moving plate of the machine, it shapes the inner surface of the molded part and contains cores and guide sleeves.
- Pad: Situated between the moving mold base plate and the moving mold plate, it adjusts the closing height and provides space for ejection mechanisms.
- Runner Plate: Also known as the middle plate, it channels molten plastic from the machine nozzle to the cavity.
The Working Principle
The injection molding process with a 3-plate mold unfolds in distinct stages:
-
Injection Stage: Molten plastic is driven through the machine’s nozzle into the runner system, subsequently entering the cavity via gates. During this stage, both fixed and moving molds remain closed to ensure complete cavity fill.
-
Mold Opening Stage: Post-injection, the moving mold retreats first, opening between the fixed mold plate and the runner plate. This action breaks off the plastic at the gate, separating it from the runner system. As the mold continues to open, it also separates the part from the core.
-
Ejection Stage: Once fully open, an ejection mechanism engages to release the molded part. This mechanism typically comprises push rods, plates, and reset rods.
Automation and Efficiency
The 3-plate mold is particularly celebrated for its ability to facilitate automation4. By automatically severing gates during mold opening, it reduces the need for additional processing steps. This capability makes it ideal for integration with robotic systems, significantly boosting production efficiency in settings demanding high throughput and precision.
Applications Across Industries
3-plate molds find applications in various industries due to their versatility in producing intricate and aesthetically demanding parts. Industries such as electronics, automotive, and healthcare rely on these molds for components like mobile phone casings, automotive parts, and medical equipment casings. The molds’ ability to maintain high precision and minimize blemishes makes them invaluable in these sectors.
3-plate molds have an automated gate removal feature.True
3-plate molds automatically sever gates during mold opening, reducing post-processing.
The runner plate is part of the moving mold plate.False
The runner plate, also known as the middle plate, channels plastic from the nozzle.
What Are the Advantages of Using a 3-Plate Mold?
The 3-plate mold is a game-changer in plastic injection molding, offering unique benefits that enhance production quality and efficiency. Dive in to uncover its advantages.
The advantages of using a 3-plate mold include automated gate removal, high production efficiency, and superior part appearance. These molds are ideal for complex shapes and precise requirements, facilitating automation and reducing post-processing work.
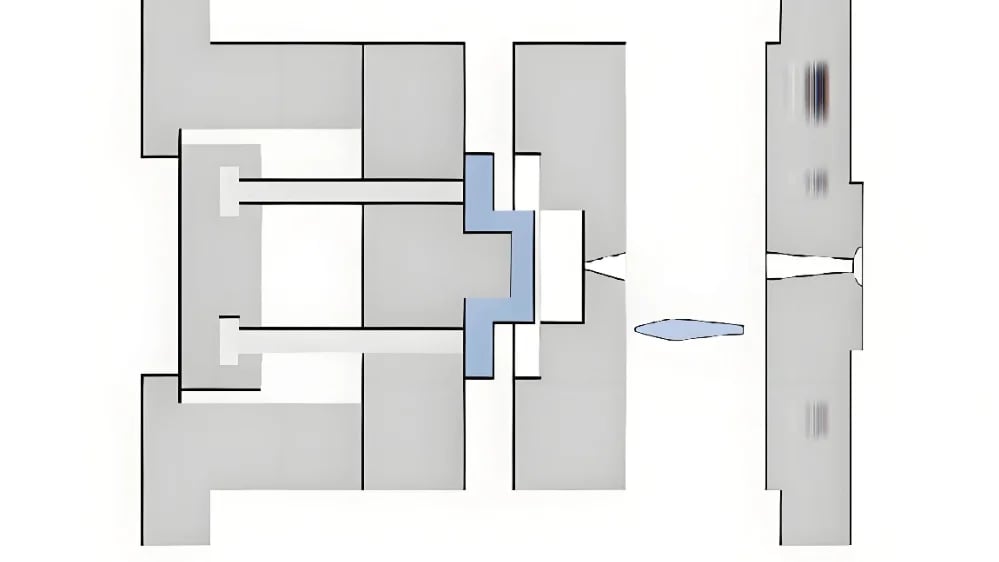
Enhanced Automation and Efficiency
One of the standout benefits of a 3-plate mold is its ability to automate the gate removal process. During the mold opening phase, the design allows for the automatic severing of gates, which significantly reduces manual labor and post-processing time. This automation not only speeds up the overall production process but also minimizes human error, enhancing consistency and quality in mass production.
A study on manufacturing efficiency5 highlights that reducing manual interventions can lead to a substantial increase in throughput and cost savings.
Superior Part Appearance
3-plate molds accommodate various gate designs like point gates and latent gates, which result in minimal vestiges on finished parts. The clean separation of the gate during the mold opening ensures high-quality surface finishes, making these molds particularly suitable for parts requiring aesthetic precision. This feature is crucial in industries where appearance matters, such as consumer electronics and automotive interiors.
Versatility Across Applications
With their ability to produce complex geometries and meet high precision requirements, 3-plate molds are versatile. They are effective across a broad range of applications, from intricate medical devices to durable automotive components. This versatility stems from their structural composition, which supports intricate designs without compromising strength or accuracy.
For instance, the use of 3-plate molds in electronics6 demonstrates their capability to produce parts with fine details and exact dimensions.
Reduced Production Steps
By integrating automated ejection systems, 3-plate molds reduce the need for additional processing steps. The ejection mechanism typically involves push rods and plates that efficiently release the molded parts without damage. This not only accelerates production but also ensures that each part meets stringent quality standards without additional handling.
Manufacturers employing advanced ejection mechanisms7 report a notable decrease in cycle times and increased capacity for high-volume orders.
High Suitability for Automation
The inherent design of 3-plate molds makes them highly compatible with robotic systems and other automated equipment. This compatibility enhances production lines by allowing seamless integration with manipulators and conveyors, further driving production efficiency. Automated systems can handle parts immediately after molding, preparing them for subsequent processes or packaging.
Incorporating robotics in injection molding8 has been shown to significantly boost production rates while maintaining high-quality standards across various industries.
3-plate molds automate gate removal.True
3-plate molds automatically sever gates during mold opening, reducing manual labor.
3-plate molds are unsuitable for complex shapes.False
They are ideal for complex shapes due to their structural versatility.
In Which Industries Are 3-Plate Molds Most Commonly Used?
From electronics to automotive, 3-plate molds find applications across diverse industries due to their efficiency and versatility in producing high-quality plastic components.
3-plate molds are predominantly used in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. Their ability to produce complex parts with fine details and excellent surface finish makes them ideal for high-precision applications.

Electronics and Electrical Appliances
In the fast-paced electronics industry, where precision and quality are paramount, 3-plate molds play a critical role. They are extensively used in manufacturing components like mobile phone casings9, connectors, and computer peripherals. The ability of these molds to produce intricate designs with minimal finishing makes them indispensable in electronics.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector benefits significantly from the high-volume, precision manufacturing capabilities of 3-plate molds. These molds are used to create various auto parts10 such as dashboards, bumpers, and air conditioning vents. Their efficiency in automated production lines helps manufacturers meet stringent industry standards for durability and safety.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, 3-plate molds are essential for producing high-precision components used in devices like syringes11, diagnostic equipment, and surgical tools. The molds’ capability to deliver parts with exceptional quality and consistency is vital to ensuring patient safety and compliance with rigorous health standards.
Consumer Goods
Consumer goods, including plastic tableware, toys, and packaging materials, frequently utilize 3-plate molds. Their versatility12 in handling different shapes and sizes ensures manufacturers can offer a wide range of products while maintaining high appearance and functional standards.
Key Advantages Across Industries
The widespread use of 3-plate molds across these industries is largely due to their advantages:
- Automated Gate Removal: Simplifies post-production processes.
- High Precision: Enables the creation of detailed and complex parts.
- Reduced Waste: Efficient use of materials minimizes scrap rates.
The combination of these benefits underscores why 3-plate molds are a preferred choice in industries that demand high-quality plastic components.
3-plate molds are used in the automotive industry.True
They manufacture auto parts like dashboards and bumpers.
3-plate molds are rarely used in electronics.False
They are critical for making precise components like connectors.
Conclusion
Three-plate molds deliver unparalleled automation and precision in crafting top-notch plastic parts. By grasping their structure and function, we can elevate manufacturing processes to meet diverse industry needs effectively.
-
Explore detailed designs and applications in injection molding.: Often referred to as a “double parting surface mold,” a 3-plate mold serves multiple purposes. A runner stripper plate is inserted between the top clamping … ↩
-
Learn why maintaining mold integrity is vital for quality output.: Consistency and Precision: Quality control measures in injection mold manufacturing ensure the consistent production of precise plastic parts. ↩
-
Explore detailed structures of 3-plate molds enhancing understanding.: This assembly’s first component is the feed plate. · The core plate assembly is the third component, and the intermediate or cavity plate is the second. · The … ↩
-
Discover how automation in 3-plate molds increases efficiency.: The cavity also allows for the cutting of the submerged gate. It is easier to achieve fully automated manufacturing with a three-plate mold, as the runner … ↩
-
Discover how automation enhances efficiency and reduces costs.: In a well-designed automated solution there will be benefits of productivity and yield improvements. These topics are well researched and here we provide … ↩
-
Explore how 3-plate molds benefit electronic device manufacturing.: The primary advantages for using a three-plate mold are central gating, multiple gates feeding a single part, multiple gates feeding multiple … ↩
-
Learn about efficient ejection systems reducing cycle times.: Also called plate ejection system, this is an election mechanism that works by pushing and pulling them off the mold crate once the cooling process is done. ↩
-
See how robotics integrate with injection molding for efficiency.: A robot can lift a moulded part out of one injection moulding machine and place it into another for the over-moulding process. This reduces labour and assembly … ↩
-
Discover how 3-plate molds enhance manufacturing in the electronics industry.: Two-plate molds may be constructed to handle various part designs and sizes and can work for both development and production runs. This gives two-plate molds a … ↩
-
Explore the impact of 3-plate molds on automotive part production.: The most fundamental difference between a 2 plate mold and 3 plate mold is that the latter type contains an additional runner plate. ↩
-
Learn how 3-plate molds ensure precision in medical device manufacturing.: Injection, cooling, and removal of products are the phases of the plastic injection molding process that occur in a machine with three plates. ↩
-
Understand the adaptability of 3-plate molds for diverse consumer products.: The most fundamental difference between a 2 plate mold and 3 plate mold is that the latter type contains an additional runner plate. ↩